High-Quality Drip Edge Roll Former Production for Efficient Roofing Solutions and Custom Designs
Drip Edge Roll Former Factory An Insight into Manufacturing Quality Roofing Components
In the world of modern construction, quality and durability are paramount, especially when it comes to roofing systems. Among the many components that contribute to a well-performing roof, the drip edge plays a crucial role. This small yet significant element helps direct water away from the roof structure, protecting it from potential damage and ensuring longevity. To meet the increasing demand for this vital accessory, drip edge roll former factories have emerged as essential players in the construction industry.
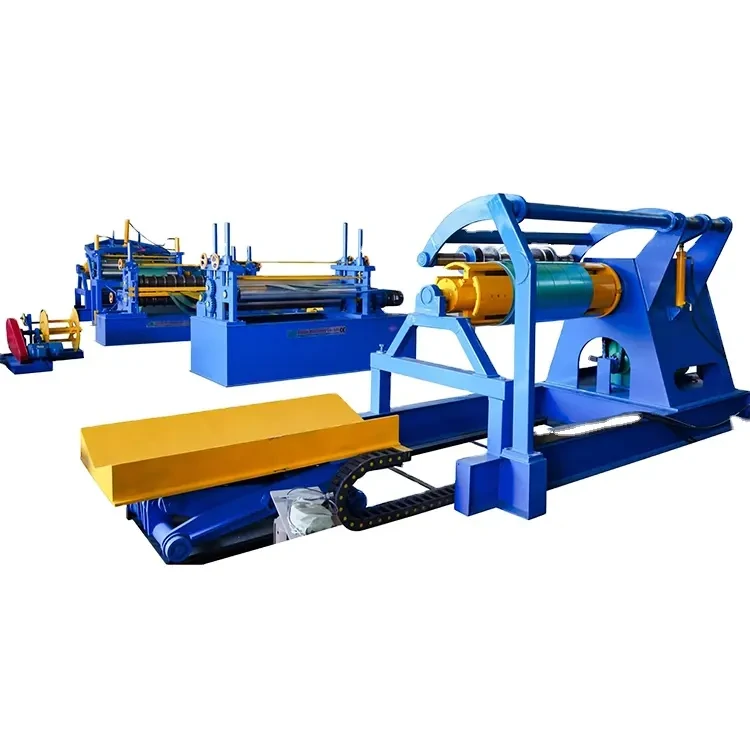
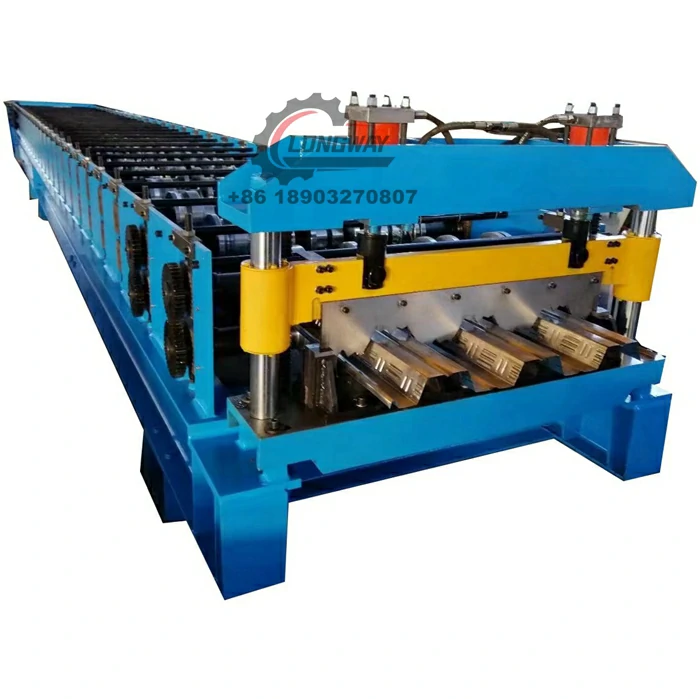
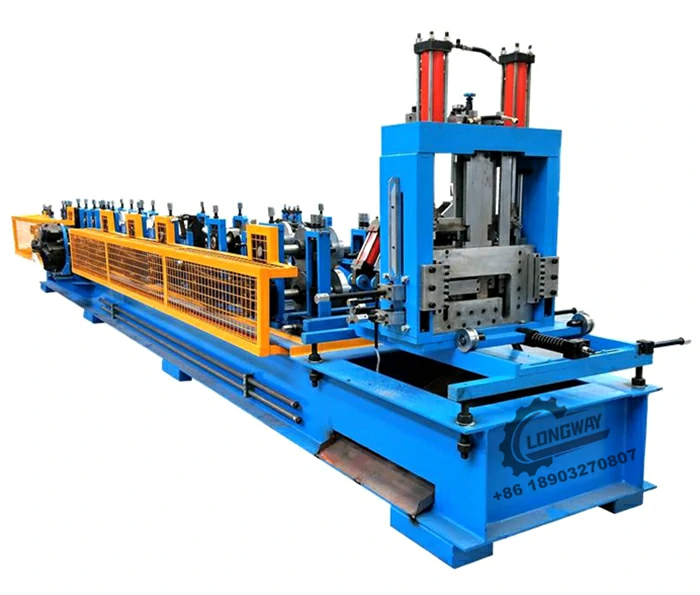
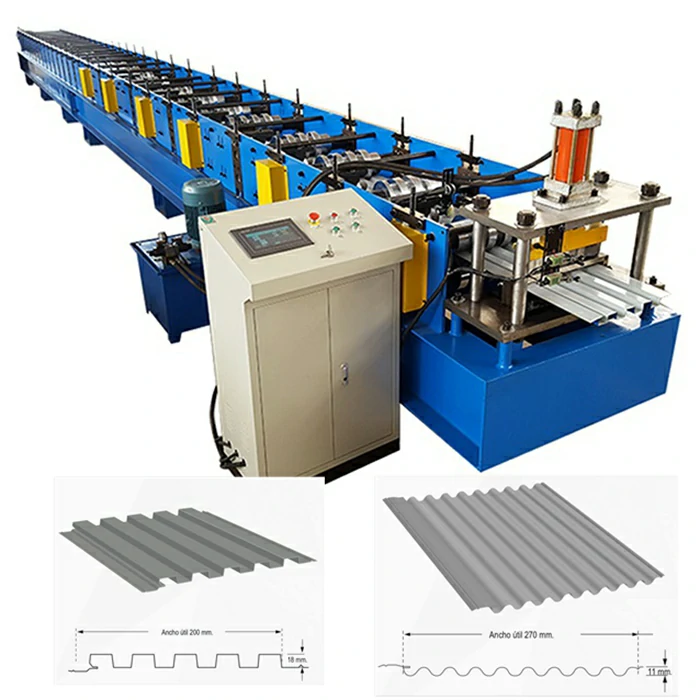
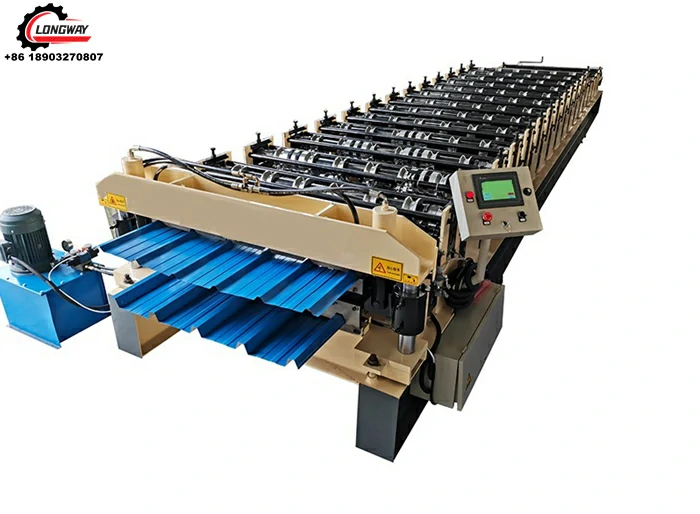
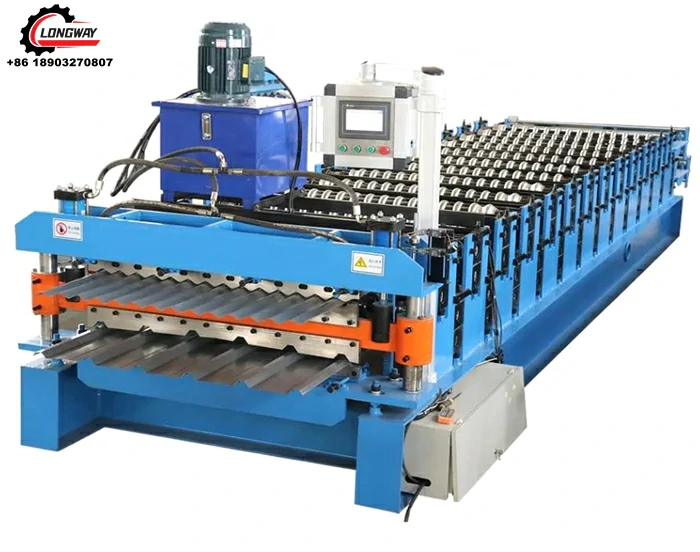
A drip edge roll former factory specializes in the manufacturing of drip edge components using advanced machinery and technology. The roll-forming process involves feeding metal coils into a machine that shapes the material into a desired profile. This method is efficient and allows for the production of long, continuous lengths of drip edge, which can be cut to size depending on the project’s requirements. Typically, materials such as aluminum, galvanized steel, or zinc are used due to their excellent corrosion resistance and longevity.
One of the primary advantages of a drip edge roll former factory is the ability to customize products. With various architectural styles and roofing systems, a one-size-fits-all approach is insufficient. Factories often work closely with architects and contractors to develop tailored solutions that match specific project needs. This customization can include varying profile heights, widths, and finishes, allowing for seamless integration into different roofing designs.
Quality control is another critical aspect of the manufacturing process in a drip edge roll former factory. Before products leave the factory, they undergo rigorous testing to ensure that they meet industry standards. This includes checking for dimensional accuracy, structural integrity, and surface finish. Factories may also perform corrosion resistance tests, particularly for products intended for harsher environmental conditions. By maintaining high standards of quality, manufacturers can provide reliable products that enhance the performance and aesthetic appeal of roofing systems.
drip edge roll former factory

Moreover, the efficiency of the roll-forming process not only minimizes waste but also significantly reduces production time. The capacity to produce drip edge components in large volumes means that construction projects can stay on schedule. Fast production times also encourage manufacturers to uphold competitiveness in pricing, benefiting contractors and builders looking for cost-effective options without compromising quality.
A proactive drip edge roll former factory keeps abreast of industry trends and technological advancements. Incorporating automation and smart technologies can enhance the manufacturing process, improve precision, and streamline operations. By embracing innovation, these factories can respond effectively to market demands and customer preferences, ensuring that they remain at the forefront of the roofing component industry.
Environmental considerations are gaining increasing importance in manufacturing processes. Leading drip edge roll former factories are implementing eco-friendly practices by sourcing sustainable materials and optimizing energy use during production. These initiatives not only help in reducing the carbon footprint but also align with the global movement towards environmentally responsible building practices.
In conclusion, the role of a drip edge roll former factory in the construction industry is invaluable. By producing high-quality, customizable drip edge components through efficient and innovative manufacturing processes, these factories play a pivotal role in ensuring the durability and functionality of roofing systems. As construction demands evolve, the factories that prioritize quality, adaptability, and sustainability will undoubtedly lead the way in shaping the future of roofing solutions. Whether it’s a residential home or a commercial building, the meticulous production of drip edges is essential for safeguarding structures against the elements, underscoring their significance in modern architecture.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025