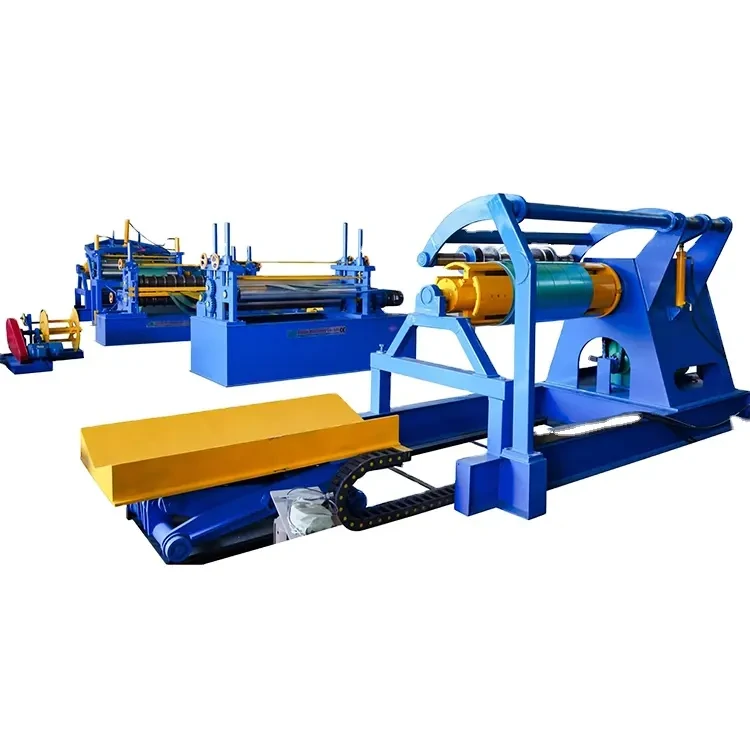
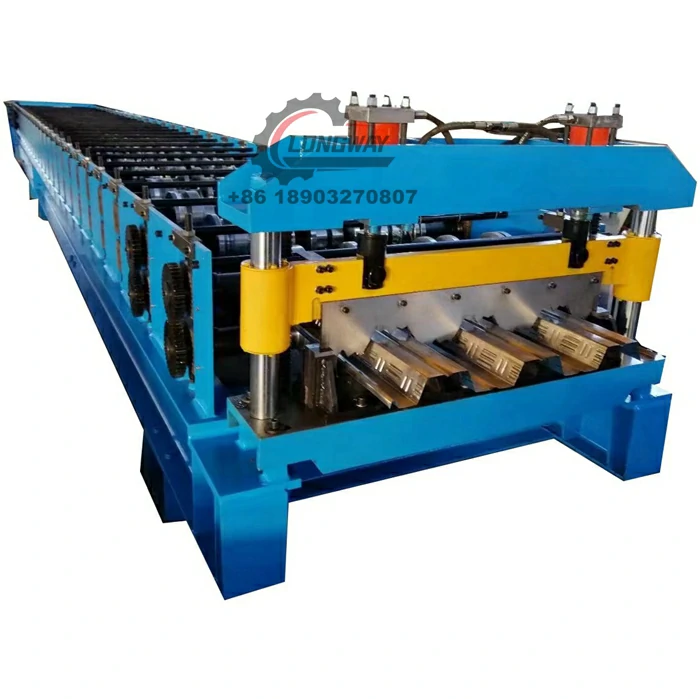
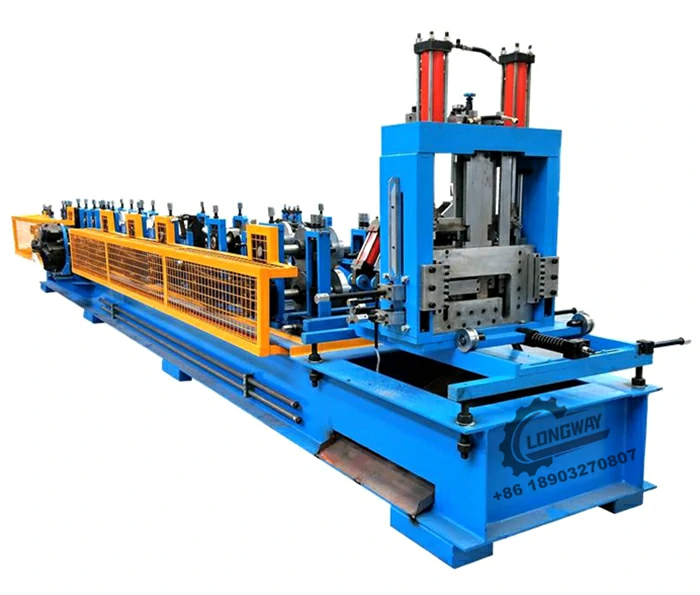
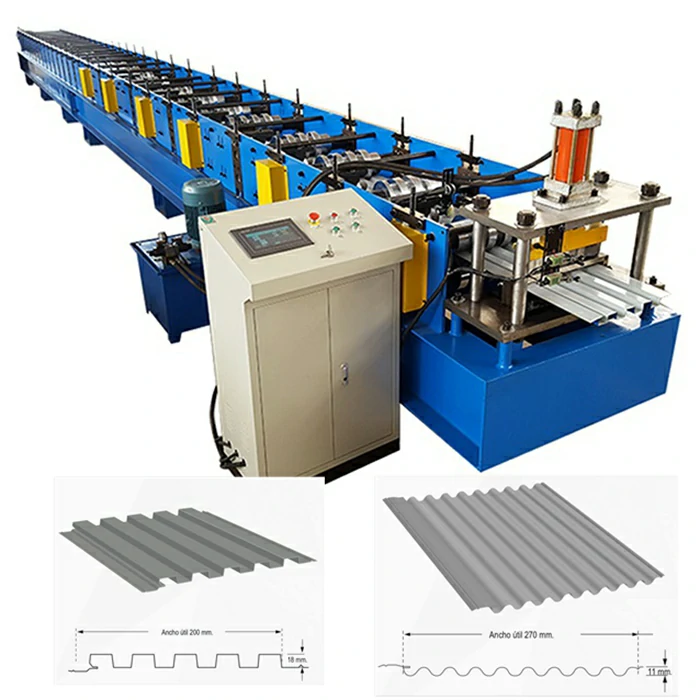
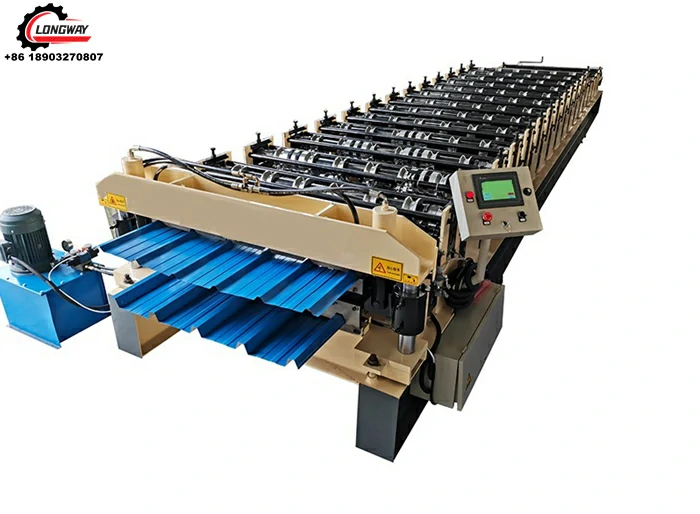
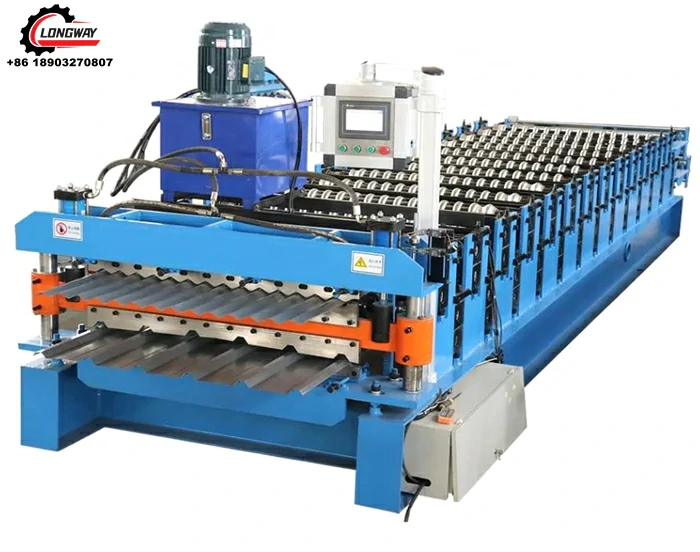
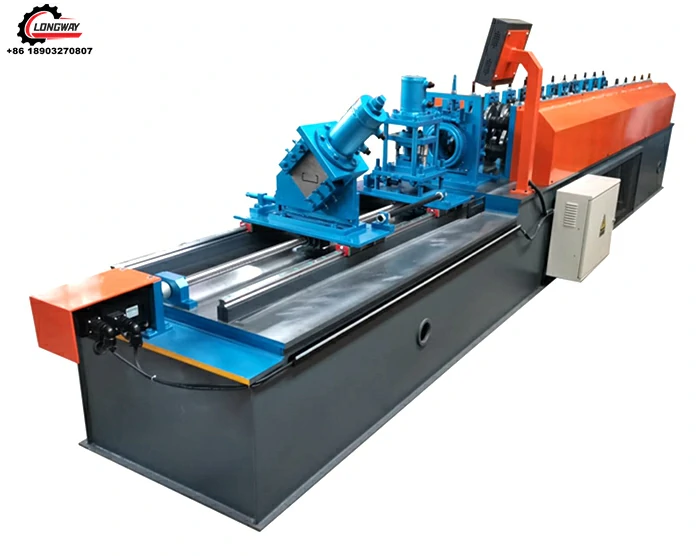
High-Quality Track Rolling Forming Machine Manufacturer for Precision Metal Fabrication Solutions
Exploring the Track Roll Forming Machine Factory Innovations in Efficient Production
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, the demand for high-quality, precision-engineered components is ever-increasing. One of the pivotal technologies driving this demand is the roll forming process, particularly in the production of track components used in various applications such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. At the heart of this technology lies the track roll forming machine, a sophisticated piece of equipment designed to create complex shapes from metal strips with remarkable efficiency and accuracy. This article delves into the significance of track roll forming machine factories, their operations, and the innovations shaping their future.
Understanding Roll Forming
Roll forming is a continuous bending process used to shape raw metal, typically a flat strip, into a desired profile through a series of rolling mills. The process involves feeding the strip through a series of rollers that gradually form it into the required shape. Track roll forming machines specifically create tracks, which are vital components for various applications, including conveyor systems, agricultural machinery, and even electric vehicles.
The advantages of roll forming are substantial. It offers an efficient method for producing long lengths of uniform sections, reduces waste material, and allows for complex shapes to be achieved without the need for additional machining. These benefits make roll forming machines essential in factories specializing in track production.
The Role of Track Roll Forming Machine Factories
Track roll forming machine factories are dedicated facilities that design, manufacture, and assemble these advanced machines. These factories utilize state-of-the-art technology and skilled personnel to ensure high-quality output. The manufacturing process generally includes several important stages
track roll forming machine factory

1. Design and Engineering The initial phase involves engineers designing the machine according to specific product requirements. Computer-aided design (CAD) software allows for precise modeling, ensuring that the end product meets all necessary specifications.
2. Material Selection The choice of raw materials is critical to the performance of the roll forming machine. Factories source high-quality steel or aluminum alloys that can withstand the stresses of the forming process while retaining durability and flexibility.
3. Assembly and Calibration After the components are manufactured, they are meticulously assembled. Accurate calibration is vital to ensure that the rollers align perfectly and produce consistent track profiles.
4. Testing and Quality Control Each machine undergoes rigorous testing to verify its functionality and precision. Quality control measures are implemented to detect any defects or deviations from specifications, guaranteeing that only the best machines are delivered to clients.
Innovations Driving the Industry Forward
As the industrial sector evolves, so does the technology behind track roll forming machines. Innovations such as automation, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI), and advancements in materials science are reshaping factories. Automation enhances production speed and consistency, while AI algorithms can predict maintenance needs, reducing downtime. Additionally, the development of advanced coatings and treatments improves the durability of the formed tracks, adding value to the end products.
In conclusion, track roll forming machine factories play a crucial role in manufacturing sophisticated track components essential for numerous industries. Through meticulous design, quality production processes, and ongoing innovations, these factories continuously improve efficiency and product quality. As global industries lean toward automation and advanced manufacturing techniques, the future of track roll forming machines looks promising, paving the way for new possibilities in production capabilities. Whether in the automotive sector or in construction, the impact of these machines resonates across various fields, underscoring their significance in modern manufacturing.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025