corrugated sheet pressing machine factory
The Significance of Corrugated Sheet Pressing Machines in Modern Manufacturing
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing and construction, corrugated sheets have gained immense popularity due to their lightweight, durability, and versatility. These sheets find applications in various industries, including building, packaging, and transportation. Central to the production of these corrugated sheets is the corrugated sheet pressing machine, a vital piece of equipment that ensures optimal efficiency and quality. This article delves into the intricate world of corrugated sheet pressing machines and their impact on manufacturing processes.
Understanding Corrugated Sheets
Corrugated sheets are primarily made from materials like steel, aluminum, or plastic, characterized by their wavy, ribbed edges. This design provides structural strength and rigidity, making them ideal for roofing, wall coverings, and protective packaging. The unique profile of corrugated sheets allows for lightweight construction without compromising on durability, making them a preferred choice in various sectors. However, to produce these sheets effectively, specialized machinery is required.
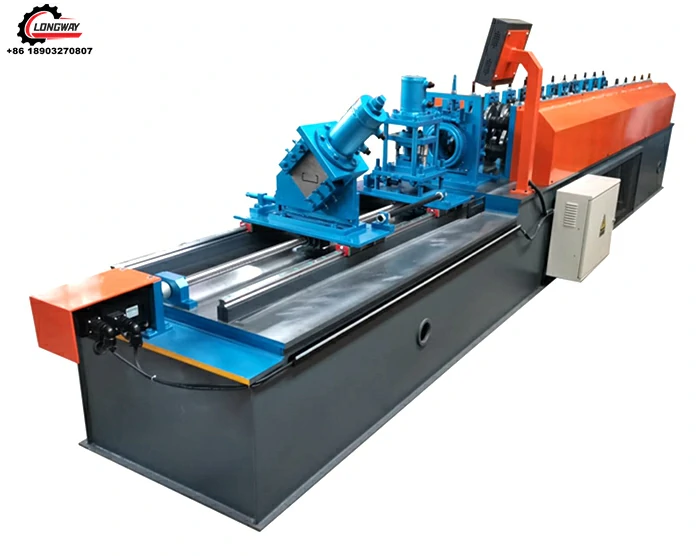
The Role of Corrugated Sheet Pressing Machines
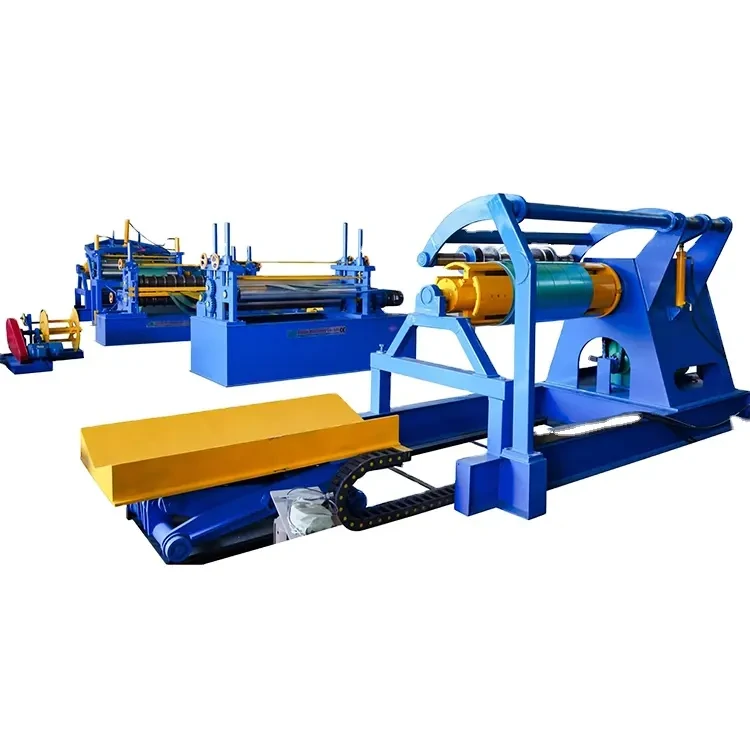
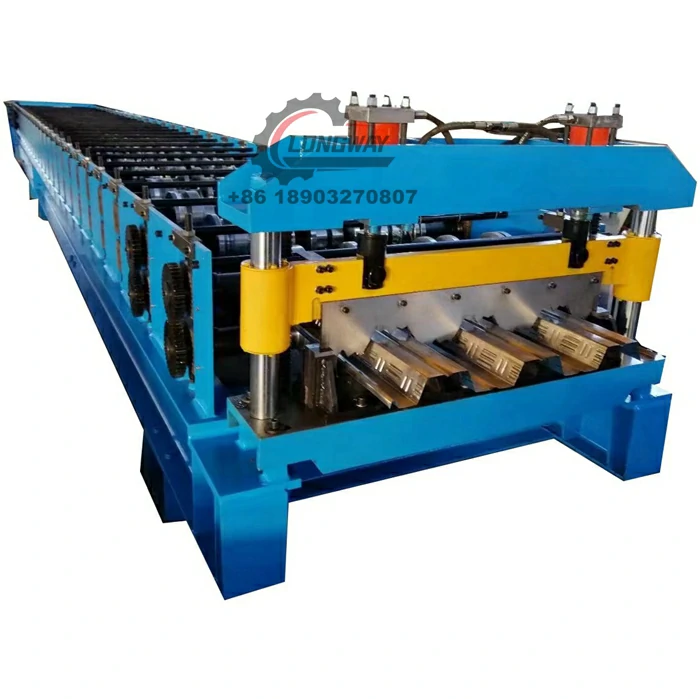
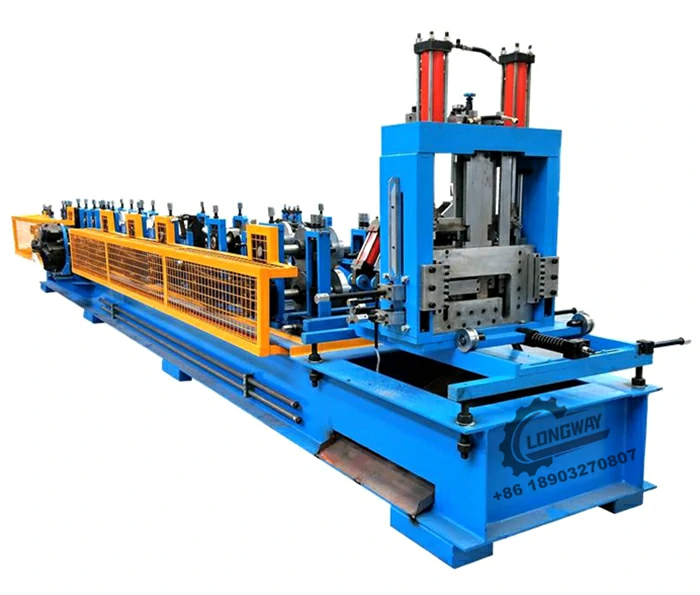
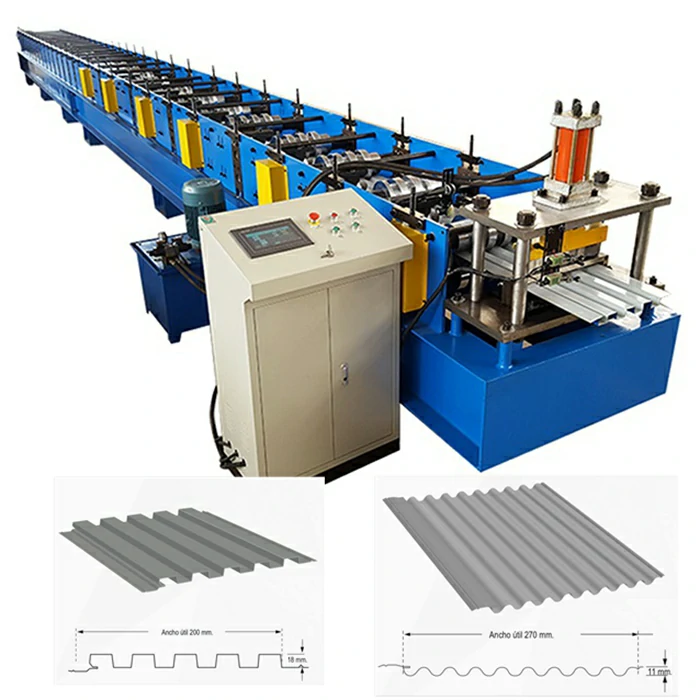
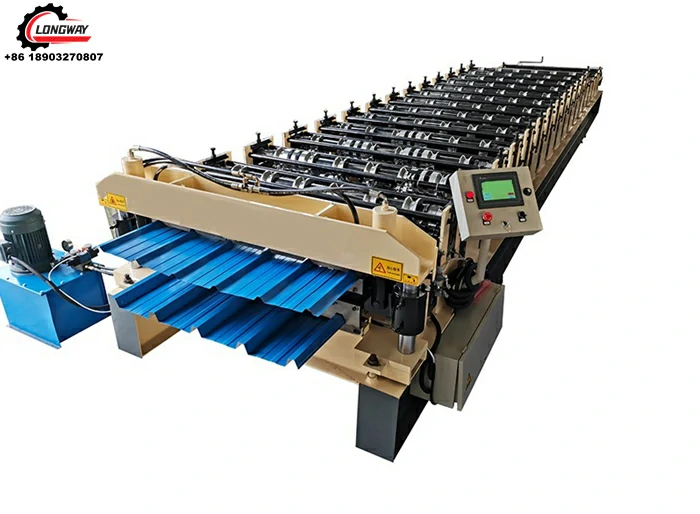
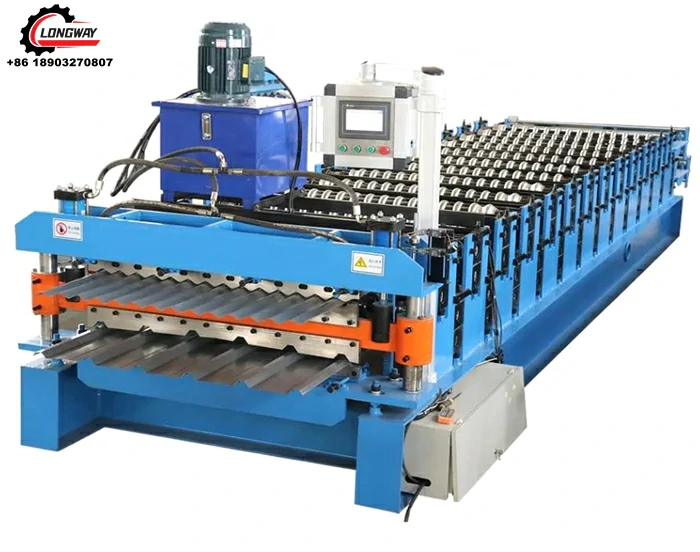
A corrugated sheet pressing machine is specialized equipment designed to create the distinctive ridged structure of corrugated sheets. The machine operates by feeding flat sheets of raw material through a series of rollers, which press and shape the material into the desired corrugated pattern. This process not only enhances the structural integrity of the sheets but also allows for high-speed production, making it economically viable for manufacturers.
Key Features
1. Precision Engineering Modern corrugated sheet pressing machines are equipped with advanced technology that ensures precision in the shaping process. With the ability to adjust the depth and frequency of the corrugation, manufacturers can produce sheets tailored to specific requirements.
2. High Efficiency The design of these machines facilitates high-volume production without sacrificing quality. With automated controls and quick changeover capabilities, manufacturers can significantly boost their output while minimizing downtime.
3. Versatility These machines can work with a variety of materials, adapting to different thicknesses and types based on the needs of the production line. Whether it’s a light plastic sheet or a heavy-duty steel plate, the pressing machine can be configured accordingly.
corrugated sheet pressing machine factory

4. Energy Savings Innovations in machine design have led to energy-efficient models that reduce power consumption during operations. This is beneficial for not only lowering production costs but also for adhering to environmental standards.
The Manufacturing Process
The production process using a corrugated sheet pressing machine typically involves several stages
1. Material Preparation Raw materials, such as coils of metal or sheets of plastic, are prepared and fed into the machine.
2. Pressing The machine’s rollers apply pressure and heat to deform the sheet into the desired corrugated pattern. This stage is crucial, as inconsistent pressure can lead to defects in the sheets.
3. Cooling After pressing, sheets may require a cooling period to stabilize their shape and ensure they maintain their integrity.
4. Cutting Once cooled, the sheets are cut to specified lengths for packaging or further processing.
5. Quality Inspection The finished products undergo rigorous quality control checks to ensure that they meet industry standards before being dispatched.
Conclusion
The role of corrugated sheet pressing machines in the manufacturing sector cannot be understated. With their ability to produce high-quality corrugated sheets efficiently and economically, these machines are a cornerstone of modern production lines. As industries continue to seek faster and more reliable solutions, investing in advanced pressing technology will be critical for manufacturers wanting to maintain a competitive edge. The continuous evolution of these machines will ensure that they meet the ever-changing demands of the market, contributing significantly to the future of manufacturing.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025