cut to length and slitting line factories
Understanding Cut to Length and Slitting Line Factories
In the modern manufacturing landscape, the demand for precision-engineered metal products continues to escalate, spurred by the rise of various industries such as construction, automotive, and consumer goods. At the heart of this manufacturing process are cut-to-length and slitting line factories, which play a pivotal role in the production of steel and metal sheets, strips, and coils.
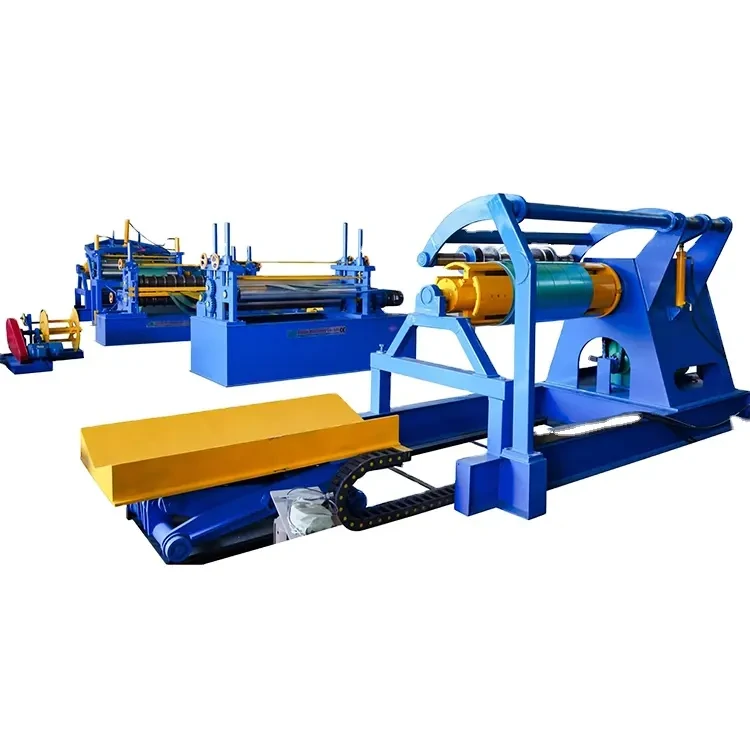
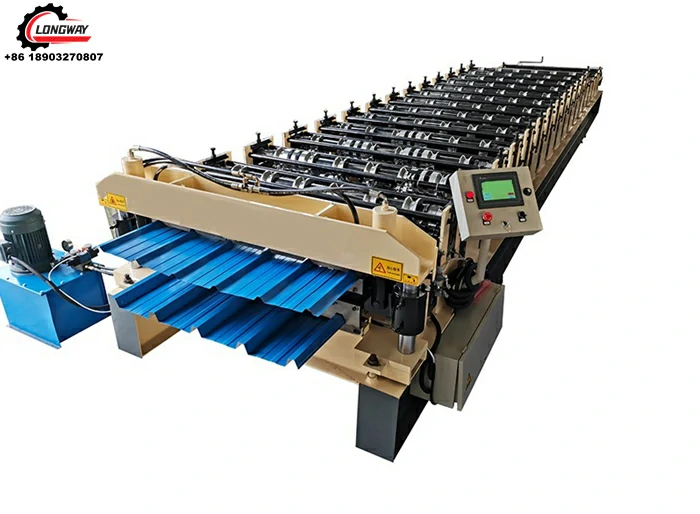
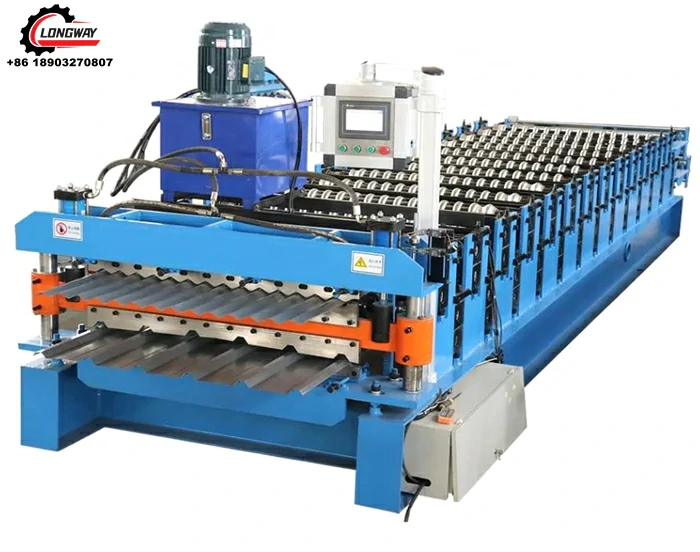
Cut to length lines are designed to process large coils of metal into sheets of specific lengths and sizes. The process typically involves unwinding the coil, leveling the material, and then cutting it to the desired dimensions before it is either stacked or wound into smaller bundles. This method allows for the efficient production of sheets that can be used directly in fabrication or further processing stages, ensuring that manufacturers receive material that meets their exact specifications.
On the other hand, slitting lines focus on transforming wide coils of metal into narrower strips according to specific width requirements. The process entails similar initial steps unwinding the coil and leveling the metal. However, after leveling, the material passes through a series of rotary knives that slice it into narrower lanes. These strips can be utilized in a variety of applications, including automotive components, packaging, and appliance manufacturing. Both processes require precision engineering to ensure that the final product meets stringent quality standards.
cut to length and slitting line factories
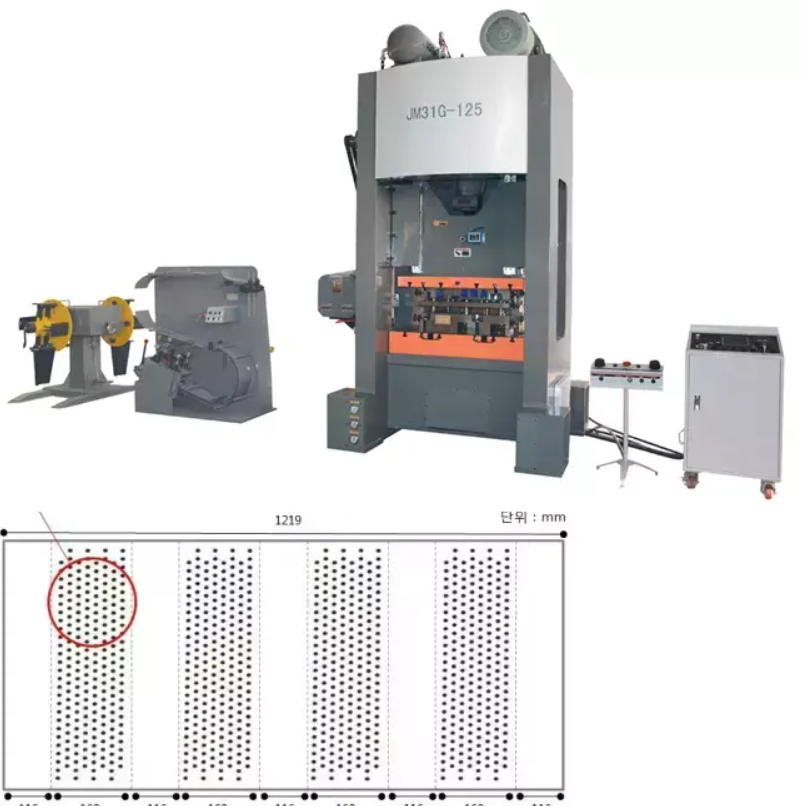

The machinery used in cut to length and slitting line factories comprises a series of advanced technologies designed to enhance performance and efficiency. Modern equipment is often equipped with sophisticated controls and automation systems that allow for quick changeovers between different product specifications, minimizing downtime and improving throughput. High-quality sensors, lasers, and cameras are also utilized to ensure cutting accuracy and product quality, significantly reducing waste and enhancing operational efficiency.
Quality control is a vital aspect of the operations in these factories. Each cut and slit must maintain tolerances that meet industry standards to prevent defects in the end products. Many factories implement rigorous testing and inspection protocols throughout the production process, allowing them to catch any issues before the material is delivered to clients. This commitment to quality not only enhances customer satisfaction but also bolsters the manufacturer’s reputation in a competitive market.
In terms of market dynamics, cut to length and slitting line factories are increasingly adopting sustainable practices. With growing environmental concerns, many manufacturers implement recycling programs and energy-efficient processes to minimize their ecological footprint. By sourcing raw materials responsibly and optimizing production methods, they are better positioned to meet the demands of environmentally conscious consumers.
In conclusion, cut to length and slitting line factories are integral to the metal processing industry, providing essential services that cater to a diverse range of applications. As technology continues to evolve, these factories are likely to see further improvements in efficiency, precision, and sustainability, enabling them to meet the growing needs of modern manufacturing. The future of these facilities looks promising, clouded with opportunities for innovation and growth as they adapt to the ever-changing industrial landscape.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025