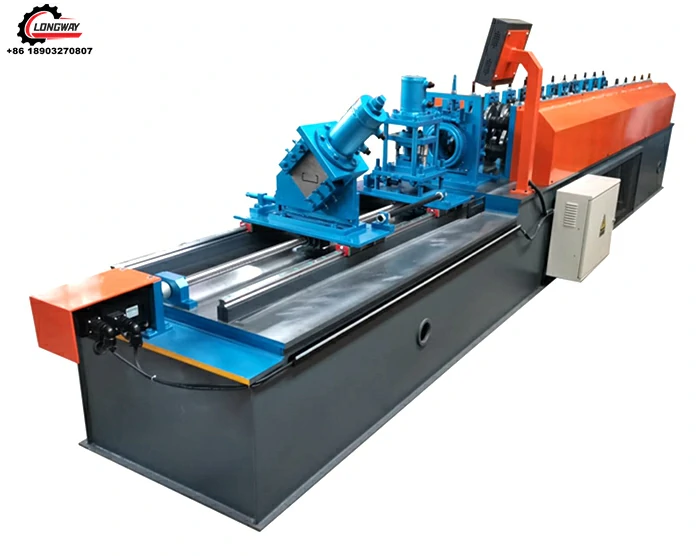
autostacker cost
Understanding Autostacker Cost in Automated Warehousing
In today’s fast-paced logistics and distribution industries, automation has become a cornerstone for efficiency and productivity. One of the key components in automated warehousing systems is the autostacker. This technology is indispensable for the storage and retrieval of goods, and it represents a significant investment. Understanding the costs associated with an autostacker is essential for businesses looking to optimize their operations.
Understanding Autostacker Cost in Automated Warehousing
Aside from the initial purchase price, ongoing operational costs also play a crucial role in the total cost of ownership (TCO) for an autostacker. Maintenance is a critical aspect that businesses often overlook. Regular upkeep is necessary to ensure optimal performance and longevity, which can involve scheduled inspections and replacement of parts. Additionally, companies should account for energy consumption, as autostackers, being part of an automated system, demand a significant amount of electricity—adding to the operational expense.
autostacker cost
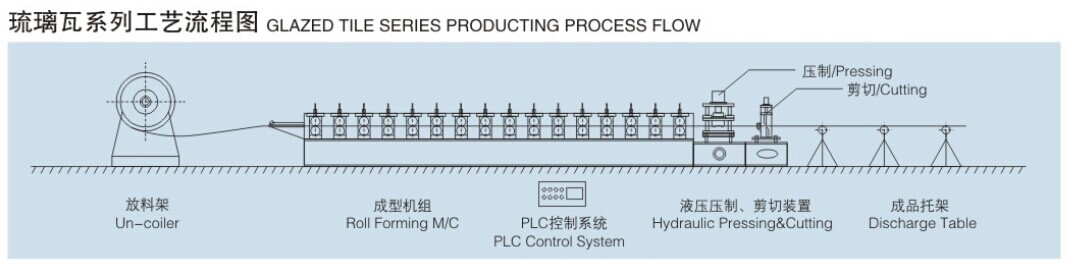
Labor costs are another vital consideration. While autostackers reduce the need for manual handling of goods, skilled personnel are still required to oversee operations, perform maintenance, and troubleshoot any issues that may arise. Investing in training programs for employees to operate and maintain these systems can further impact the overall costs.
Moreover, the financial implications of implementing an autostacker should also consider the potential savings and efficiency gains it brings. Automated systems can lead to reduced labor costs, improved accuracy, and faster order fulfillment, translating into higher customer satisfaction and retention. Companies must evaluate the return on investment (ROI) to determine how quickly the initial capital outlay will be recouped through these efficiencies.
In conclusion, while the autostacker cost involves several factors ranging from initial investment to maintenance and operational expenses, the decision to integrate such a system should be weighed against potential gains in efficiency and productivity. As the logistics industry continues to evolve towards automation, understanding and managing these costs becomes imperative for businesses aiming to stay competitive. By carefully analyzing both the costs and benefits, companies can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals in an increasingly automated world.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025