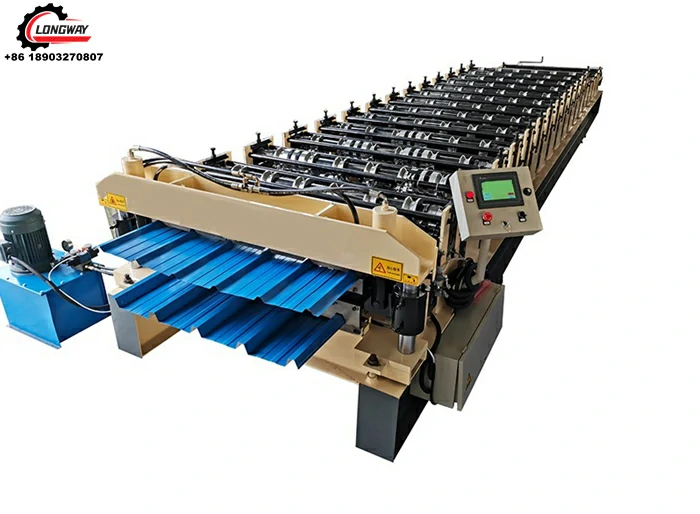
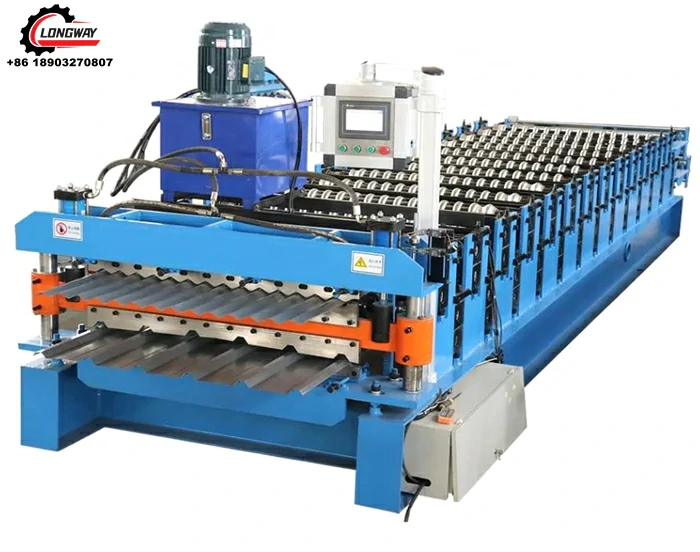
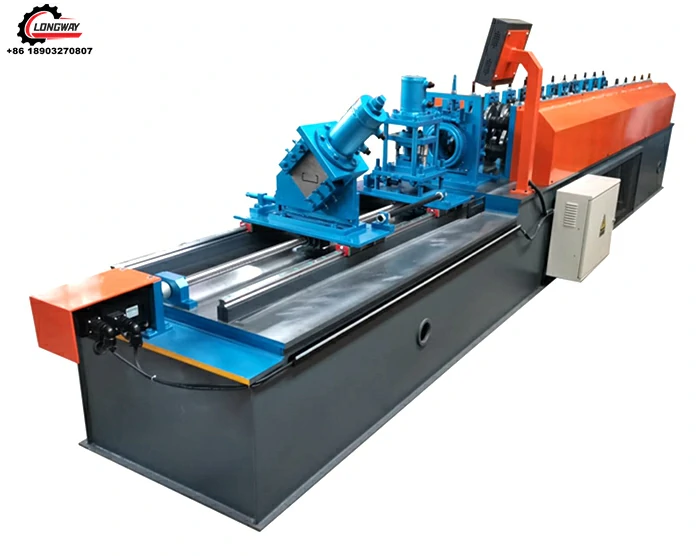
aluminium roofing sheet making machine factories
The Rise of Aluminium Roofing Sheet Making Machines An Overview of Factories and Production Processes
In recent years, the construction industry has seen a significant shift towards the use of aluminium roofing sheets, primarily due to their durability, lightweight nature, and resistance to corrosion. To meet the growing demand for these roofing materials, factories specializing in aluminium roofing sheet making machines have emerged, contributing to both the sustainability and efficiency of the building sector.
Understanding Aluminium Roofing Sheets
Aluminium roofing sheets are known for their excellent weather resistance, longevity, and minimal maintenance requirements. Unlike traditional roofing materials such as asphalt or wood, aluminium does not rot or crack, making it an ideal choice for various climates. Additionally, aluminium is a recyclable material, adding to its environmental appeal.
The Production Process
The manufacturing of aluminium roofing sheets involves several مراحل, starting with the procurement of raw aluminium coils. These coils undergo a series of processes, including cutting, shaping, and profiling, to create the final sheet products. Here are the main steps in the production process
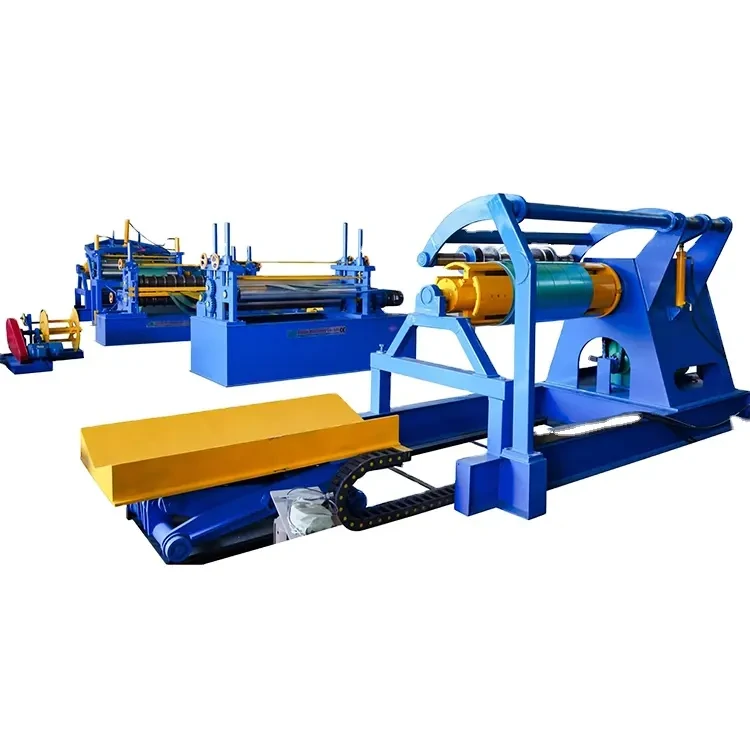
1. Coil Preparation Large rolls of aluminium are received and inspected for quality. If the materials meet the required standards, they are fed into the sheet-making machines.
2. Shearing and Cutting The aluminium coils are cut into specific sizes depending on the final product specifications. This step often requires precision machinery to ensure accuracy and minimize waste.
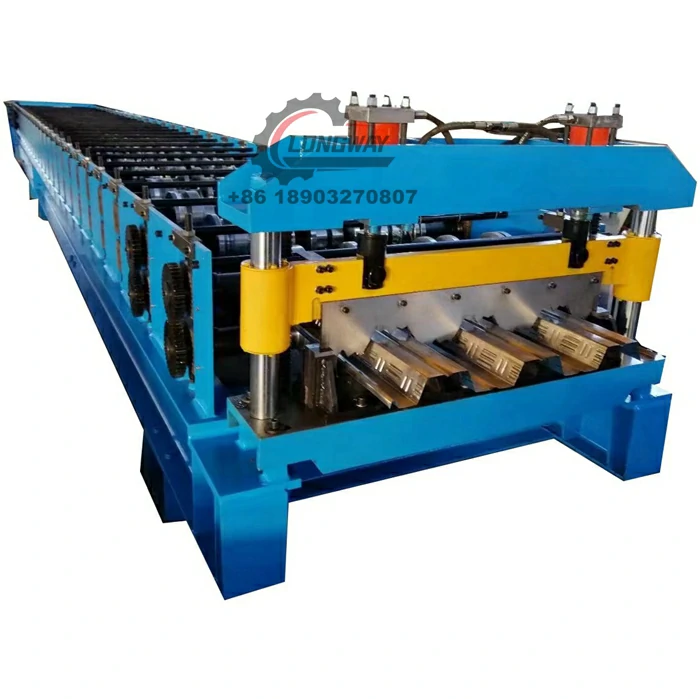
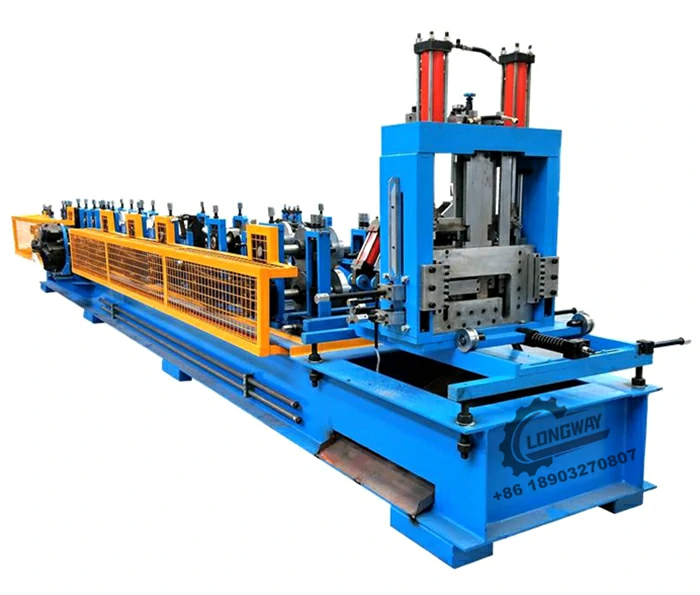
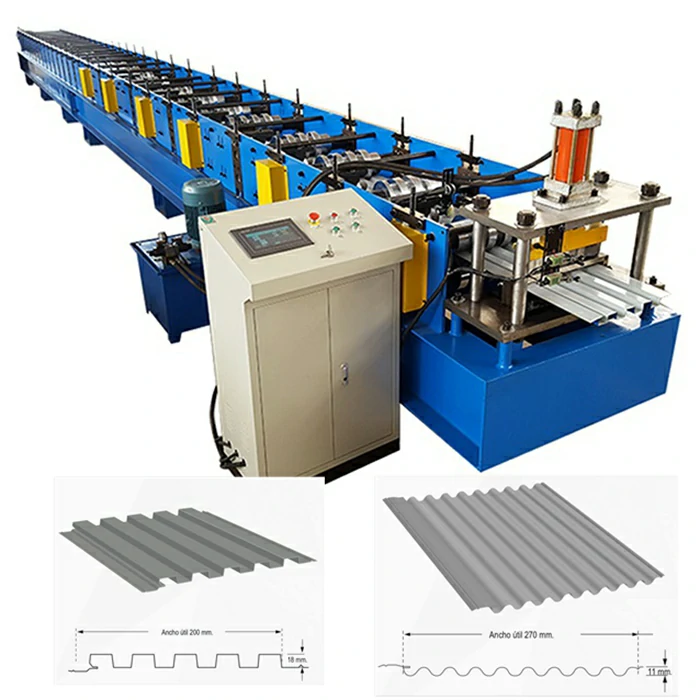
3. Forming and Profiling Using advanced forming machines, the cut aluminium pieces are shaped into various profiles, such as corrugated, flat, or ribbed sheets. This process adds structural integrity and aesthetic appeal to the roofing materials.
4. Coating and Finishing To enhance corrosion resistance and appearance, the sheets are coated with protective finishes. Different coatings can be applied depending on the desired color and texture.
aluminium roofing sheet making machine factories
5. Quality Control Throughout the production process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the finished roofing sheets meet industry standards. This includes checks for thickness, strength, and finish quality.
6. Packaging and Distribution Once the roofing sheets have passed quality checks, they are packaged and prepared for distribution to suppliers, contractors, and other clients across various regions.
The Role of Factories
Factories that produce aluminium roofing sheet making machines play a crucial role in the overall industry. These facilities not only manufacture the machines but also invest in research and development to innovate more efficient and cost-effective production techniques. By aligning themselves with the requirements of modern construction, these factories contribute to the creation of advanced machinery that enhances productivity and reduces operational costs.
Market Trends and Future Prospects
As construction trends lean towards sustainability, the demand for aluminium roofing sheets is expected to rise. This demand is further fueled by the growing awareness of energy efficiency and the benefits of using recyclable materials in building projects. Factories are responding to this trend by developing machines that can produce a wider variety of profiles and styles, catering to the diverse needs of consumers.
Moreover, with the advent of automation and smart technology, the future of aluminium roofing sheet production looks promising. Factories are beginning to incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning into their operations, leading to more streamlined processes and reduced human error.
Conclusion
In conclusion, aluminium roofing sheet making machines and the factories that produce them are key players in the construction industry. As businesses continue to harness innovative technologies and sustainable practices, the production of aluminium roofing sheets is set to expand, providing durable and eco-friendly solutions for modern architecture. This growth not only enhances the building landscape but also contributes significantly to environmental conservation efforts.
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Purlin Machines: Types, Features, and Pricing GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Metal Embossing Machines: Types, Applications, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Gutter Machines: Features, Types, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Cut to Length Line: Overview, Equipment, and Buying GuideNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Auto Stacker: Features, Applications, and Cost BreakdownNewsJul.04, 2025
-
Top Drywall Profile Machine Models for SaleNewsJun.05, 2025