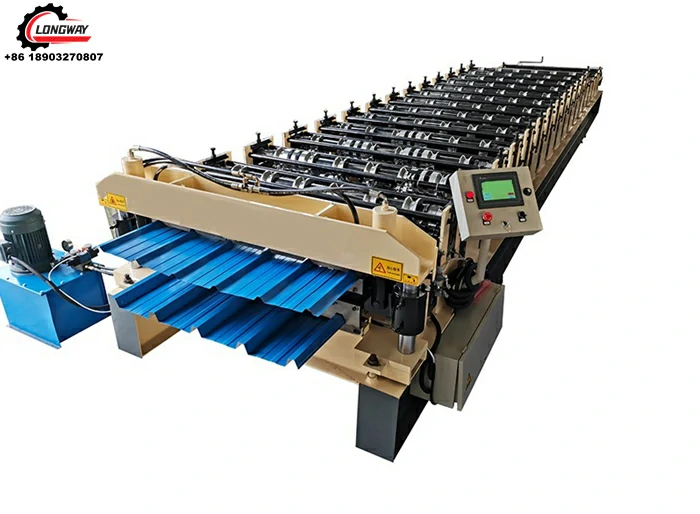
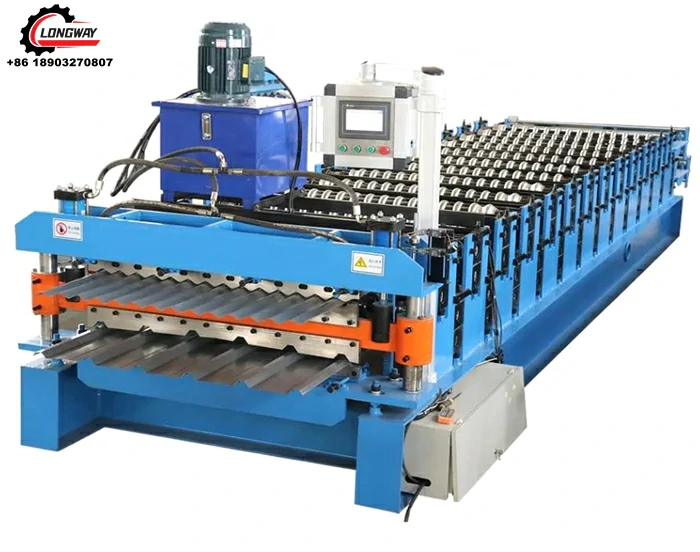
maquina para zinc acanalado
Understanding the Machinery for Channelized Zinc Production
The increasing demand for lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant materials has made zinc a popular choice in various industries. Among its many applications, one significant process involves creating channelized zinc products. This article delves into the machinery specifically designed for producing channelized zinc, revealing both its importance and operational aspects.
Channelized zinc typically refers to zinc that has been shaped into specific channels or profiles, often used in construction, automotive parts, and diverse manufacturing applications. The machinery designed for this purpose includes several critical components that together facilitate the transformation of raw zinc into finished products.
The Core Machinery Components
1. Zinc Melting Furnaces The initial step in the process involves melting zinc ingots, as pure zinc has a melting point of approximately 419.5°C (787.1°F). This essential machinery ensures uniform heating and allows for the removal of impurities, providing high-quality molten zinc for further processing.
2. Die Casting Machines Once the zinc is melted, it is poured into specially designed molds through die casting machines. These machines enable precision shaping of the molten zinc into desired profiles. The die-casting process allows for intricate designs, flexibility in production, and reduces waste, making it a vital part of channelized zinc production.
3. Rolling Mills After the initial casting, the channelized zinc pieces often undergo further processing with rolling mills. These machines apply pressure to flatten and further shape the zinc product, enhancing its mechanical properties and ensuring uniform thickness across the width of the material.
maquina para zinc acanalado
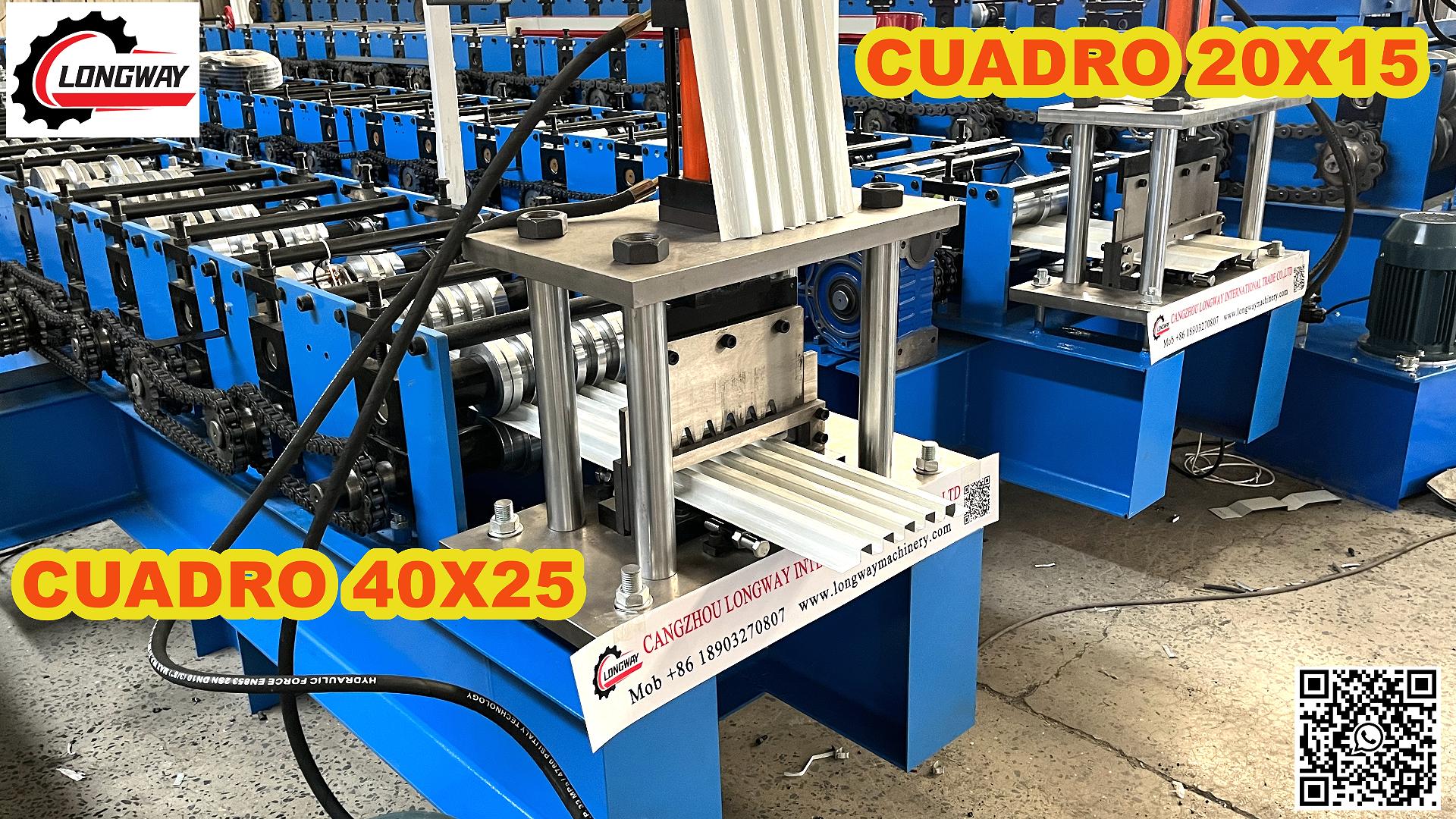

4. Extruders For producing complex shapes, extrusion machinery is employed. Extrusion allows for continuous profiles to be manufactured, meaning that lengths of channelized zinc can be produced with consistent quality and minimal labor input.
5. Surface Treatment Equipment After shaping, surface treatment is essential to enhance corrosion resistance and improve the aesthetic quality of the finished product. This may include painting, plating, or applying specialized coatings, all of which extend the life and durability of the zinc items.
The Importance of Automation
Modern machinery for producing channelized zinc increasingly employs automation. Automated systems not only enhance production efficiency but also improve safety by minimizing human involvement in hazardous processes. Sensors and robotics can monitor temperatures, mold filling, and cooling cycles, ensuring consistent product quality.
Conclusion
The machinery designed for producing channelized zinc plays a pivotal role in several industries. From melting furnaces to extruders, each component is tailored to optimize efficiency and quality in the production process. As the demand for zinc products continues to grow, advancements in machinery and technology will undoubtedly drive further innovations, leading to even higher standards in the manufacturing of channelized zinc and its applications. Understanding this machinery not only highlights its significance but also points toward the future of zinc production.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025