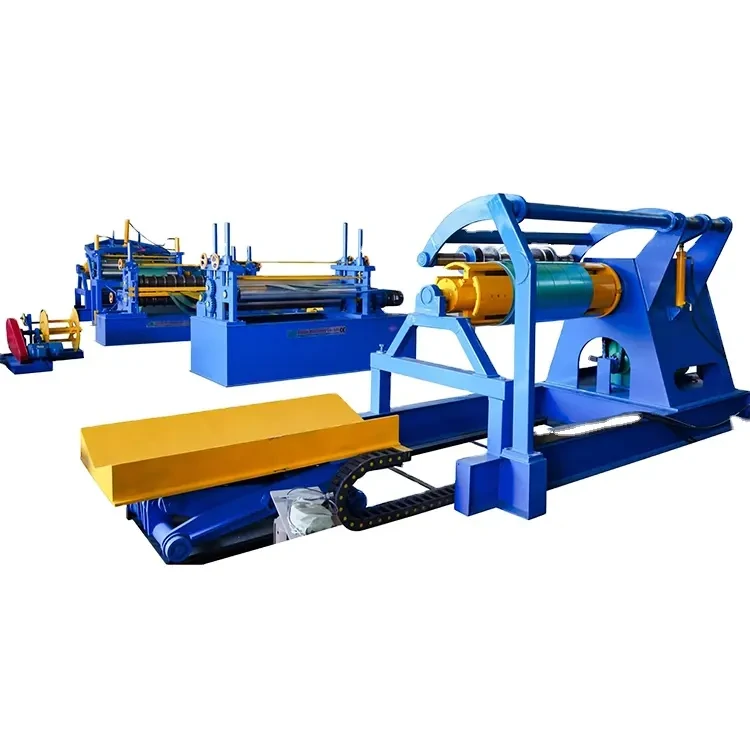
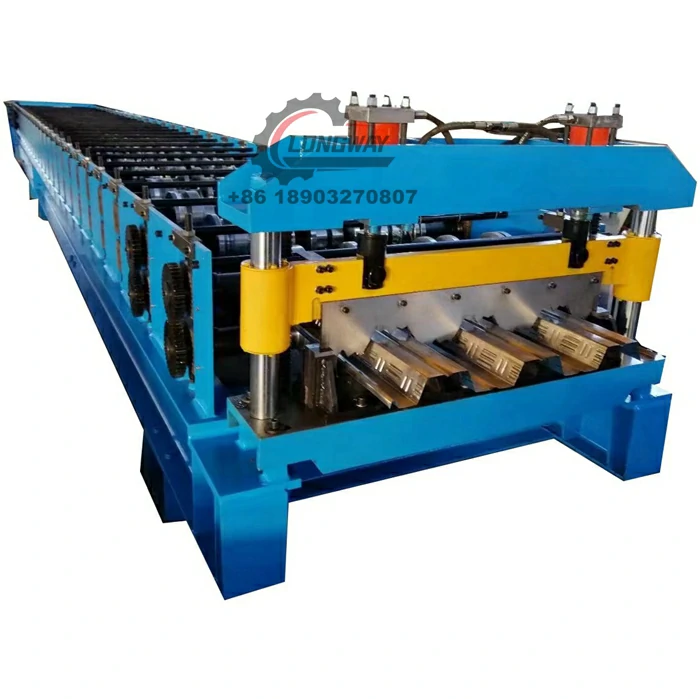
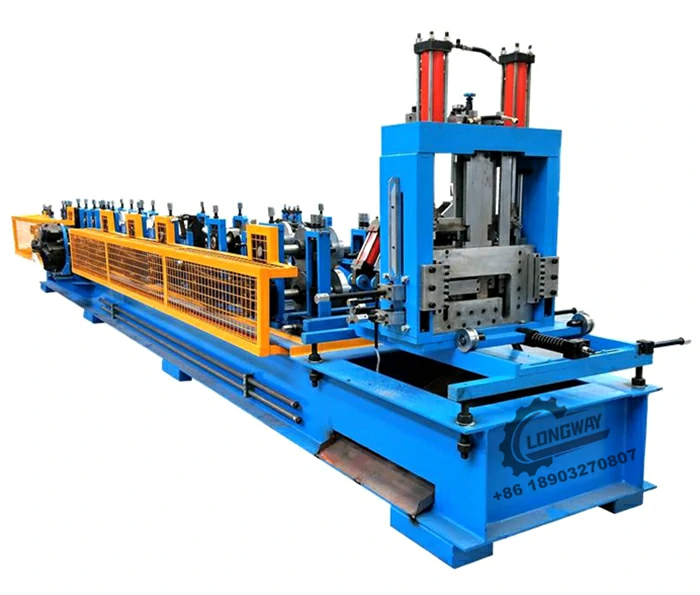
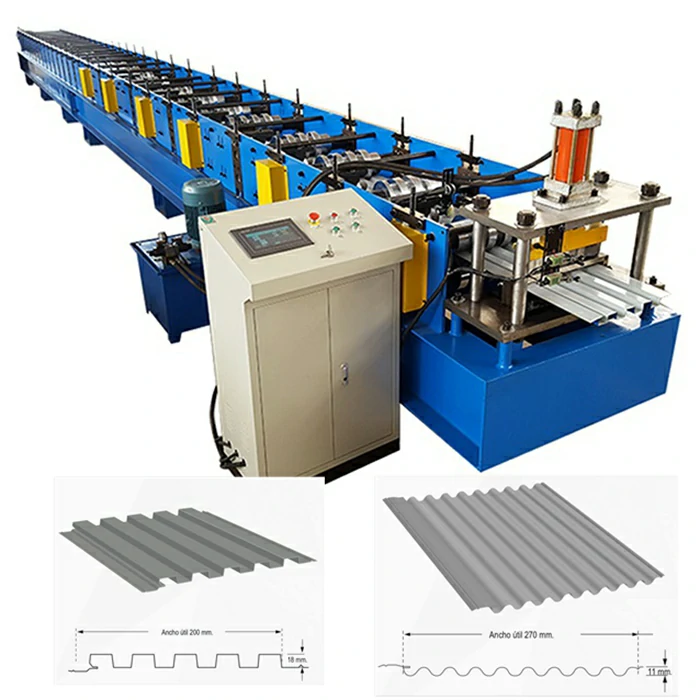
channel making machine factory
The Evolution and Significance of Channel Making Machine Factories
In the industrial landscape of today, the demand for precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes has led to the development of specialized machinery tailored to specific production needs. One such innovation is the channel making machine, a device critical in various industries, from construction to automotive and beyond. Understanding the significance and functionality of channel making machine factories unveils the importance of these machines in modern manufacturing.
Understanding Channel Making Machines
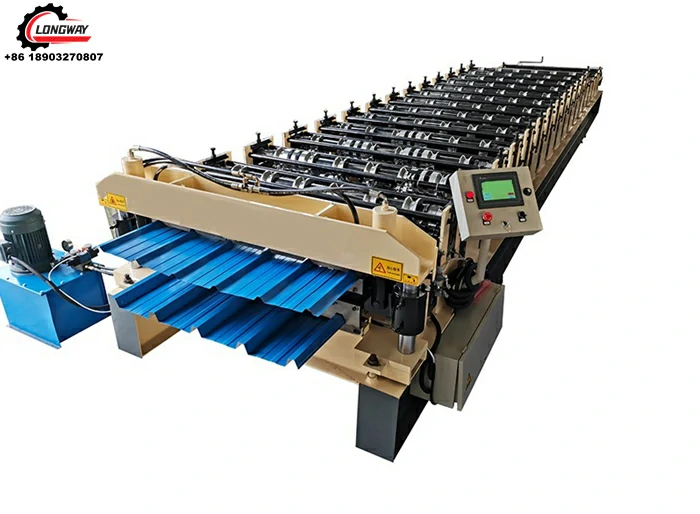
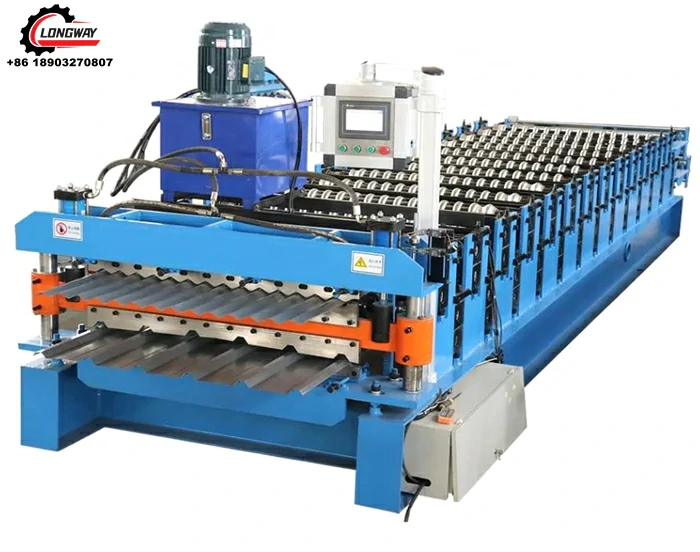
Channel making machines are specialized tools designed to create channels, which are essential for structural applications. These machines can manufacture various types of channels, including U-channels, C-channels, and other custom shapes suited for different purposes. Typically made from metal, these channels are vital components in building frameworks, electrical conduits, HVAC systems, and more. The precision-engineered output of channel making machines ensures that these components fit perfectly within specific design parameters, maintaining structural integrity and safety.
The Role of Channel Making Machine Factories
Channel making machine factories play a pivotal role in the manufacturing ecosystem. These factories are equipped with advanced technology and skilled personnel capable of designing, producing, and maintaining channel making machines. The production process within these factories involves several stages
1. Design and Engineering Initially, engineers work on designing machines that meet the particular requirements of clients. This process often involves the use of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, allowing for detailed and precise specifications.
2. Material Selection and Processing The choice of materials impacts the durability and performance of channel making machines. Factories typically use high-grade steel or aluminum, ensuring the final product can withstand rigorous industrial processes.
channel making machine factory
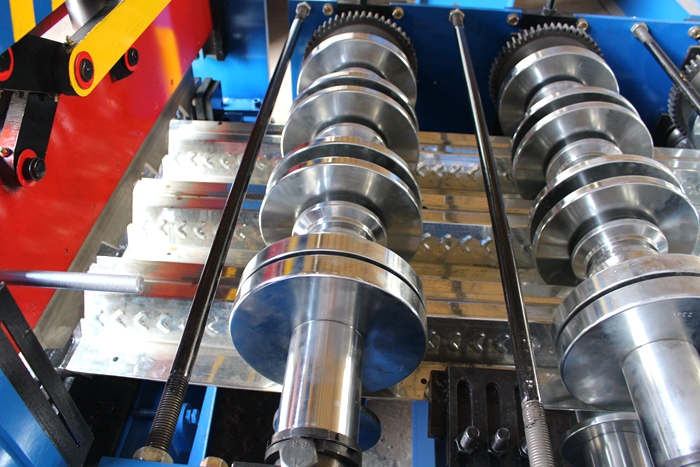

3. Fabrication In this stage, various components of the machine are fabricated through cutting, bending, and welding. This phase requires expertise to guarantee alignment with design specifications.
4. Assembly and Quality Control Once components are fabricated, they are assembled into complete machines. Rigorous quality control measures are employed to ensure that each machine meets industry standards and functions effectively.
5. Testing and Delivery After assembly, machines undergo testing to ensure performance reliability before being delivered to clients. This step is crucial to minimize any operational disruptions once the machines are in use.
Importance of Channel Making Machine Factories
The significance of channel making machine factories extends beyond just producing machines. They contribute to the overall efficiency of the manufacturing sector. By providing high-quality machinery, these factories enable other industries to enhance productivity, reduce waste, and improve the quality of their own products. Moreover, with the ongoing evolution of technology, many factories are incorporating automation and smart technologies, leading to increased efficiency and reduced labor costs.
With sustainability being a critical concern in today's world, many channel making machine factories are also adopting eco-friendly practices. This includes the use of energy-efficient technologies and recycling materials, reflecting a growing commitment to environmental responsibility.
Conclusion
In conclusion, channel making machine factories are vital contributors to the industrial manufacturing landscape. By producing advanced machinery that meets the precise needs of various industries, these factories enhance the efficiency and quality of production processes. As technology continues to advance, the role of these factories will likely expand, ensuring they remain at the forefront of manufacturing innovation. The synergy created between channel making machines and the industries they serve is a testament to the importance of this specialized sector in the larger framework of global manufacturing.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025