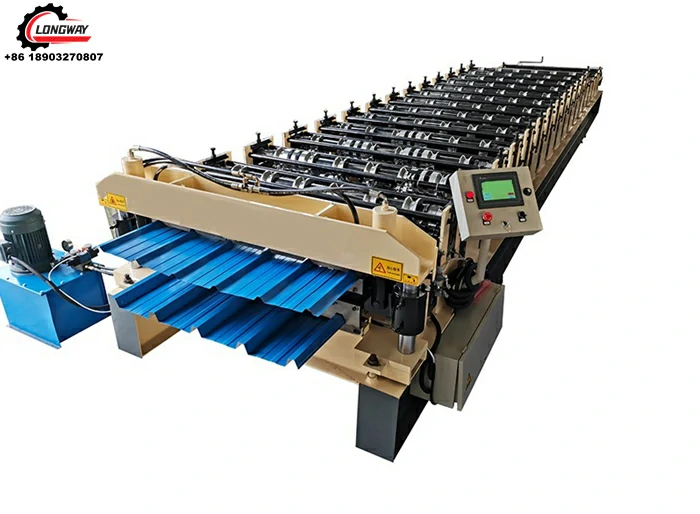
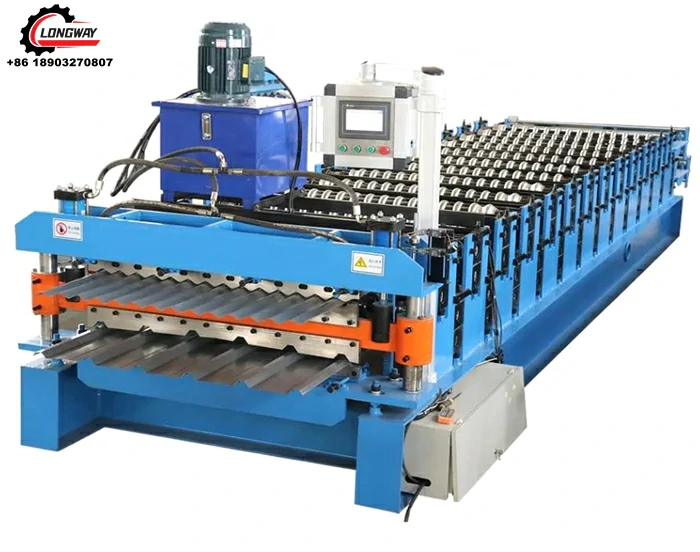
slitting line machine factories
The Evolution and Impact of Slitting Line Machine Factories
Slitting line machines play a crucial role in the metal processing industry, serving as essential equipment for the cutting and processing of sheets and coils. As industrial demands grow, so does the need for advanced slitting line machinery and the factories that manufacture them. This article explores the evolution of slitting line machine factories, the technology involved, and their impact on various industries.
The Basics of Slitting Line Machines
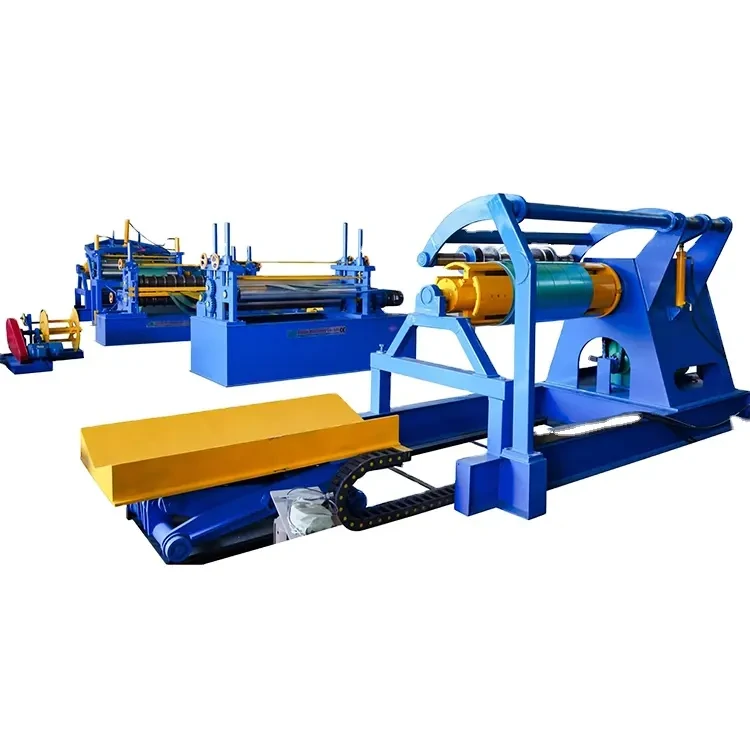
At its core, a slitting line machine is designed to take wide strips of metal, typically steel or aluminum, and cut them into narrower strips with precision. This process is vital for many industries, including automotive, construction, and appliance manufacturing. The ability to convert large coils into manageable sizes increases efficiency and minimizes waste.
Slitting lines generally operate in several stages. First, a coil of metal is loaded onto the slitting line, then passed through a series of rollers and cutting tools that slice it into the desired dimensions. Advanced systems often incorporate automated mechanisms that enhance speed and accuracy, allowing factories to increase production rates while maintaining quality.
Technological Advancements
In recent years, slitting line machine technology has advanced significantly. Innovations such as servo-driven slitters, integrated control systems, and advanced coil handling mechanisms have transformed the efficiency of these machines. Manufacturing factories are increasingly adopting robotics to streamline operations, further reducing the risk of human error and improving overall efficiency.
The integration of Industry 4.0 concepts has also become prominent in slitting line machine factories. This includes the use of IoT (Internet of Things) devices that monitor machine performance in real time, predictive maintenance analytics, and machine learning algorithms that optimize production processes. These technologies ensure that plants can adapt quickly to changing market demands while reducing operational costs.
slitting line machine factories
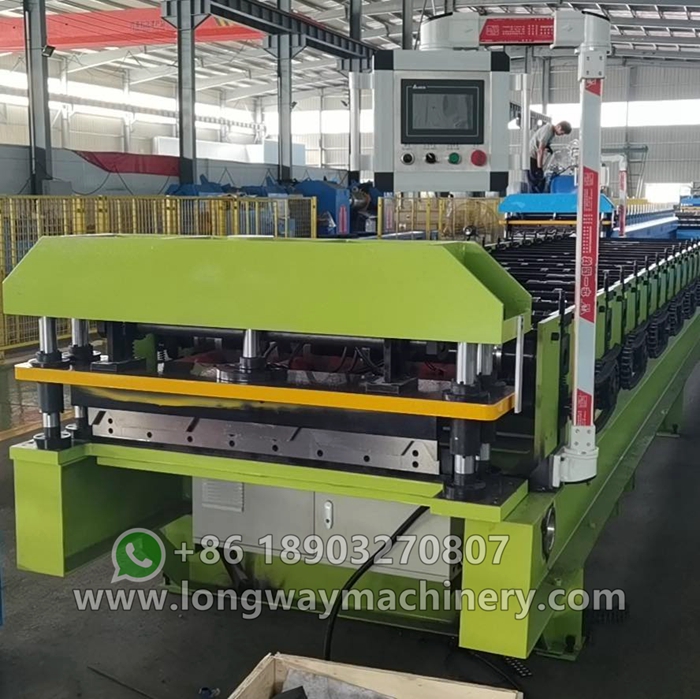

Global Manufacturing Landscape
As the demand for slitting lines has surged globally, so has the growth of factories that specialize in their production. Primarily located in industrial hubs, these factories employ a skilled workforce capable of designing and assembling complex machinery. Countries like China, Germany, and Japan are leaders in slitting line manufacturing, exporting their technologies worldwide.
The global nature of the slitting line machine industry has fostered competition, driving improvements in technology and service delivery. Factories are now focusing not just on producing machines but also on offering comprehensive customer support, including installation, training, and maintenance services. This holistic approach enhances customer satisfaction and builds long-term business relationships.
Economic Impact
The significance of slitting line machine factories extends beyond the manufacturing floor. They contribute to the local economy by providing jobs and supporting ancillary industries such as raw materials supply and logistics. Additionally, by enhancing the efficiency of metal processing, these factories play a crucial role in reducing production costs across various industries, ultimately benefiting consumers.
Furthermore, as companies increasingly prioritize sustainability, slitting line machine factories are adopting eco-friendly practices. Innovations in machinery design have led to reduced energy consumption and lower emissions, aligning with global trends towards greener manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
In summary, slitting line machine factories represent a vital segment of the manufacturing industry. As technology continues to evolve, these factories will play an increasingly important role in supporting diverse sectors around the globe. Their contributions to efficiency, economic stability, and sustainability underscore their significance in our modern industrial landscape. As the industry progresses, we can expect smarter machines and more agile factories that not only adapt to the present but also shape the future of metal processing.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025