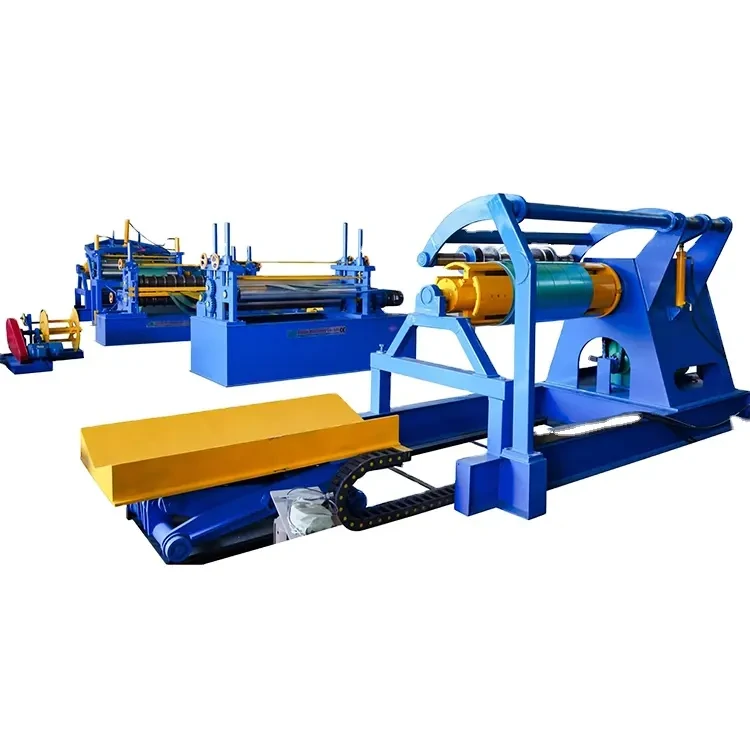
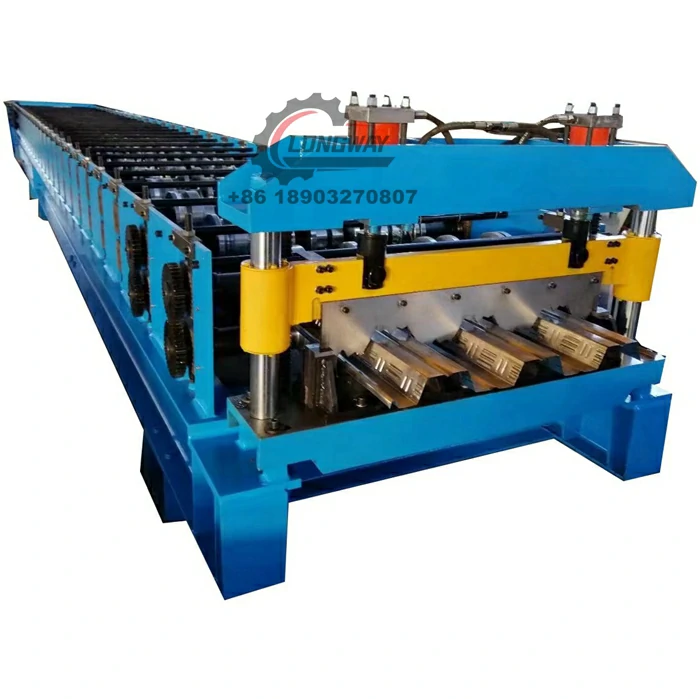
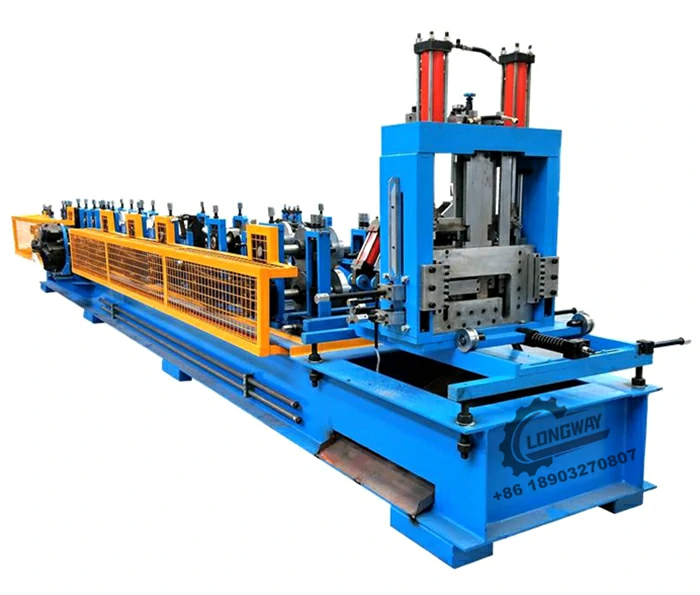
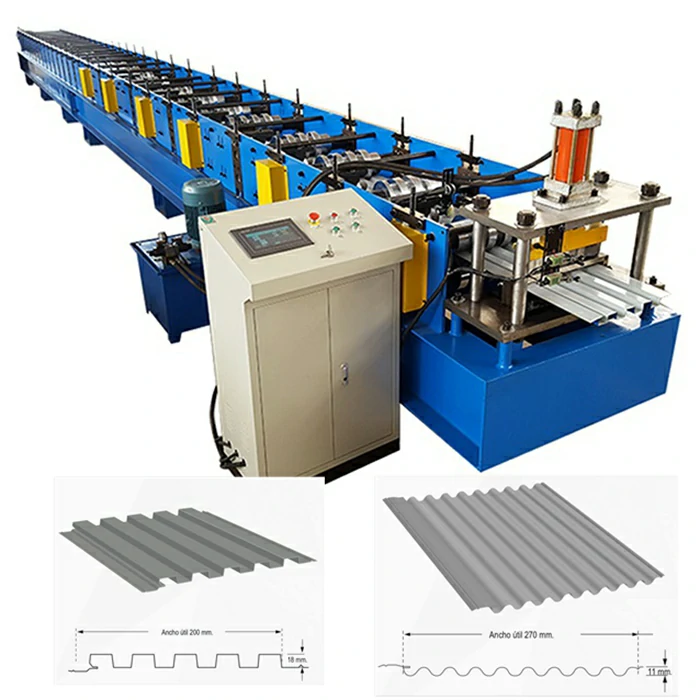
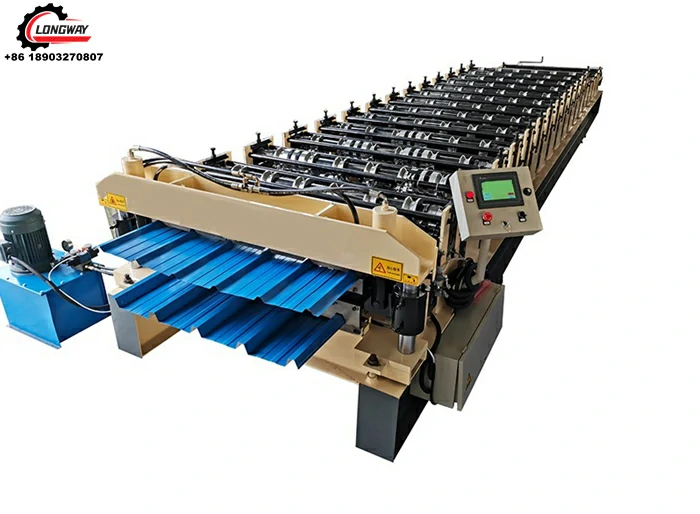
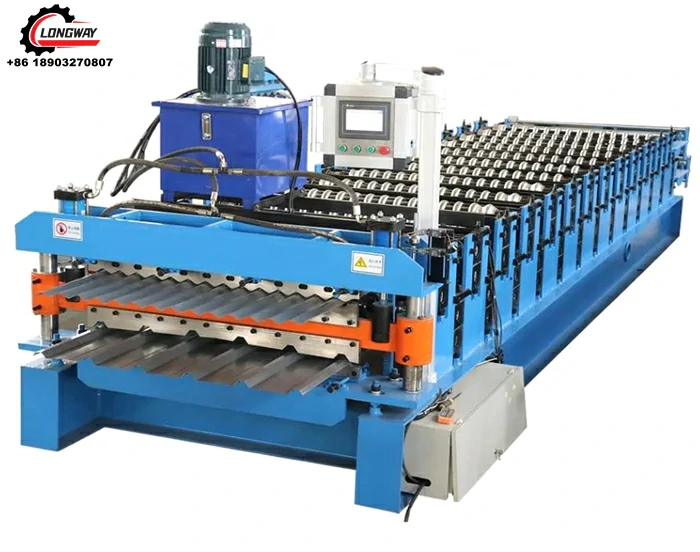
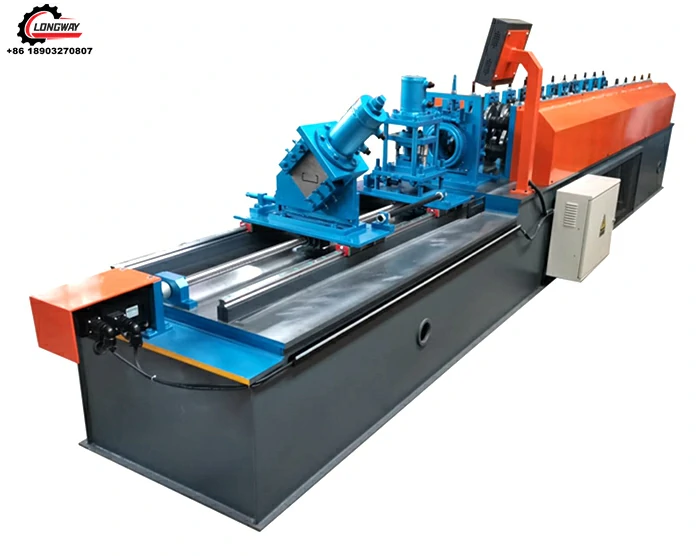
Roller Machine for Forming Corrugated Sheet Metal Efficiently and Accurately
The Versatility and Application of Corrugated Sheet Metal Rollers
Corrugated sheet metal has emerged as a popular choice in various industries due to its strength, lightweight nature, and aesthetic appeal. At the heart of its production is the corrugated sheet metal roller, a critical piece of machinery that shapes flat metal sheets into the distinctive wavy pattern of corrugation. This article will explore the functionalities, types, and applications of corrugated sheet metal rollers, highlighting their significance in metalworking and construction.
Understanding Corrugated Sheet Metal Rolls
Corrugated sheet metal is made by pressing metal sheets into a wavy design, which provides structural integrity and durability. This design enhances the strength-to-weight ratio of the material, making it ideal for a wide range of applications, from roofing to siding, and even in industrial and agricultural settings. The corrugated sheet metal roller utilizes a sequence of rollers to progressively shape the flat sheets, creating the desired profile while minimizing material waste and reducing production time.
Types of Corrugated Sheet Metal Rollers
There are several types of corrugated sheet metal rollers, each designed for specific applications and metal thicknesses
1. Single Roller Abrasion This type uses a single set of rollers to create simple corrugations; it is ideal for small production runs or custom applications where intricate designs are required. These machines often provide enhanced flexibility, adeptly handling various sheet sizes and thicknesses.
2. Double Roller Systems Often used in industrial settings, these machines consist of two sets of rollers, enabling manufacturers to produce wider sheets more efficiently. The double roller configuration increases production speed and allows for the continuous rolling of metal sheets, improving overall output.
3. Hydraulic Rollers These rollers combine hydraulic pressure with mechanical force, providing enhanced control over the shaping process. Hydraulic rollers are particularly useful for creating complex profiles and managing heavier gauge metals without compromising precision.
corrugated sheet metal roller
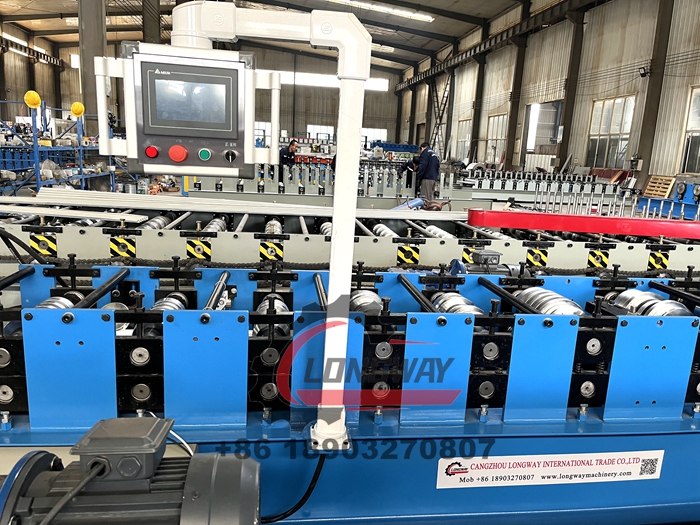

4. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Rollers The growing trend towards automation has led to the advent of CNC corrugated sheet metal rollers. These machines are programmed to execute precise specifications digitally, ensuring high accuracy and consistency in production. They are particularly valuable for industries needing large quantities of customized sheets.
Applications of Corrugated Sheet Metal
The versatility of corrugated sheet metal makes it suitable for a myriad of applications
- Construction and Roofing Corrugated sheets are prominently used in the construction industry for roofing materials, offering excellent resistance to harsh weather conditions. Their lightweight nature simplifies installation, reducing labor costs and time.
- Industrial Applications In warehouses and manufacturing plants, corrugated sheet metal serves as durable separators and walls, bettering insulation and protecting against elements. The structural integrity of the corrugated design helps safeguard any equipment, materials, or workers inside these facilities.
- Agricultural Use Farmers often utilize corrugated sheet metal for barn roofs and storage sheds due to its resistance to rust and corrosion. The durable nature provides long-term reliability while maintaining temperature and humidity levels necessary for agricultural goods.
- Architectural Design Modern architecture has adopted corrugated sheet metal as a design element, utilizing its unique aesthetic appeal. From facades to interior design, the wavy patterns can add a contemporary touch to structures and are also used for artistic installations.
Conclusion
The corrugated sheet metal roller plays an indispensable role in the manufacturing of corrugated sheets, becoming a cornerstone for many industries. As technology advances, these rollers continue to evolve, allowing for more efficiency, precision, and customization in metalworking. Given the array of applications—from construction to agriculture—it's clear that corrugated sheet metal will remain a fundamental choice for engineers, architects, and builders alike. The future of this material and its production methods looks promising, reflecting a blend of tradition with innovation, thus ensuring its place in the ever-evolving landscape of industry and design.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025