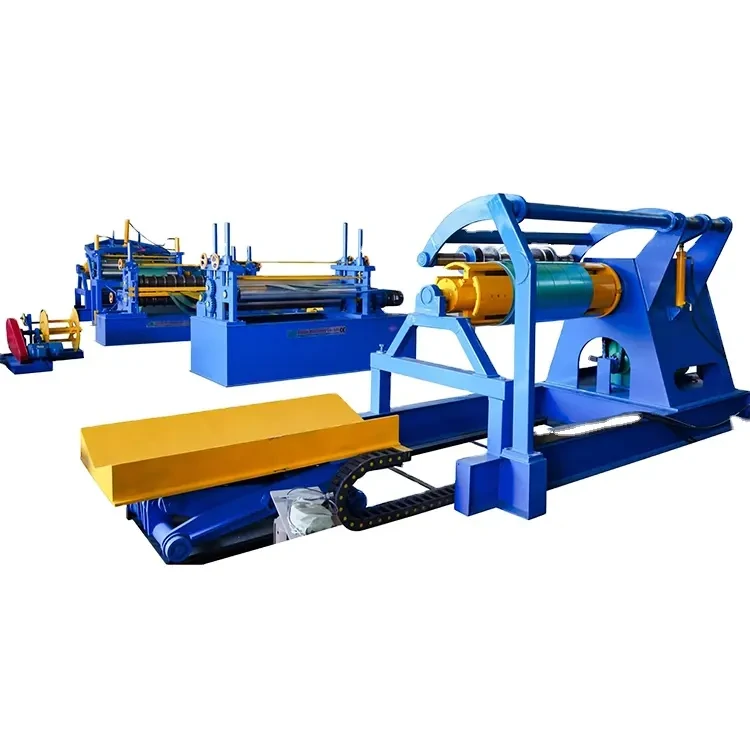
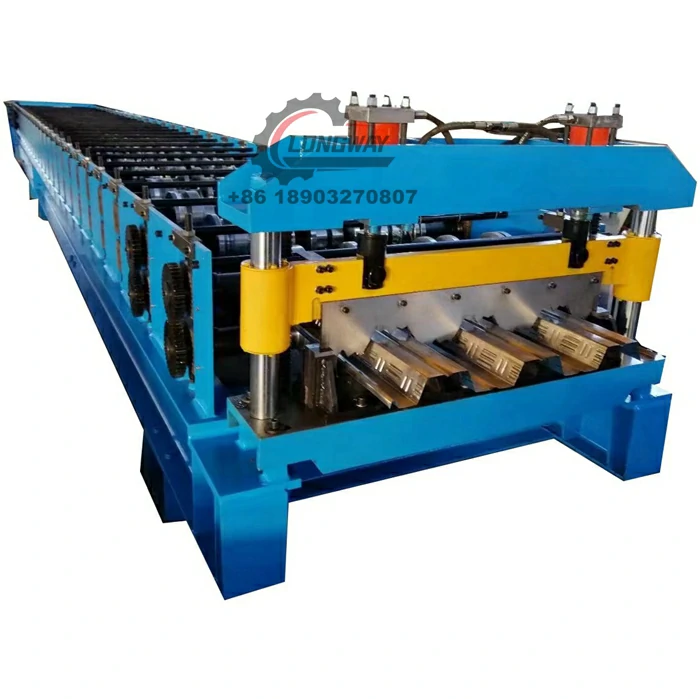
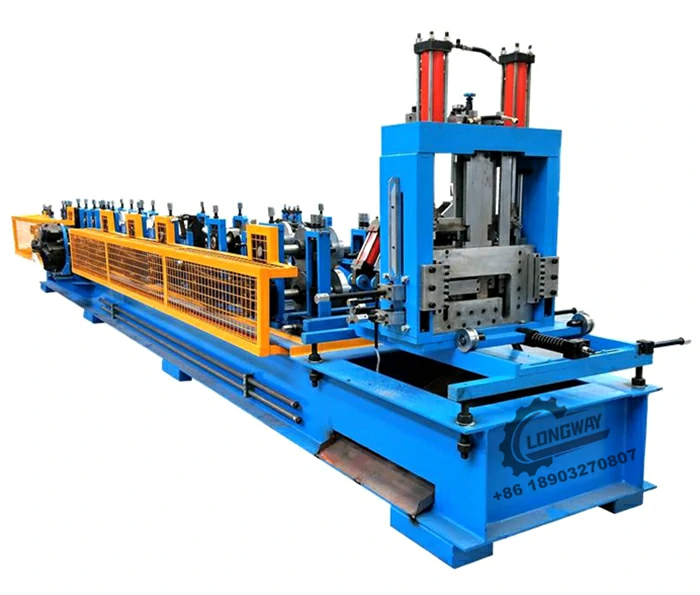
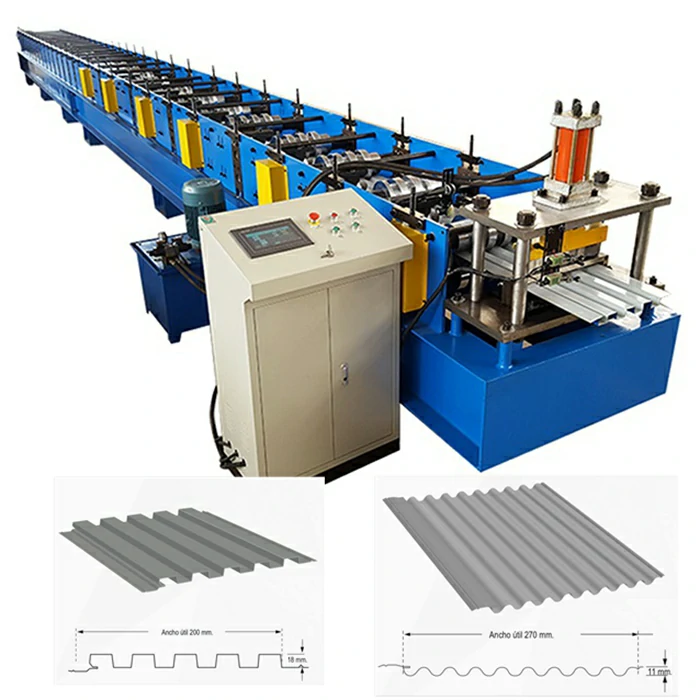
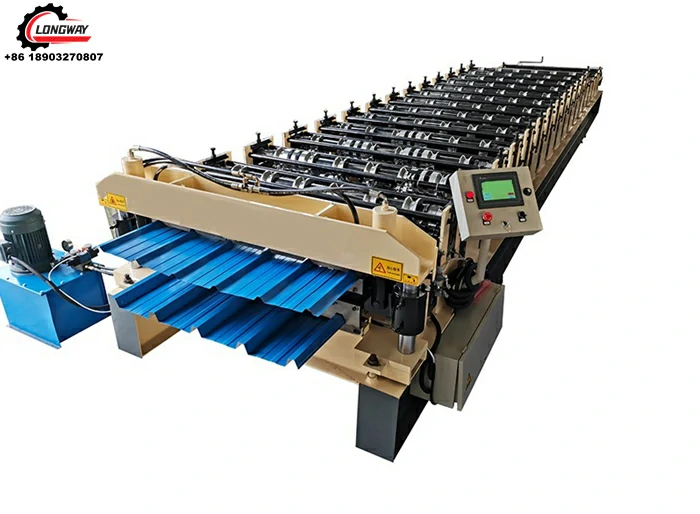
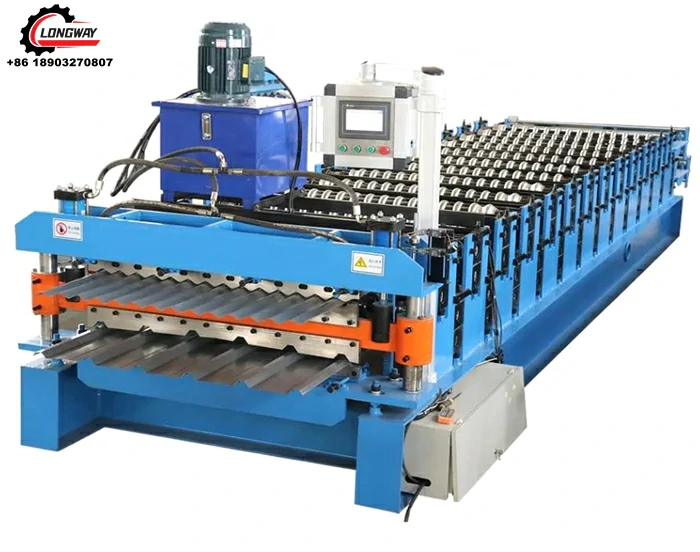
galvanized cold roll forming machine
The Advancements in Galvanized Cold Roll Forming Machines
In recent years, the demand for galvanized cold roll forming machines has surged, reflecting the increasing need for high-quality metal components in various industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing. These machines are renowned for their efficiency in producing durable and corrosion-resistant metal profiles, making them indispensable in modern production lines.
Understanding Cold Roll Forming
Cold roll forming is a metalworking process where a strip of metal, often in coil form, is continuously shaped into desired profiles through a series of rollers. Unlike hot rolling, where metal is heated above its recrystallization temperature, cold roll forming occurs at room temperature, which enhances the material's strength due to strain hardening. The galvanized aspect refers to the process where a layer of zinc is applied to the metal surface, providing excellent resistance to corrosion and extending the lifespan of the finished product.
The Benefits of Using Galvanized Cold Roll Forming Machines
One of the principal advantages of galvanized cold roll forming machines is their ability to produce precise and consistent profiles efficiently
. These machines can create various shapes, including C and Z sections, U channels, and custom profiles, which are commonly used in structural applications. The precision engineering of these machines ensures that tolerances are tight, which is critical for components that must fit together seamlessly in construction or manufacturing processes.Moreover, the galvanization process adds an additional layer of protection against environmental factors, making the products ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. These machines help in producing lightweight but sturdy components, contributing to more efficient energy usage in transport and reducing overall material costs.
Innovations in Technology
galvanized cold roll forming machine
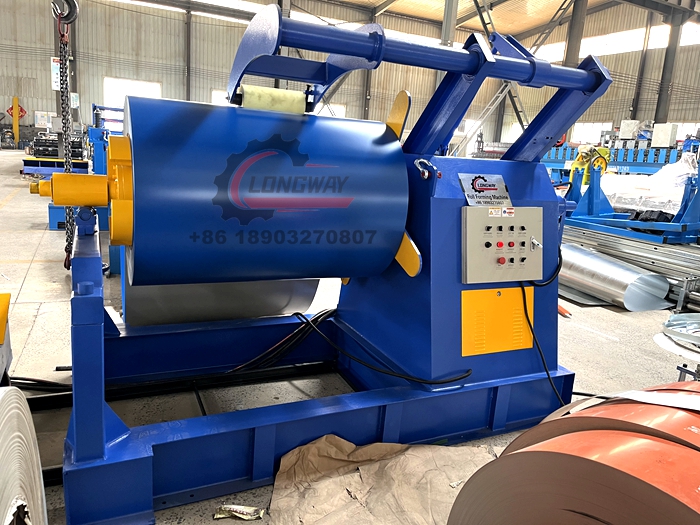

Recent advancements in technology have significantly improved the functionality and efficiency of galvanized cold roll forming machines. Automated systems equipped with advanced control software allow for quicker changeovers between production runs, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. Additionally, modern machines come with integrated quality control features, ensuring that any defects are identified and rectified in real-time.
The incorporation of robotics and smart manufacturing technologies further optimizes the roll forming process. For instance, by using Artificial Intelligence (AI), manufacturers can predict maintenance needs, thereby minimizing disruptions in production workflows. These innovations not only enhance the quality of the final products but also improve the overall sustainability of the manufacturing process, as they reduce waste and energy consumption.
Applications Across Industries
Galvanized cold roll forming machines are versatile and find applications in numerous industries. In construction, they are used to produce structural components, roof trusses, and framing systems that require high strength and durability. The automotive industry benefits from these machines through the creation of robust body parts and chassis components that meet the stringent safety standards.
In the manufacturing sector, these machines are employed to manufacture various goods ranging from furniture to shelving systems. Their capability to produce customized profiles means that manufacturers can quickly respond to market demands and create tailored solutions for clients.
Conclusion
As industries continue to evolve, the importance of galvanized cold roll forming machines will only grow. They provide a crucial link in the supply chain by producing high-performance components that meet the needs of modern infrastructure and manufacturing. Investing in these machines not only enhances production capabilities but also ensures that companies remain competitive in a rapidly changing market. With ongoing advancements, the future of galvanized cold roll forming looks promising, making it an essential aspect of modern manufacturing processes.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025