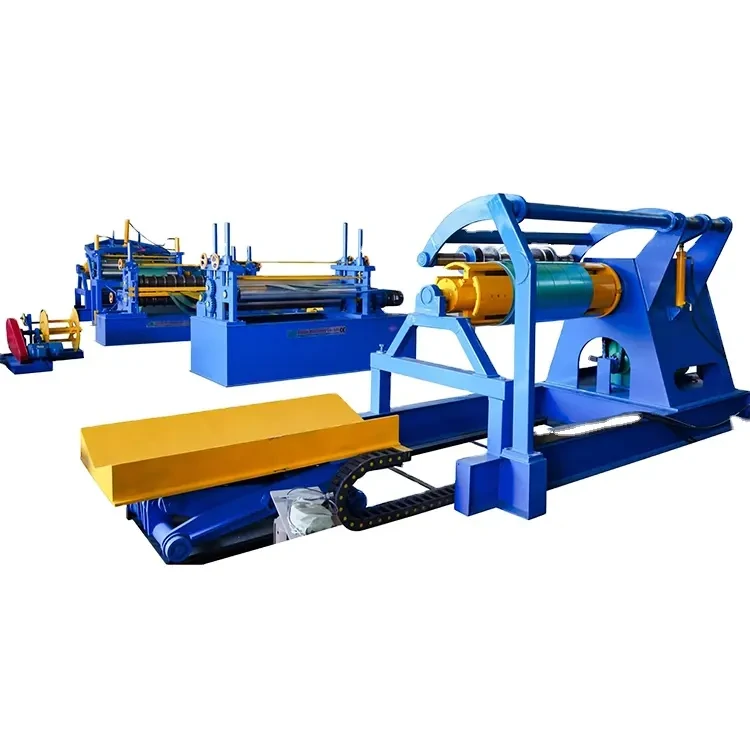
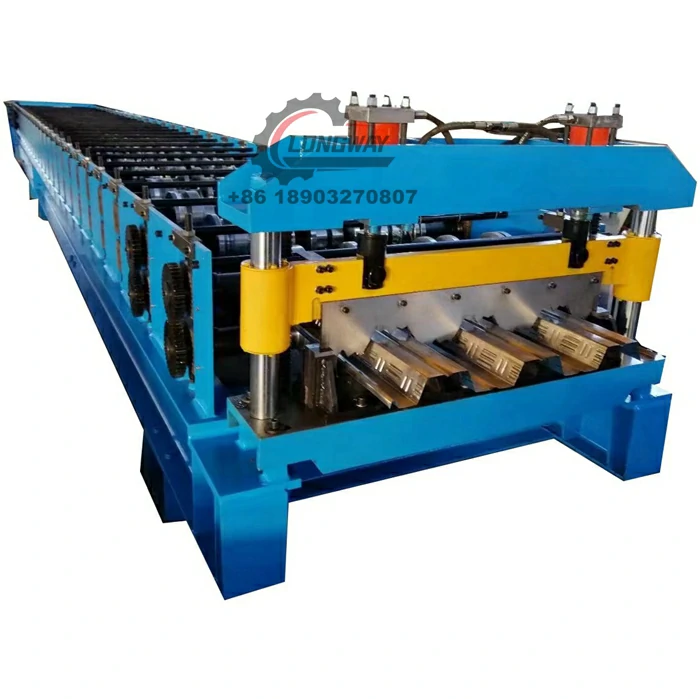
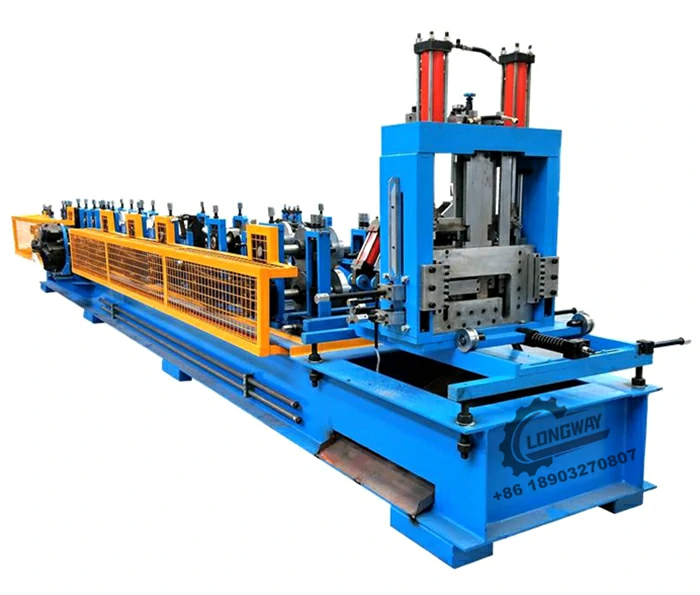
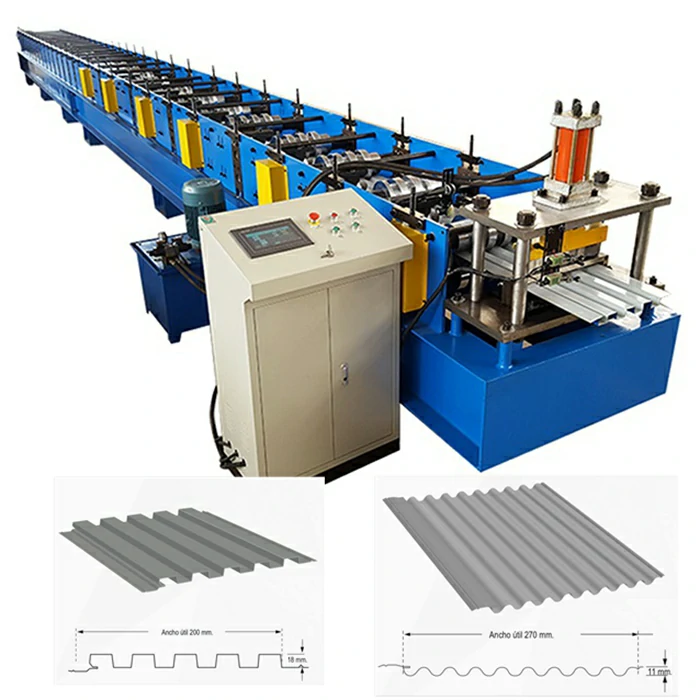
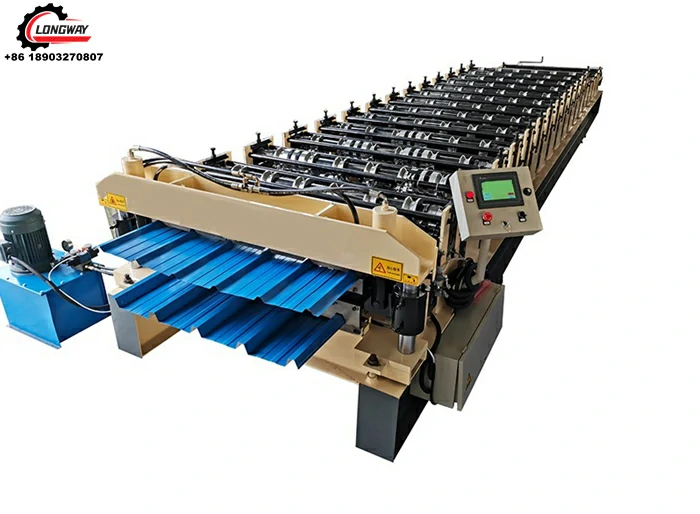
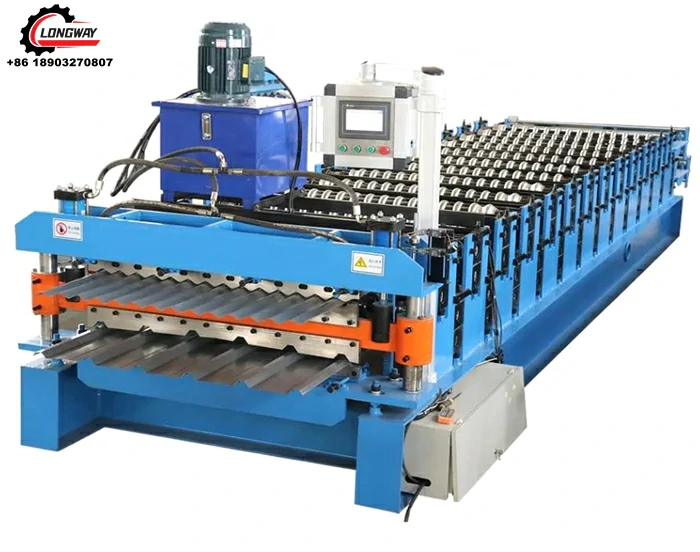
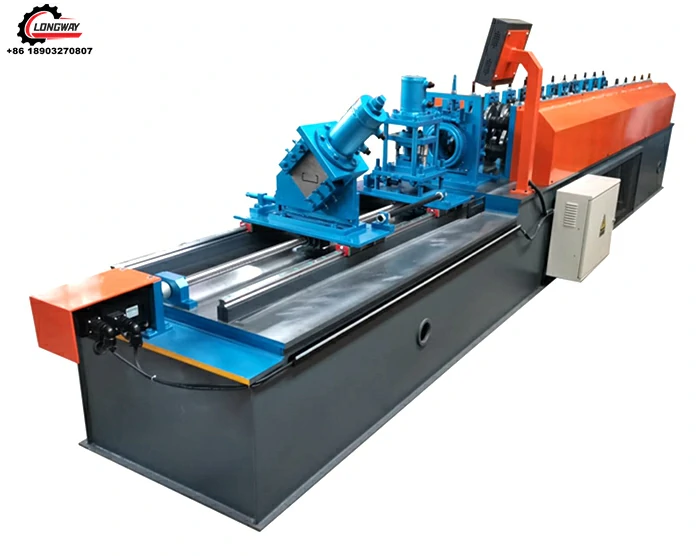
angle iron roll forming machine factory
Angle Iron Roll Forming Machine Factory Revolutionizing Metal Fabrication
In recent years, industrial production has been greatly influenced by advancements in technology, particularly in the realm of metal fabrication. One of the standout innovations in this field is the angle iron roll forming machine. These machines are specifically designed to transform metal sheets into angle iron, a fundamental component widely used in construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure projects. In this article, we will explore the significance of angle iron roll forming machines, the processes involved, and what goes into the making of a factory dedicated to their production.
The Importance of Angle Iron
Angle iron, also known as angle steel, is a type of metal profile that has a distinctive L shape. It is often utilized in structural applications due to its strength and versatility. Common uses for angle iron include frameworks for buildings, support structures, and braces for various applications. The demand for high-quality angle iron has necessitated the need for efficient and precise manufacturing processes, where roll forming machines play a vital role.
The Roll Forming Process
The angle iron roll forming process involves continuously feeding metal sheets into a series of rollers that shape the material into the desired angle profile. This method ensures high precision and uniformity, leading to a smooth finish and reliable structural integrity. The key steps in the roll forming process are as follows
1. Material Selection High-quality raw materials, typically mild steel, are chosen for the production of angle iron. The material's thickness and yield strength are critical factors that influence the machine settings.
2. Tooling Design The design of the rollers and cutting tools is a critical aspect of roll forming. Custom tooling is often required to produce specific angles and dimensions, ensuring that the finished product meets stringent industry standards.
3. Roll Forming Machine Setup Once the tooling is in place, the machine is calibrated for the specific production run. This includes adjustments to the speed, tension, and alignment of the rollers to ensure consistent output.
4. Production Run The metal sheets are fed into the machine, where they undergo a series of shaping processes as they move through different sets of rollers. The continuous nature of roll forming allows for high throughput, making it an efficient process for large-scale production.
angle iron roll forming machine factory
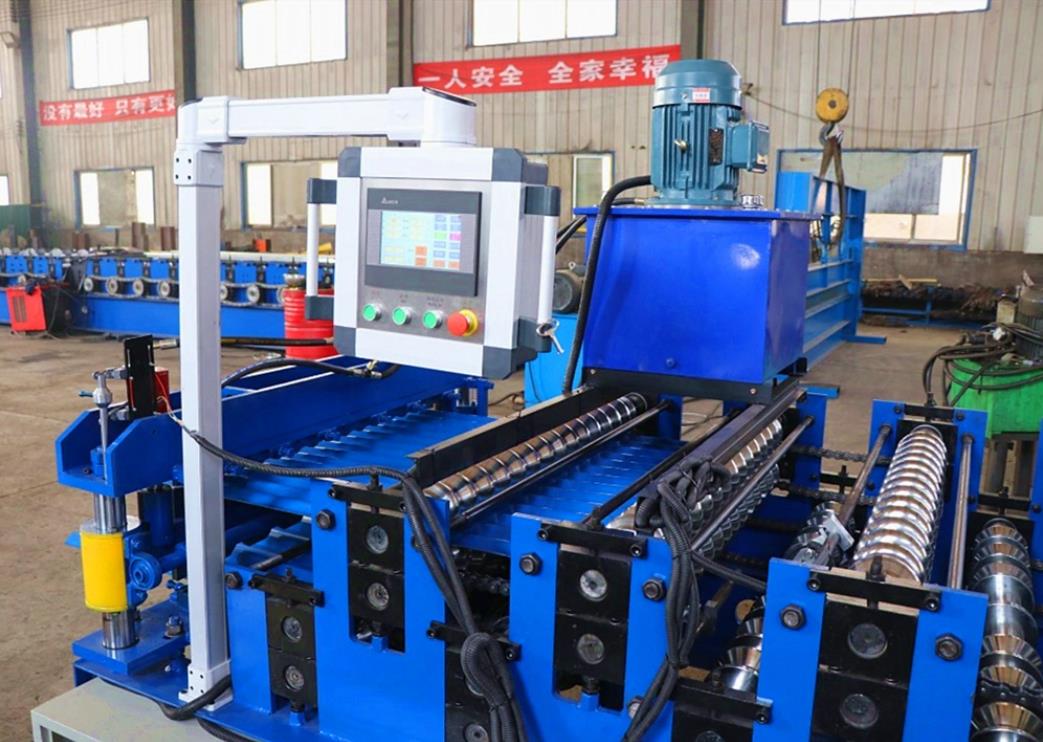

5. Cutting and Finishing After the desired angle profile is achieved, the formed angle iron is cut to length. Additional finishing processes may include deburring, surface treatment, and quality inspection to ensure that every unit meets the required specifications.
Establishing a Factory
Setting up an angle iron roll forming machine factory involves several key considerations. It begins with market research to understand demand and competition. Once this is established, the following steps are essential
1. Location Selection The factory should be strategically located to facilitate easy access to raw materials, distribution channels, and a skilled labor force. Proximity to key markets can also reduce transportation costs.
2. Machinery Investment Investing in high-quality roll forming machines and auxiliary equipment is crucial. The choice of machinery will directly affect production efficiency and product quality.
3. Skilled Workforce Employing skilled technicians and engineers is essential to operate the machinery and maintain production quality. Training programs can enhance employee skills and ensure operational efficiency.
4. Quality Control Systems Implementing stringent quality control measures throughout the production process helps guarantee that the finished angle iron meets industry standards. Regular maintenance of tools and machinery also plays a crucial role in maintaining production quality.
5. Sustainability Practices Integrating sustainable practices into the factory operations not only enhances corporate responsibility but can also lead to cost savings. This includes recycling scrap metal and reducing energy consumption.
Conclusion
As industries continue to evolve, the relevance and application of angle iron remain significant. Angle iron roll forming machine factories are at the forefront of meeting this demand, driving innovation in metal fabrication. With proper planning, investment, and execution, these factories play a pivotal role in shaping the future of construction and manufacturing, ultimately contributing to building a stronger infrastructure. As the industry progresses, staying attuned to advancements in technology and techniques will further enhance the capabilities of angle iron roll forming, ensuring its continued prominence in the market.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025