Cost Analysis for Roofing Sheet Production Facility Setup
The Cost Factors of Setting Up a Roofing Sheet Manufacturing Plant
Manufacturing roofing sheets is a lucrative business opportunity that has gained significant attention in recent years due to the increasing demand for quality roofing materials. The establishment of a roofing sheet manufacturing plant involves various costs and considerations that potential investors must understand to ensure the project's success. This article explores the main cost factors associated with setting up a roofing sheet manufacturing plant.
1. Land Acquisition and Location Costs
The first step in establishing a roofing sheet manufacturing plant is acquiring suitable land. The cost of land can vary significantly based on the location, size, and the proximity to suppliers and customers. A site that is well-connected to major roads, railways, or ports can help reduce transportation costs, thereby enhancing profitability. Moreover, zoning regulations and local government policies can influence land cost, so it's crucial to conduct thorough research before making a purchase.
2. Building and Infrastructure Development
Once the land is secured, the next major cost involves constructing the manufacturing facility and related infrastructure. The size of the plant will depend on the anticipated production capacity. An efficient layout that optimizes workflow can enhance productivity and minimize operational costs. Key infrastructure components may include production lines, storage areas for raw materials, a quality control lab, and administrative offices. Additionally, utilities such as electricity, water, and drainage systems must be installed, which adds to the overall cost.
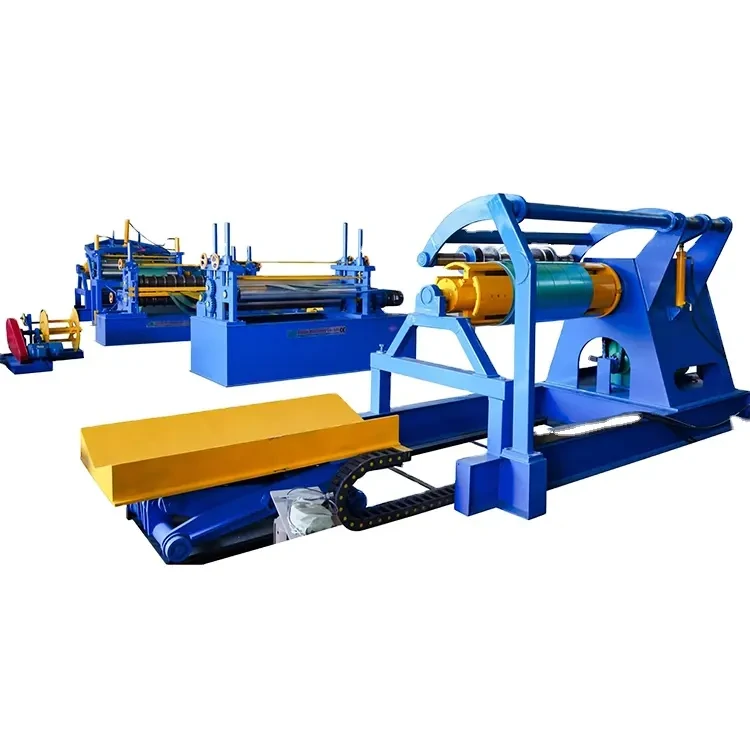
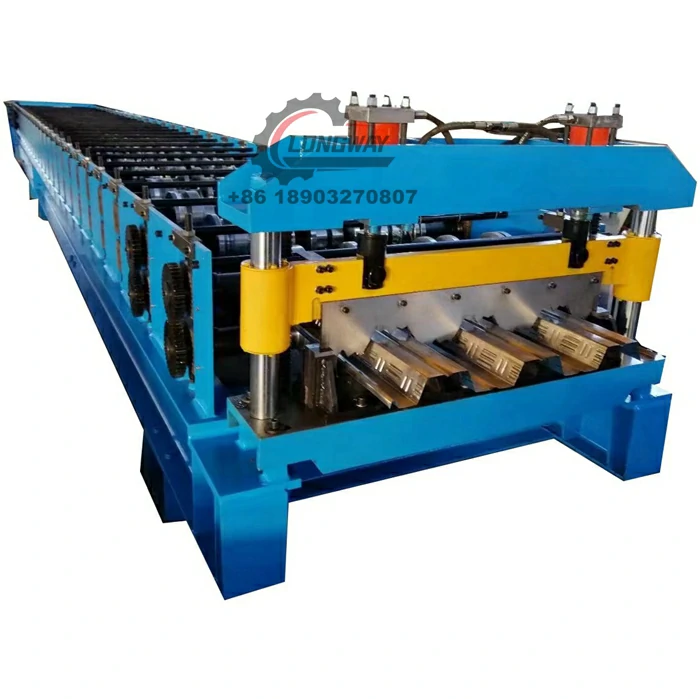
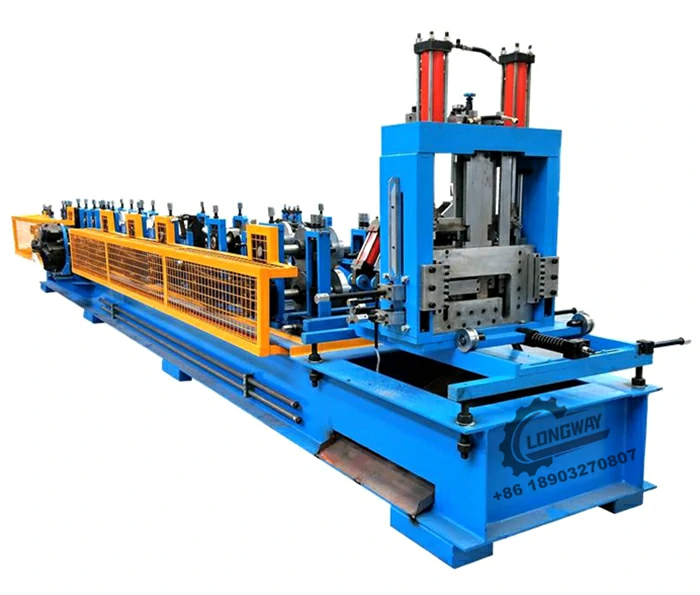
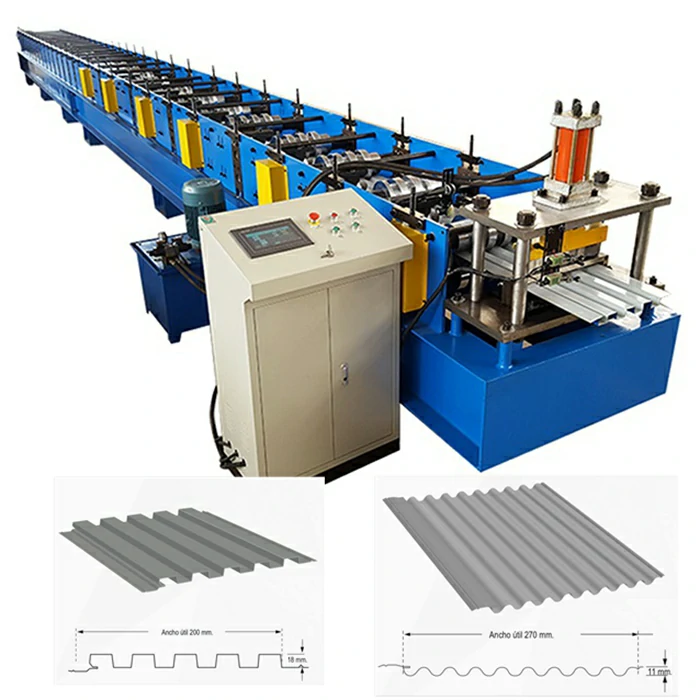
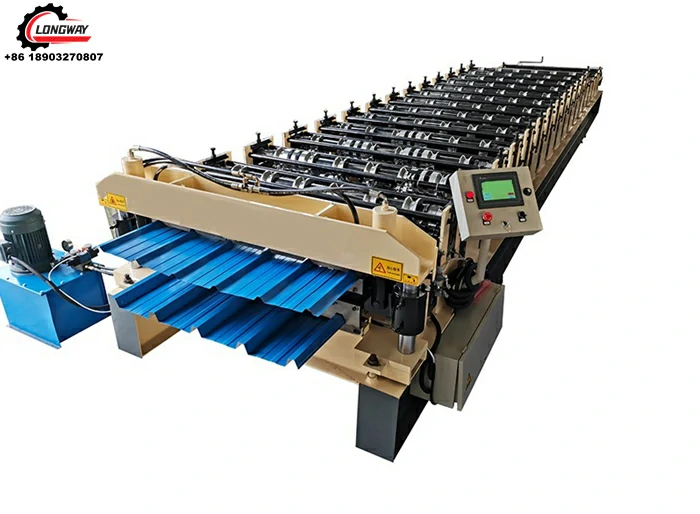
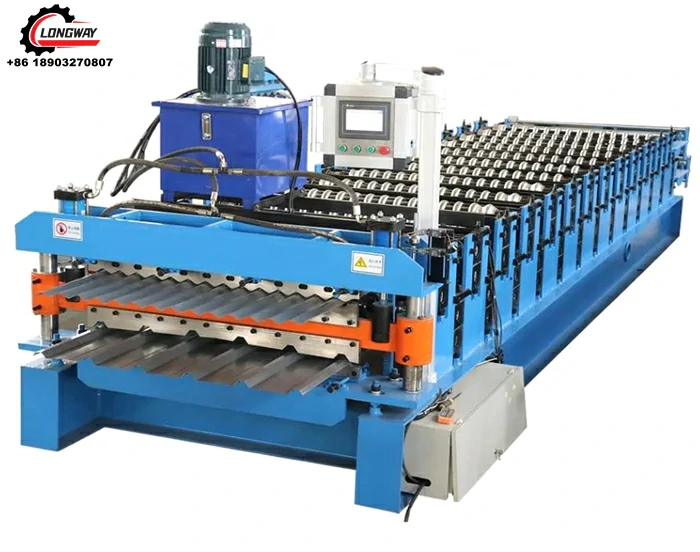
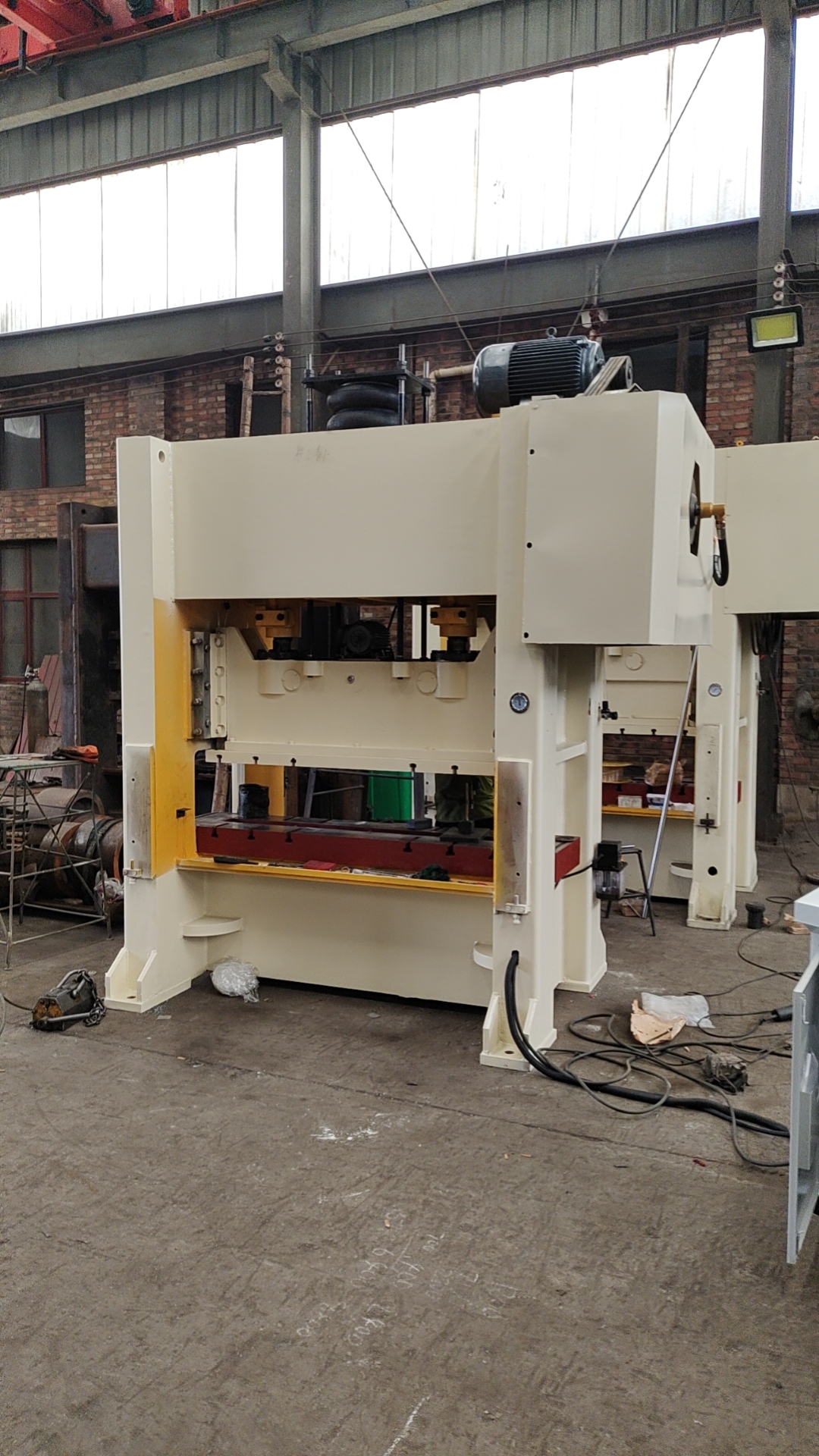
3. Machinery and Equipment Investment
The heart of a roofing sheet manufacturing plant lies in its machinery and equipment. This includes roll-forming machines, cutting machines, and various auxiliary equipment for handling materials. The choice of technology impacts the cost, quality, and efficiency of production. Advanced machinery may require a higher initial investment but can lead to lower operational costs and improved product quality in the long run. It's essential to assess the production capacity, automation levels, and maintenance costs of the machinery when budgeting for this segment.
4. Raw Materials and Supply Chain Management
roofing sheet manufacturing plant cost company

The cost of raw materials is a significant component of the total expenditure in roofing sheet manufacturing. Typical materials include steel, aluminum, and polymer-based products, each with its own market price fluctuations. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can help secure favorable pricing and ensure a consistent supply of quality materials. Additionally, effective supply chain management, including transportation and storage of raw materials, is vital to minimize costs and avoid production delays.
5. Labor Costs
Labor costs encompass salaries, benefits, and training for employees. Skilled labor is often required for operating sophisticated manufacturing equipment and managing quality control processes. Investing in training programs can enhance workforce efficiency and product quality, but it also adds to initial costs. Furthermore, considering labor laws and regulations in the chosen location is essential, as they can affect wage standards and operational costs.
6. Marketing and Sales Expenses
To ensure the longevity and profitability of the roofing sheet manufacturing plant, an effective marketing and sales strategy must be developed. This includes market research, branding, advertising, and establishing a sales team. Allocating a budget for marketing is vital for creating awareness about the products and attracting customers. Networking within the construction industry and attending trade shows can also help in building valuable connections.
7. Regulatory Compliance and Permits
Navigating the legal landscape is crucial when setting up a manufacturing plant. Acquiring necessary permits and licenses, as well as ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, can incur significant costs. These might include environmental assessments, safety inspections, and adherence to standards set by local, state, or national authorities. Investing in legal counsel familiar with manufacturing regulations can help streamline this process and avoid potential fines.
Conclusion
Investing in a roofing sheet manufacturing plant presents a promising opportunity, but it requires careful planning and budgeting. Understanding the various cost factors—from land acquisition and infrastructure development to machinery investment and labor costs—can help prospective investors make informed decisions. With the right strategy, a roofing sheet manufacturing plant can not only meet the increasing demand for quality roofing materials but also yield substantial returns on investment.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025