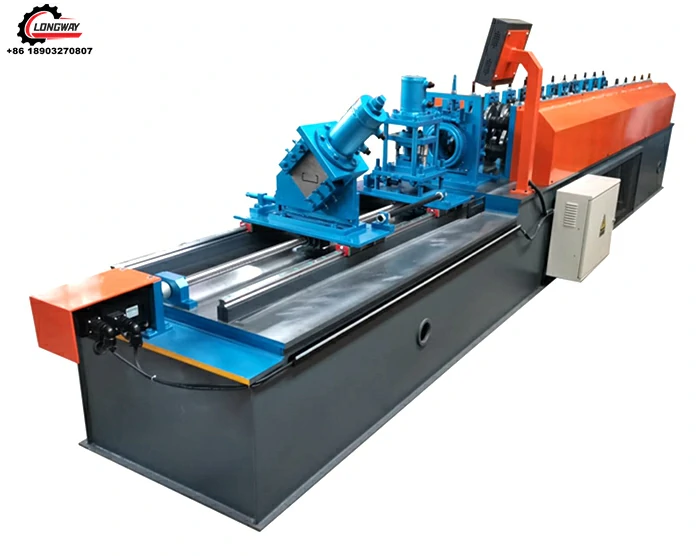
High-Precision Steel Slitting Line Manufacturing Solutions for Optimal Production Efficiency
Understanding Steel Slitting Line Factories
In today's industrial landscape, the demand for precision-engineered metal products has seen a dramatic rise. One of the critical processes in the fabrication of these products is steel slitting, a method that transforms large coils of steel into narrower strips tailored for various applications. To meet this need, steel slitting line factories have emerged as essential hubs for metal processing. This article explores the functionality, components, and significance of steel slitting line factories in modern manufacturing.
What is Steel Slitting?
Steel slitting is a mechanical operation that involves cutting wide rolls of steel, known as coils, into narrower ones. The process begins with large steel coils being passed through a slitting machine, where sharp blades slice the coil into strips of predetermined widths. The slitted strips are then recoiled, allowing for easy handling and transportation. This process is fundamental to various industries, including automotive, construction, and appliance manufacturing, where precision and material specifications are paramount.
The Layout of a Steel Slitting Line Factory
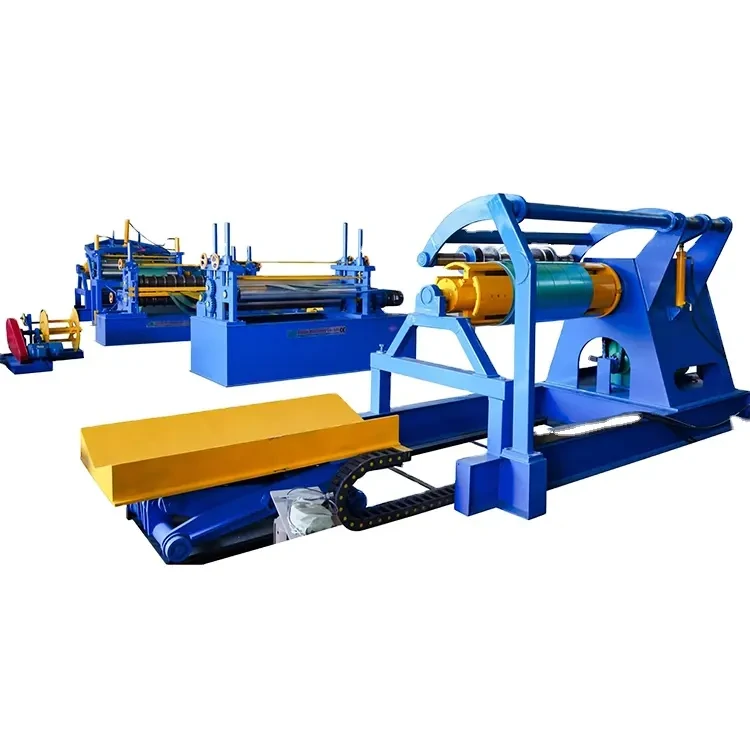
A typical steel slitting line factory is designed to streamline the slitting process, optimizing both efficiency and safety. The layout is usually linear, facilitating the flow of materials from one stage to the next. Here are the key components of a steel slitting line
1. Coil Carousel System This section houses multiple coils of steel, enabling the factory to maintain a constant supply of raw materials. The carousel allows for efficient swapping of coils during the slitting process.
2. Uncoiler The uncoiler is responsible for feeding the steel coil into the slitting machine. This component lifts and unwinds the coil, ensuring a steady flow of material.
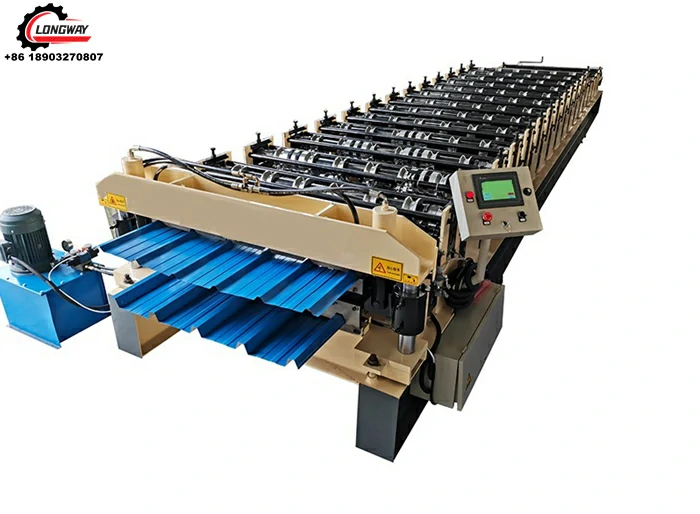
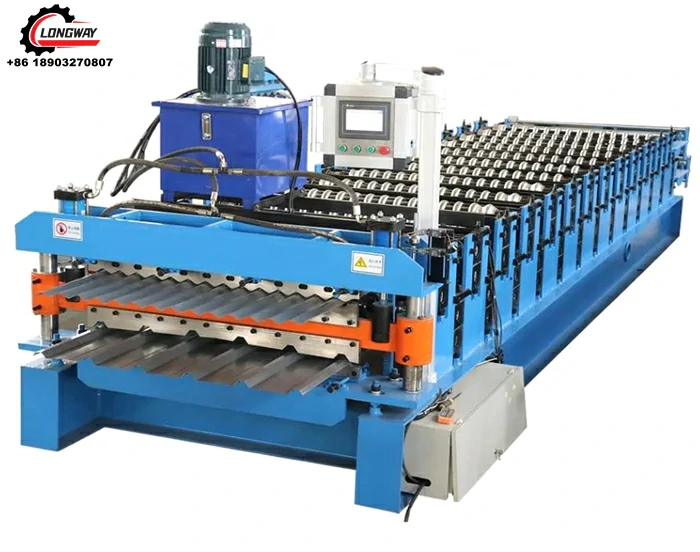
3. Slitting Machine At the heart of the factory, the slitting machine slices the steel coil into desired widths using multiple rotating blades. These blades can be adjusted to meet varying specifications, making the slitting line highly versatile.
4. Recuperator After slitting, the strips are collected by a recuperator, which rewinds them into new coils. This system minimizes downtime and maintains continuous operations.
5. Shear and Stack Unit For some applications, slitted strips may need to be cut to specific lengths and stacked for later use. The shear and stack unit automates this process, enhancing productivity.
6. Quality Control Station Quality control is crucial in steel production. This station checks the thickness, width, and quality of the slitted strips to ensure they meet industry standards.
steel slitting line factory
The Importance of Steel Slitting Line Factories
Steel slitting line factories play a pivotal role in the supply chain of the steel industry. Here are some of the key reasons why these factories are significant
- Customization The ability to produce steel strips of various widths and qualities allows manufacturers to cater to specific market needs. Customization aids industries that require tailored metal products for distinct applications.
- Efficiency Advanced machinery in steel slitting lines significantly reduces waste and improves production rates. Automated processes minimize manual labor and enhance safety by reducing the chances of accidents.
- Cost-Effectiveness By producing slitted steel strips in large volumes, factories can lower overhead costs, leading to more competitive pricing for end-users.
- Innovation in Design Continuous advancements in slitting technology, including the use of robotics and AI, improve product quality and operational efficiency. This innovation drives the steel industry toward smarter manufacturing solutions.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite their significance, steel slitting line factories face challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices and stringent regulatory requirements related to environmental standards. Additionally, the shift towards more sustainable manufacturing practices necessitates innovation in waste management and energy efficiency.
Looking forward, the future of steel slitting line factories appears promising. As industries increasingly embrace automation and Industry 4.0 principles, these factories are well-positioned to leverage technology for improved performance. Moreover, the growing demand for green products is driving factories to adopt environmentally friendly practices, ensuring they remain relevant in a changing market landscape.
Conclusion
Steel slitting line factories are integral to the modern manufacturing ecosystem. They not only fulfill the growing demand for precision-engineered steel products but also contribute to the overall efficiency and sustainability of the production process. By understanding their operation and significance, we can appreciate the critical role they play in the global economy, shaping the future of various industries that rely on metal fabrication.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025