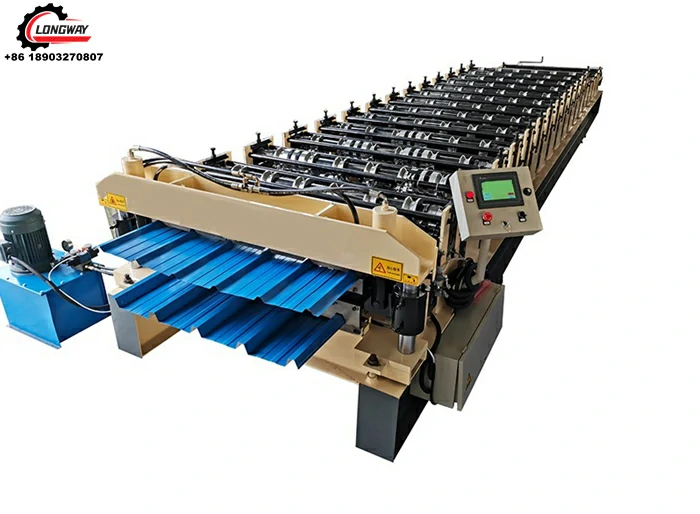
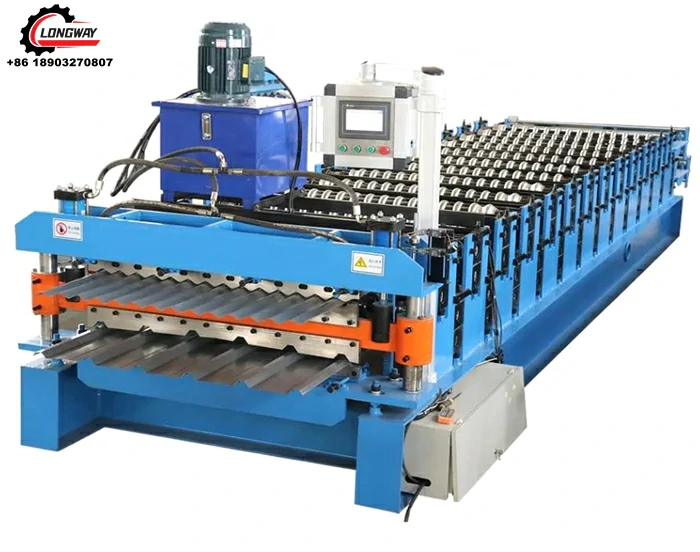
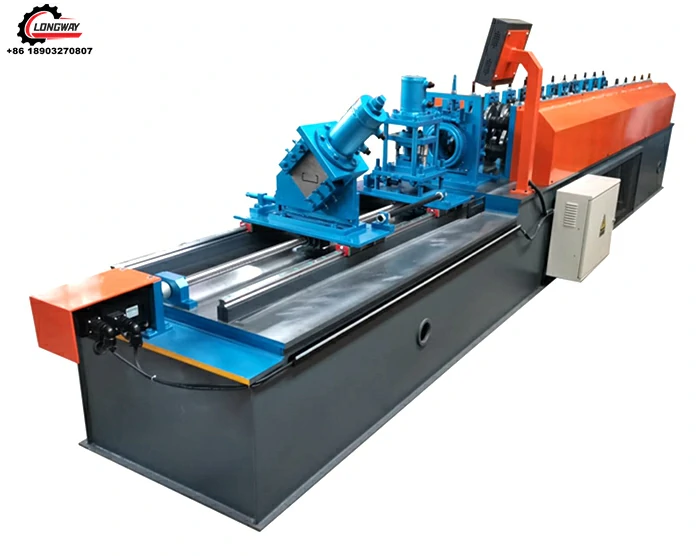
Machine for Producing Corrugated Zinc Sheets for Various Industrial Applications and Construction Needs
The Process of Manufacturing Corrugated Zinc Sheets
The manufacturing of corrugated zinc sheets, also known as corrugated galvanized iron, plays a significant role in the construction and manufacturing sectors due to their durability, lightweight nature, and versatile applications. The process of producing these sheets involves several steps, utilizing specialized machinery designed for efficiency and quality output.
Understanding the Material
Zinc is a popular choice for coating steel to prevent corrosion. The galvanized steel starts as a flat sheet of steel, which is then coated with a layer of zinc. This forms a protective barrier against moisture and other environmental factors, significantly extending the lifespan of the metal. The introduction of a corrugated pattern not only adds to the aesthetic appeal but also enhances the structural integrity of the sheets, making them more rigid and capable of withstanding various loads.
The Manufacturing Process
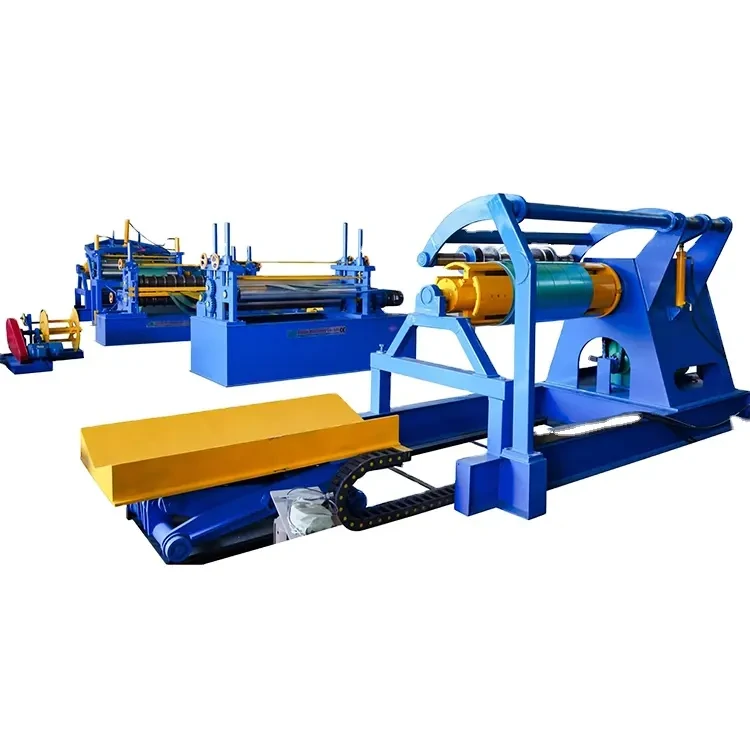
The manufacturing process for corrugated zinc sheets begins with the preparation of raw materials. High-quality steel sheets are first immersed in molten zinc in a process called hot-dipping, ensuring that the zinc adheres well to the surface of the steel. The thickness of the zinc layer can be controlled, allowing manufacturers to customize the level of corrosion resistance based on customer requirements.
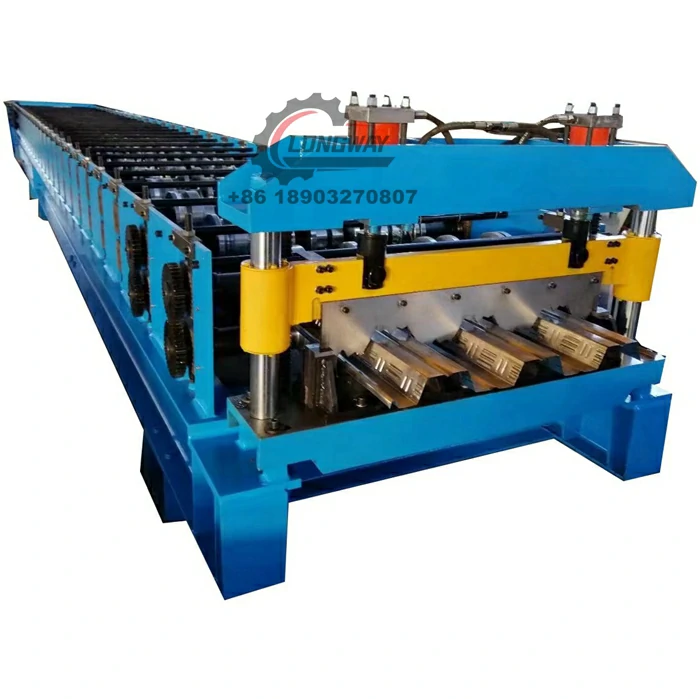
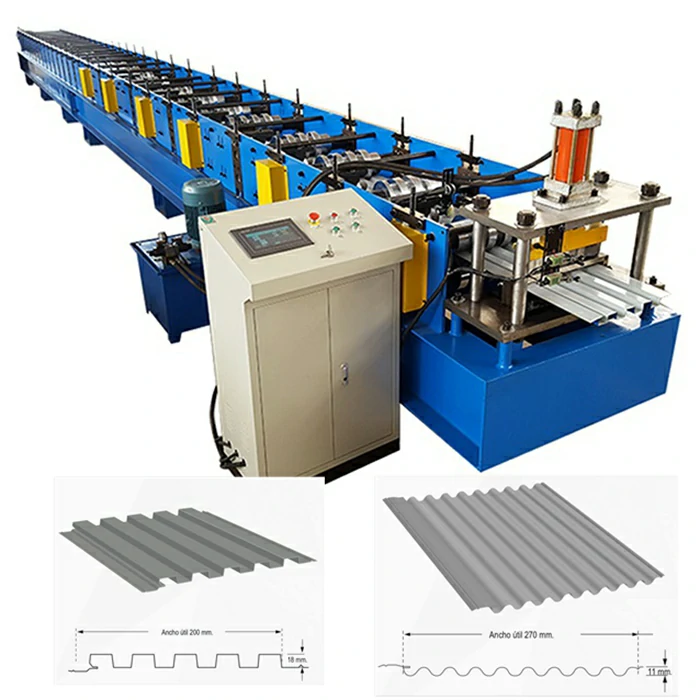
Once the steel sheets are coated, they proceed to the corrugating machine. Here, the flat sheets pass through a set of rollers that create the characteristic wavy shape. This process is critical as it contributes to the sheet's strength and ability to shed water effectively. The design of the corrugation can vary based on intended use; for example, deeper corrugations may provide sturdier support for roofing applications.
Quality Control and Finishing
maquina para fabricar zinc acanalado
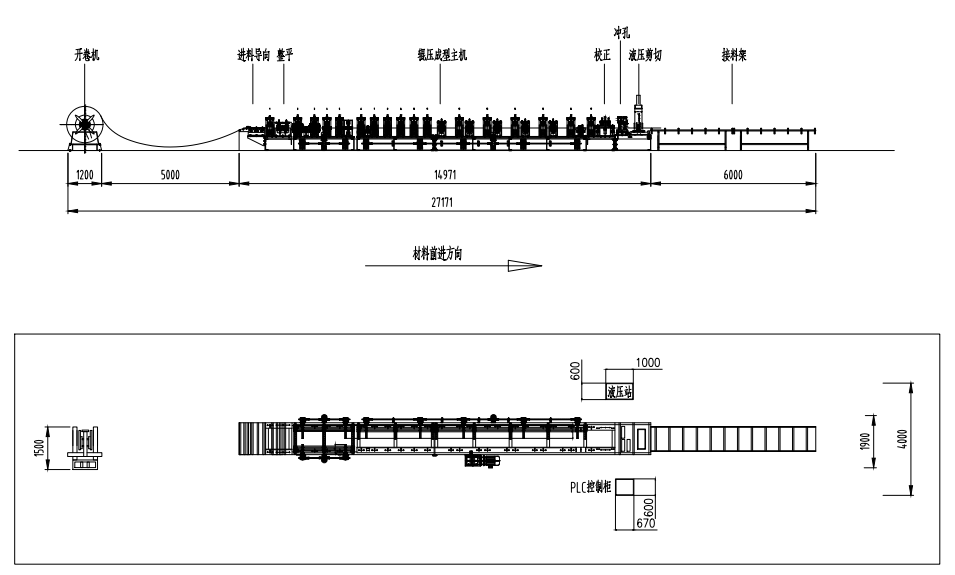
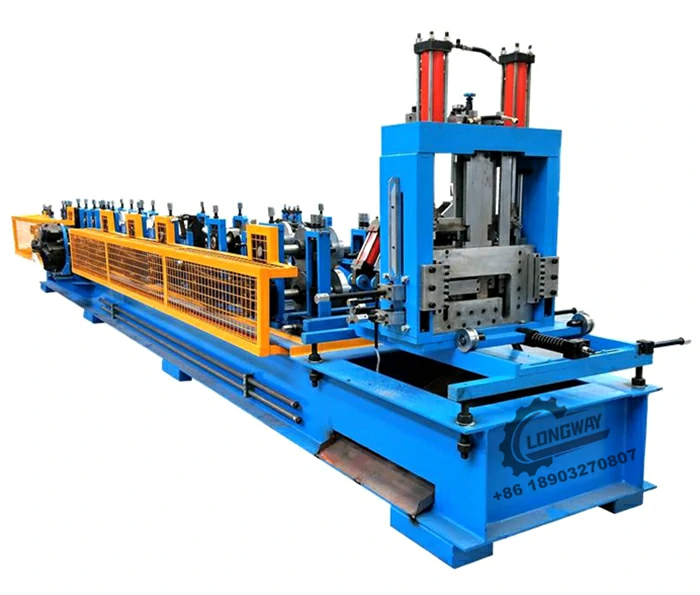
Quality control is paramount throughout the manufacturing process. After forming the corrugated pattern, the sheets undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet industry standards for thickness, coating, and durability. Many manufacturers apply additional treatments, such as painting or applying a protective layer, to further enhance the product's longevity and aesthetic appeal.
After passing quality control, the sheets are cut to size and prepared for distribution. Many facilities utilize automated systems to package the sheets efficiently, ensuring they are ready for shipment to construction sites or distributors.
Applications and Advantages
Corrugated zinc sheets find use in various applications, including roofing, fencing, cladding, and container construction. Their lightweight nature makes them easier to transport and install than traditional roofing materials, while their resistance to the elements ensures they maintain their integrity over time.
Furthermore, these sheets are environmentally friendly. Zinc is a recyclable material, and many manufacturers aim to minimize waste during production, contributing to sustainable construction practices. The longevity of the material also means less frequent replacements, further reducing environmental impact.
Conclusion
The machine for manufacturing corrugated zinc sheets demonstrates a blend of technology and materials science. From the initial hot-dipping process to the final corrugation and quality control, every step is designed to produce a robust product that meets the demands of modern construction. As industries continue to strive for sustainability and durability, the popularity of corrugated zinc sheets is likely to remain strong, proving that innovation in manufacturing can lead to practical and eco-friendly solutions.
-
Top Metal Roofing Machine ManufacturersNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Production Line with a Gutter Forming Machine for SaleNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Production Capacity with a Purlin Machine for SaleNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Exploring Roofing Sheets Manufacturing Machine PriceNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Drywall Roll Forming Machine for SaleNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Best Roof Panel Machine for SaleNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025