Innovative Solutions for Efficient Cold Roll Forming Production in Modern Manufacturing Facilities
Cold Roll Forming Factory The Backbone of Modern Manufacturing
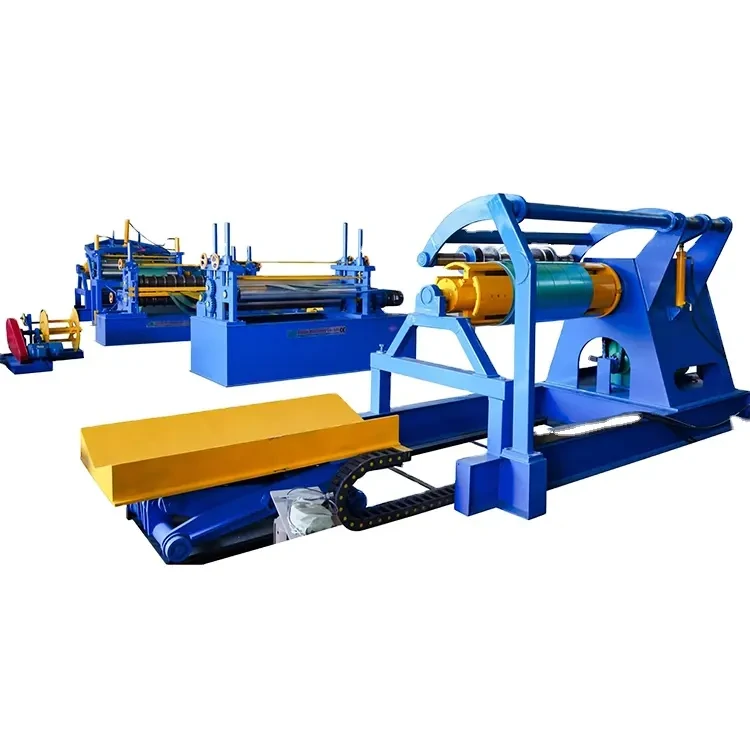
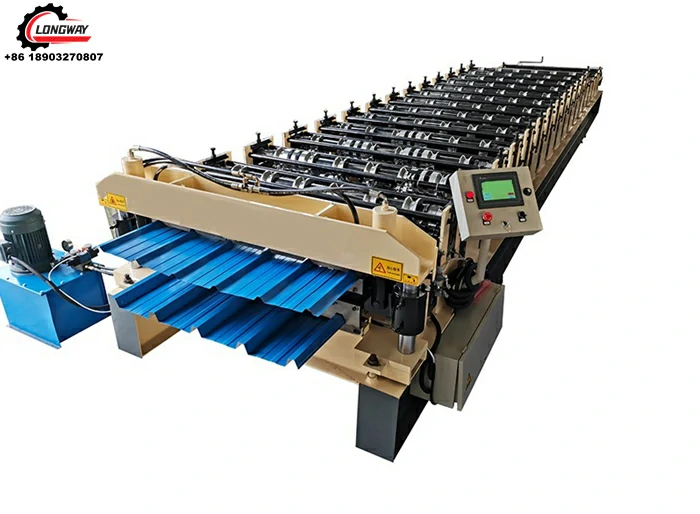
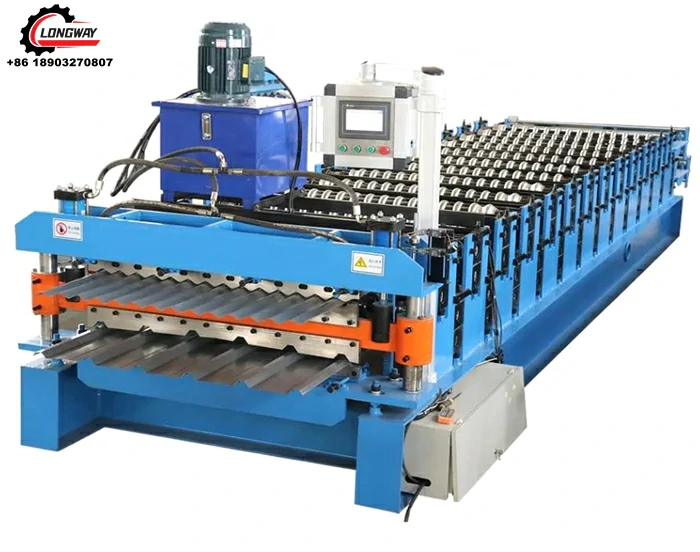
Cold roll forming is a crucial process in the manufacturing sector, especially in the production of high-strength, lightweight structural components. A cold roll forming factory specializes in this intricate process, utilizing advanced technology and skilled workforce to create precision-engineered products for various industries.
What is Cold Roll Forming?
Cold roll forming is a method used to shape metal into specific profiles at room temperature. Unlike traditional metalworking processes that often require heating, cold roll forming involves continuously feeding a flat strip of metal through a series of rollers that progressively shape it into the desired cross-section. This technique boasts several advantages, such as improved dimensional accuracy, superior surface finish, and increased mechanical properties due to work hardening.
Applications of Cold Roll Formed Products
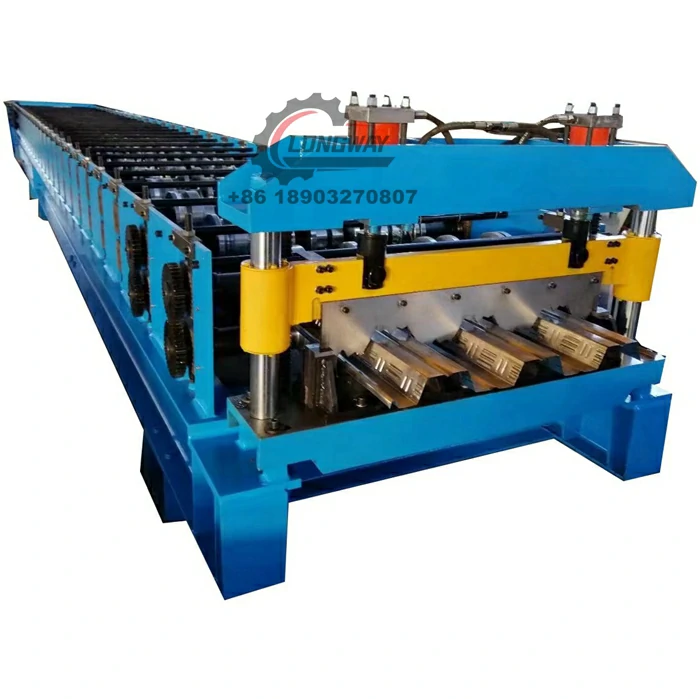
Products manufactured through cold roll forming are widely used in several sectors including construction, automotive, aerospace, and furniture industries. Common applications include structural components like steel channels, angles, and frames, as well as specialized sections for roofing, siding, and even shelves. The versatility of cold roll formed products makes them a preferred choice for architects and engineers who seek to create innovative designs while ensuring structural integrity and cost-effectiveness.
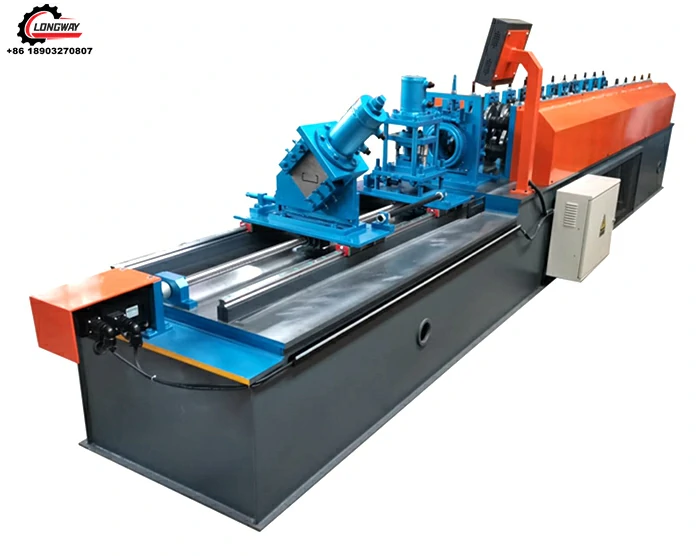
The Cold Roll Forming Process
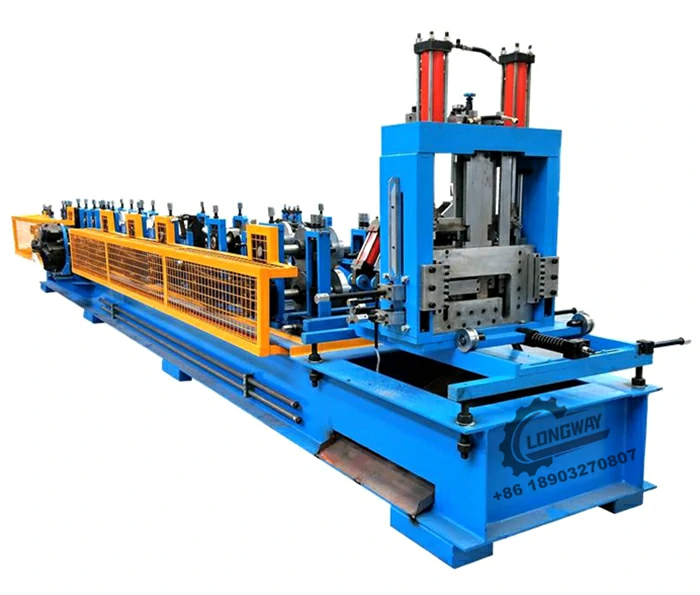
A cold roll forming factory operates through a series of well-defined stages. Initially, high-quality raw material, typically in the form of coils, is sourced and inspected for quality. The coil is then uncoiled, flattened, and cut to length before it is fed into the roll forming machine. The machine features multiple sets of rollers that gradually shape the metal into the desired profile.
cold roll forming factory
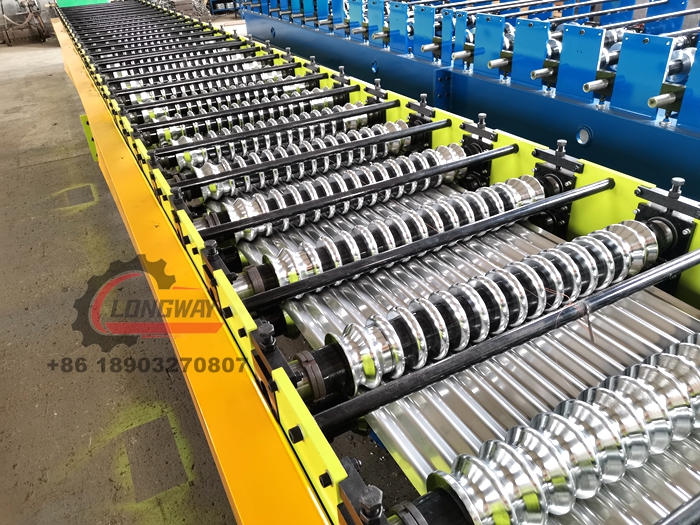

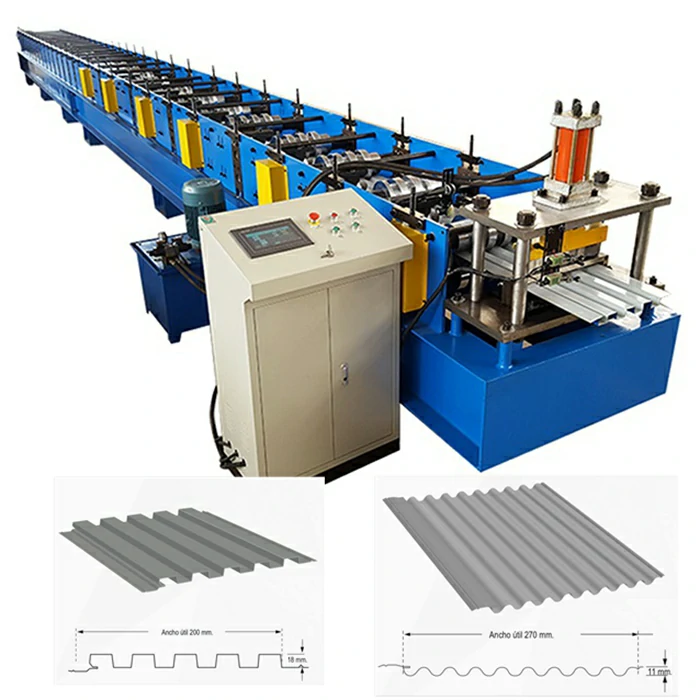
Throughout this process, constant monitoring and control are essential to maintain accuracy and quality. Advanced technologies such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) systems aid in designing the profiles and automating the production process. Quality control measures, including dimensional checks and material testing, ensure that the finished products meet stringent industry standards.
Advantages of Cold Roll Forming in Manufacturing
One of the primary benefits of cold roll forming is the ability to produce components with higher strength-to-weight ratios compared to those made using other methods. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in industries like automotive manufacturing, where reducing weight can lead to improved fuel efficiency without compromising safety.
Additionally, the process allows for significant material savings, reducing waste due to the efficient use of raw materials. The high-speed production capabilities of cold roll forming lines lead to increased output, making it a cost-effective solution for manufacturers. Furthermore, the process allows for customization, enabling factories to produce specific profiles tailored to unique customer requirements.
Challenges and Future of Cold Roll Forming
Despite its numerous advantages, cold roll forming is not without challenges. The initial setup costs for tooling and machinery can be high, which necessitates a careful analysis of market demand and production volume. Additionally, achieving intricate profiles with sharp bends may require advanced equipment and a high level of expertise.
The future of cold roll forming appears promising, especially with ongoing advancements in technology. Innovations such as automation, artificial intelligence, and robotics are expected to further enhance production efficiency and product quality. As industries continue to evolve towards sustainability, cold roll forming’s ability to utilize lightweight materials and reduce waste aligns well with global trends towards more environmentally friendly manufacturing practices.
In conclusion, cold roll forming factories play a vital role in modern manufacturing by producing essential components that support various industries. With their focus on precision, efficiency, and sustainability, these factories are well-positioned to meet the growing demands of the market and contribute to the advancements in manufacturing technology.
-
Key Features to Look for in a Roof and Wall Panel MachineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Key Features of a Roller Shutter Door Forming MachineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Key Features of a Purlin Roll Forming MachineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Key Features of a Cut to Length & Slitting LineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Benefits of Using a Downspout Gutter Forming MachineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Advantages of Using a Steel Deck Floor Roll Forming MachineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Revolutionize Your Gutter Production with a Gutter MachineNewsMay.23, 2025