cold formed steel machine factories
The Role of Cold-formed Steel in Modern Manufacturing An Insight into Cold-formed Steel Machine Factories
In the realm of construction and structural engineering, cold-formed steel (CFS) has carved a significant niche due to its versatility, strength, and weight advantages. Cold-formed steel machine factories play a pivotal role in producing standardized components required for various applications, ranging from residential buildings to commercial infrastructures. This article delves into the core aspects of cold-formed steel, the manufacturing processes prevalent in machine factories, and the benefits that these materials bring to modern engineering.
Understanding Cold-formed Steel
Cold-formed steel refers to steel sections that are formed at room temperature through a process of shaping and bending. This method differentiates it from hot-rolled steel, which is processed at elevated temperatures. The cold-forming process enhances the strength of steel due to strain hardening while allowing for tighter tolerances and varied profiles. Common shapes produced include C-sections, Z-sections, and angles, which can be used in stud frames, floor systems, and roof trusses.
Manufacturing Process in Cold-formed Steel Machine Factories
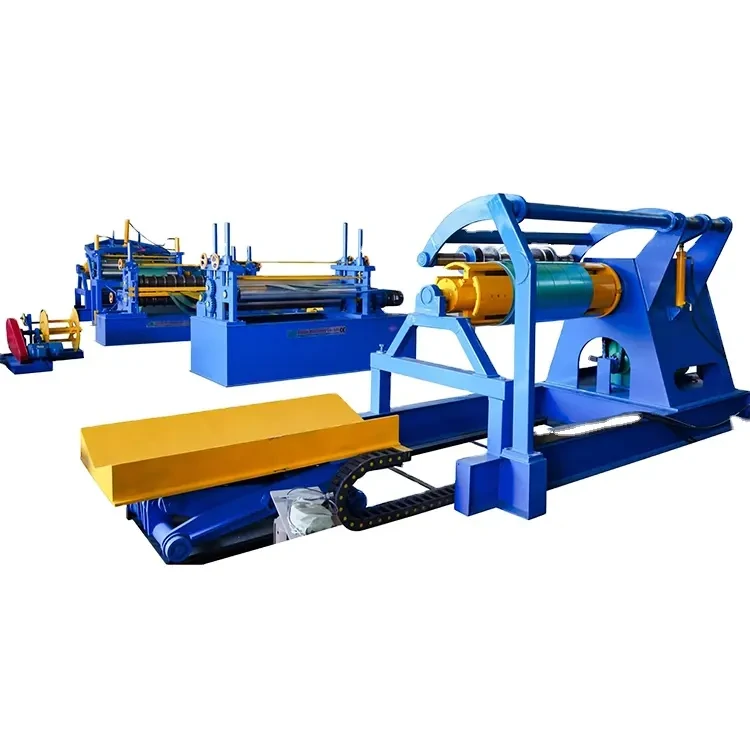
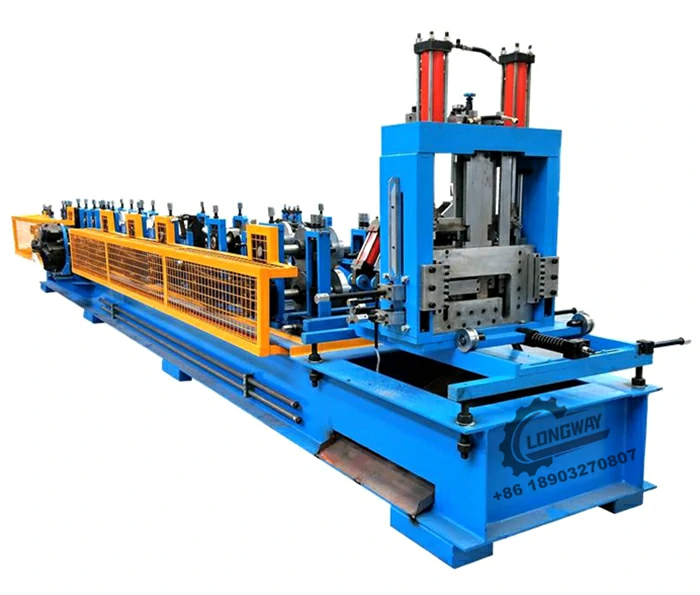
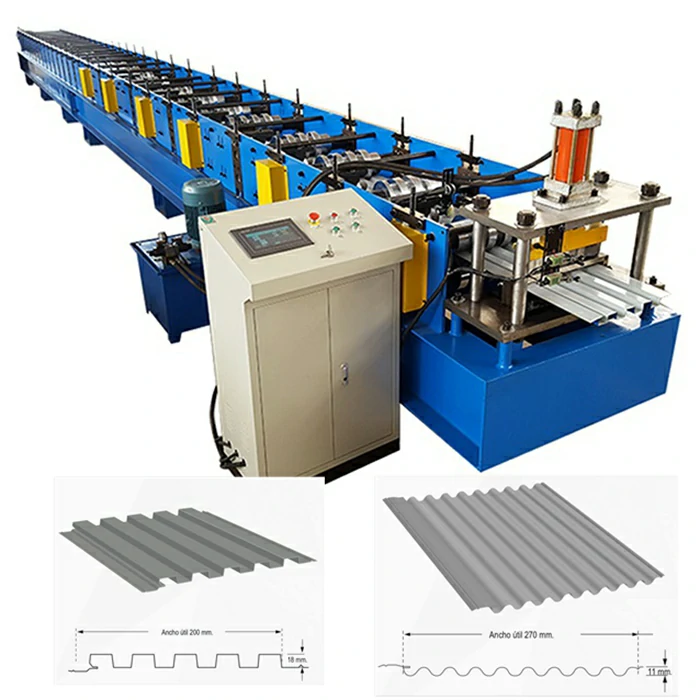
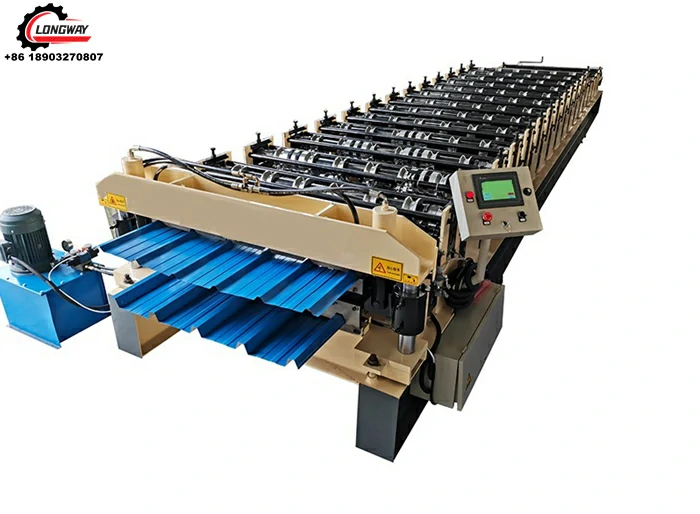
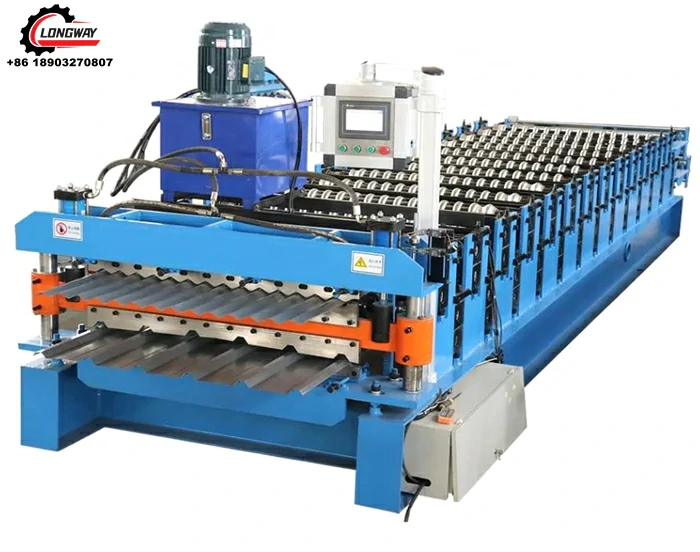
Cold-formed steel machine factories utilize specialized machinery to convert raw steel coils into fabricated components. The manufacturing process typically involves several key steps
1. Material Preparation Raw steel coils are inspected for consistency in thickness and quality. They are then unwound and fed into the roll forming machine.
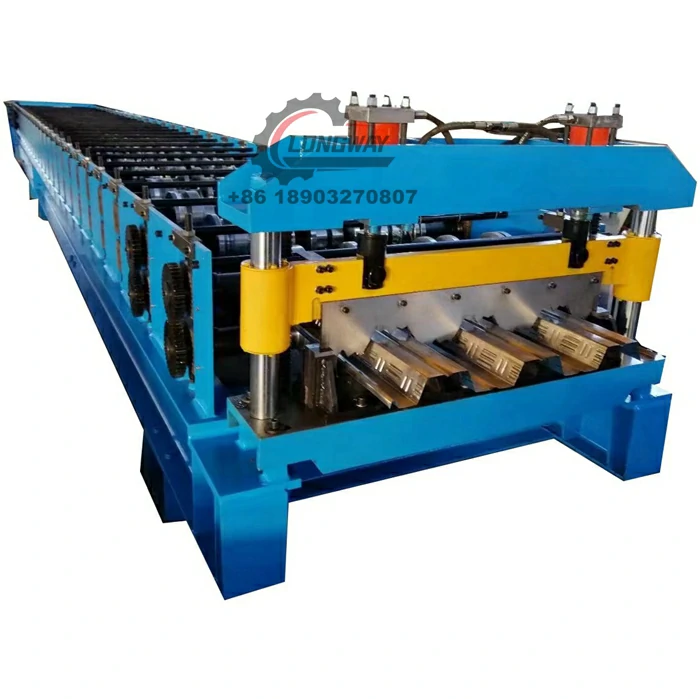
2. Roll Forming In this critical stage, the steel coil is shaped into the desired profile. Roll forming involves passing the steel through a series of rollers that gradually mold it into its final shape. This method is efficient and allows for high-volume production of consistent profiles.
3. Cutting and Edging Once the steel has been formed, it is cut to precise lengths according to project specifications. Additional procedures, such as edging or punching, can be performed at this stage to prepare the components for assembly.
4. Finishing and Coating To enhance durability and resistance to corrosion, cold-formed steel products often undergo finishing processes such as galvanization or painting. These coatings not only extend the life of the steel but also improve its aesthetic appeal.
cold formed steel machine factories
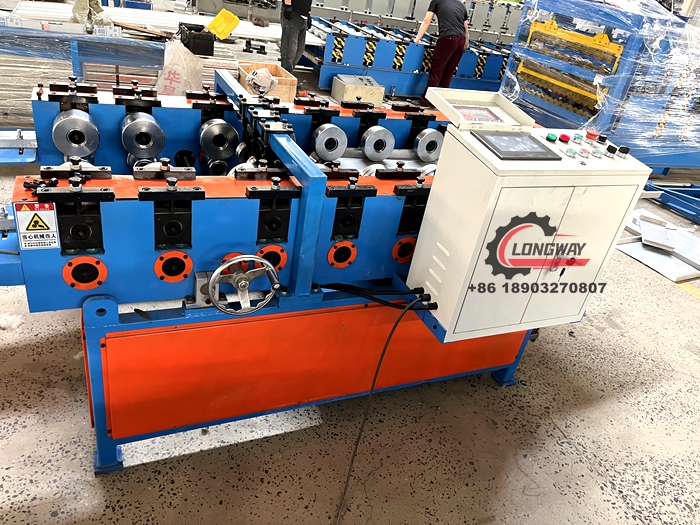

5. Quality Control Rigorous quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process. This includes routine inspections and testing to ensure that the finished products meet industry standards for strength and performance.
Benefits of Cold-formed Steel
The advantages of using cold-formed steel in construction are numerous and compelling
- Strength-to-Weight Ratio Cold-formed steel is relatively lightweight yet possesses high tensile strength. This characteristic makes it easier to handle and reduces transportation costs while maintaining structural integrity.
- Design Flexibility The versatility of cold-formed steel allows architects and engineers to create complex designs and structures that may be difficult or impossible with traditional materials. Its adaptability leads to innovative architectural solutions.
- Rapid Assembly Factory-produced cold-formed steel components are designed for quick assembly on-site. This helps accelerate construction timelines and minimizes labor costs.
- Eco-friendliness As a recyclable material, cold-formed steel offers an environmentally friendly option for construction. Many factories adopt sustainable practices, further reducing the ecological footprint of their operations.
- Fire Resistance Steel is naturally non-combustible, providing an added level of fire safety. Cold-formed steel structures can withstand high temperatures and reduce the risk of fire-related incidents.
Conclusion
Cold-formed steel machine factories are instrumental in modern manufacturing, contributing to the efficient production of high-quality steel components essential for contemporary construction projects. The unique properties of cold-formed steel enhance its applicability across various sectors, promoting sustainability and innovation in building practices. As industries continue to evolve, the importance of adaptive and resilient materials like cold-formed steel will only grow, solidifying its place in the future of construction and design.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025