FAQ About Roll Forming Machine-Roll Forming Machine
-
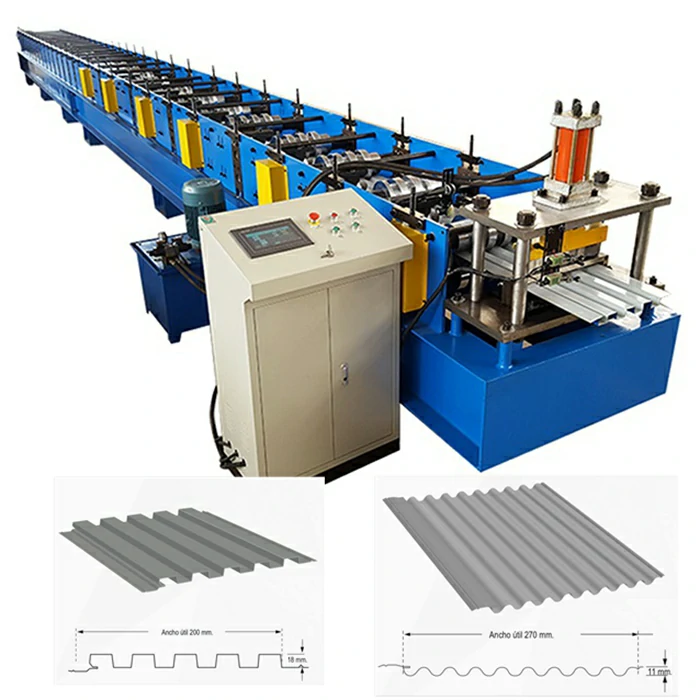
What is a roll forming machine? Roll forming machine is a manufacturing equipment used to shape sheet metal or coiled material into a specific profile or shape by passing it through a series of rollers, also known as roll tooling.
-
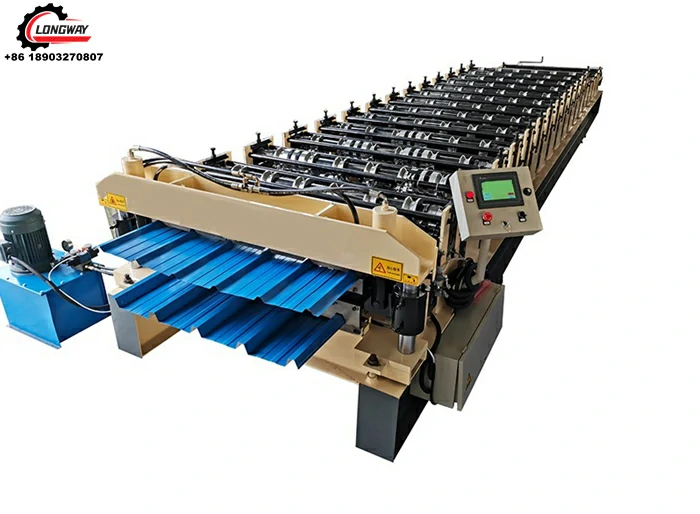
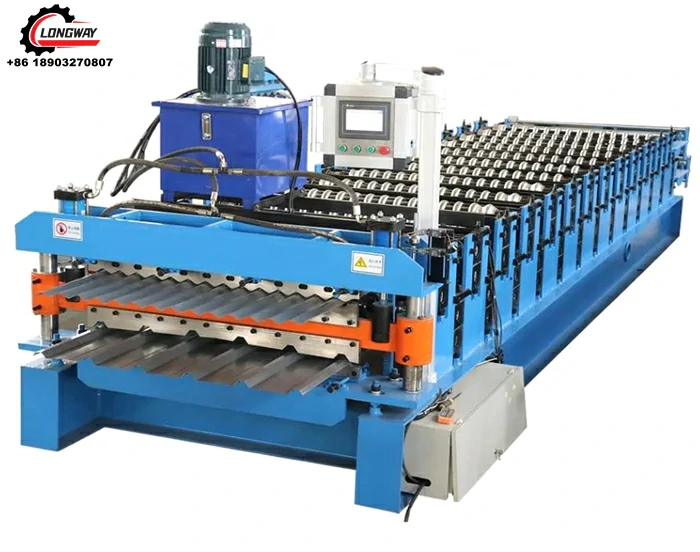
What types of products can be produced using roll forming machines? Roll forming machines are versatile and can produce a wide range of products, including steel studs, roofing panels, metal channels, window frames, and automotive parts, among others.
-
How does a roll forming machine work? Roll forming machines work by gradually bending and forming the metal strip as it passes through a series of rollers. Each roller set performs a specific bending or forming operation, gradually shaping the material into the desired profile.
3mm Steel C U channel roll forming machine
-
What materials can be processed in a roller shutter door machine? Roller shutter door machines are primarily used with materials like steel, aluminum, and other metals. However, they can also process materials like plastic and composites in certain applications.
-
What are the advantages of using roll forming machines? Some advantages of roll forming machines include high production efficiency, precise and consistent shaping, minimal material waste, and the ability to create complex profiles.
-
Are rolling shutters making machines customizable for specific profiles? Yes, rolling shutters making machines are highly customizable. They can be designed and equipped with different sets of rollers and tooling to produce specific profiles tailored to the customer’s needs.
-
What is the difference between roll forming and press braking? Roll forming is a continuous bending process that shapes long strips of material, while press braking is a discrete process that forms materials using a punch and die. Roll forming is more suitable for high-volume production of long profiles.
-
What maintenance is required for roll forming machines? Regular maintenance of roll forming machines includes lubricating moving parts, inspecting and replacing worn tooling, and checking for alignment issues. Preventative maintenance helps ensure consistent product quality and prolongs the machine’s lifespan. Some parts need lubricating once a day before using the machine, some parts needs once a week, other parts may need it once a month. Please get in contact with a representative from the manufacturing company for these informations.
-
Can roll forming machines handle different thicknesses of material? Roll forming machines can be adjusted to accommodate various material thicknesses, but there are limitations based on the machine’s design and capabilities. It’s essential to select a machine that suits the specific material and profile requirements.
-
What safety measures should be taken when operating a roll forming machine? Safety precautions include training operators, using appropriate personal protective equipment, ensuring emergency stops are in place, and conducting regular safety inspections to prevent accidents and injuries.
-
What is the typical speed of a roll forming machine? The speed of a roll forming machine varies depending on factors like the material, profile complexity, and machine design. It can range from a few feet per minute to over 20 meter per minute.
-
Can roll forming machines handle coated or painted materials? Yes, roll forming machines can process coated or painted materials. However, care should be taken to prevent damage to the surface finish during the forming process.
-
What industries commonly use cold roll forming machines? Cold roll forming machines are widely used in industries such as construction, automotive, appliance manufacturing, aerospace, and the production of various building components.
-
Is roll forming suitable for both straight and curved profiles? Roll forming is ideal for producing straight profiles. While it can create slight curves or bends, more complex curved profiles are typically formed using other methods, such as press braking or tube bending.
-
What is the difference between open-profile and closed-profile roll forming? Open-profile roll forming is used for profiles that do not have a closed cross-section (e.g., U-channels, hat channels), while closed-profile roll forming creates profiles with a closed cross-section (e.g., tubes, pipes, and closed box shapes).
-
Can roll forming machines handle stainless steel or other special alloys? Yes, roll forming machines can process stainless steel and other special alloys, but the machine and tooling may need to be designed to handle the specific material properties.
-
Are there limitations to the length of products that can be roll formed? The length of products that can be roll formed is determined by the machine’s design and the available space. Some roll formers can create very long profiles, while others are better suited for shorter lengths. Long or short lengths for profiles is specially needed to be told and the machine will be designed with these informations.
-
What is the role of computer control in modern roll forming machines? Computer control systems are used to program and control the roll forming process. They can store profiles, adjust settings, monitor production, and ensure precision and consistency.
-
Can roll forming machines be used for prototyping and small production runs? Roll forming machines are typically more suitable for high-volume production due to setup and tooling costs. Prototyping and small runs are possible but may be less cost-effective.
-
How do I choose the right roll former machine for my specific application? Selecting the right roll former machine involves considering factors like the material, required profile, production volume, budget, and available space. Consulting with a roll former machine manufacturer or expert can help in making an informed choice.
-
What is the role of tooling in roll forming, and can it be changed easily for different profiles? Tooling, including rollers and other forming components, is critical in determining the profile. Changing tooling for different profiles is possible but can be time-consuming. Some roll forming machine are designed for quicker tooling changes.
-
Are there environmental considerations when using roll forming machines? Roll forming is generally considered a more environmentally friendly manufacturing process than other methods, as it often produces less scrap material, which can be recycled. Additionally, modern roll formers are designed for energy efficiency.
-
Can roll forming machines work with non-metallic materials, such as plastics or composites? While roll forming is traditionally used for metals, some roll forming machines can also process non-metallic materials like plastics and composites. The suitability depends on the machine’s design and material characteristics.
-
Are there safety certifications or standards for roll forming machines? Safety standards and certifications vary by region, but organizations like OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) in the United States provide guidelines and regulations for machine safety, including roll forming machines.
-
What are the hazards of roll forming machine?Hazards of Roll Forming Machines:Pinch Points: Roll forming machines have multiple rollers and moving parts where hands or clothing can get caught, leading to severe injuries.Material Handling: Heavy coils or sheets of metal can cause material handling hazards, including crushing or trapping workers.Noise and Vibration: Roll forming machines can generate high levels of noise and vibrations, leading to hearing damage and discomfort.Flying Debris: The cutting and forming processes can produce sharp or hot metal fragments that pose a risk to operators.Electrical Hazards: Wiring and electrical components can lead to electrical shock or fire hazards if not properly maintained.Ejection of Materials: During forming, there’s a risk of materials being ejected suddenly, endangering workers.Falls and Slips: Slippery floors, especially in areas with coolant or lubricant, can lead to falls.Maintenance Hazards: Performing maintenance tasks on moving machinery without proper lockout/tagout procedures can result in accidents.
-
What are the main components of a roll forming machine?
-Decoiler: This component holds and feeds the material, such as coils of metal, into the machine.
-Rolling Stations (Molds): These are the sets of rollers and tooling that gradually shape the material into the desired profile.
-Cut-off or Guillotine: This component is responsible for cutting the formed profile into the desired lengths.
-Drive System: The motor and transmission system that powers the rollers and advances the material.
-Control System (PLC): The computer or control panel that regulates the machine’s settings, speed, and precision.
-
What is the purpose of a roller shutters roll forming machine? The primary purpose of a roller shutters roll forming machine is to efficiently and continuously shape long strips of metal or other materials into specific profiles or shapes. It’s commonly used in manufacturing various products, such as building components, automotive parts, and industrial equipment, by forming and cutting continuous material into precise shapes.
-
What is the most common cutting method of roll forming? Most Common Cutting Method in Roll Forming: The most common cutting method in roll forming is shear cutting. This involves using a set of blades or shearing mechanisms to cut the continuous strip or profile into individual lengths as it exits the roll forming machine.
-
What are the disadvantages of roll bending?
Disadvantages of Roll Bending:
Limited to simpler shapes: Roll bending is not suitable for complex or highly contoured shapes.
Slow process: The process can be slower compared to other forming methods.
Limited thickness range: Roll bending is typically limited to thin and medium-thickness materials.
Material distortion: It can cause material distortion, particularly at the ends of the workpiece.
Tooling costs: Custom tooling can be expensive, making it less cost-effective for small production runs.
-
What are common machine shop hazards? Common Machine Shop Hazards:Machine Hazards: Moving machine parts, such as rotating shafts and gears, can pose pinch or crush hazards. Electrical Hazards: Faulty wiring or electrical components can lead to electrical shocks or fires. Noise and Vibration: High levels of noise and vibration can cause hearing damage and physical discomfort. Chemical Hazards: Exposure to chemicals used in the machining process, such as coolants or lubricants, can be harmful. Heat and Burns: Hot metal parts, chips, or cutting tools can cause burns. Fall Hazards: Slippery floors, uneven surfaces, or elevated work areas can result in falls. Tool Hazards: Cutting tools and machining equipment can cause cuts and injuries if not handled properly. Dust and Fumes: The generation of dust and fumes from machining processes can lead to respiratory hazards.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025