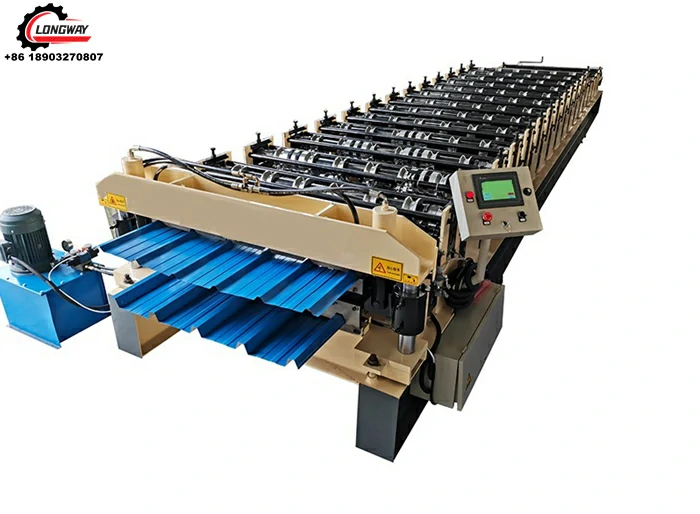
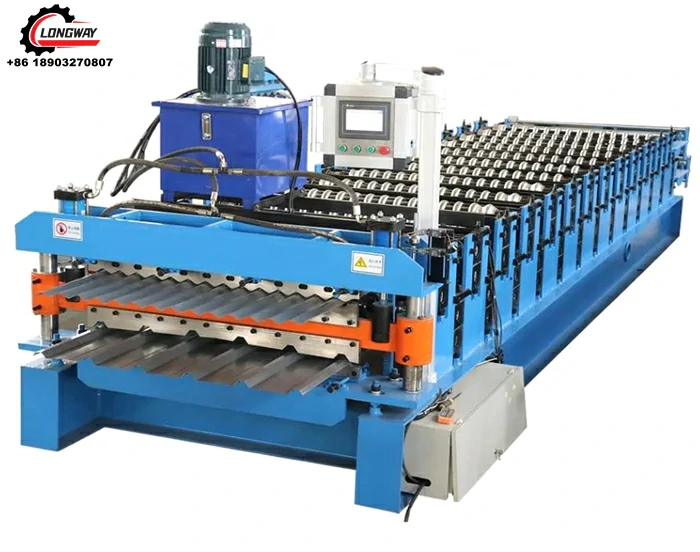
sheet metal roll forming machine manufacturer
The Evolution and Importance of Sheet Metal Roll Forming Machines
In the modern manufacturing landscape, the demand for precision and efficiency has steadily risen, leading to advances in various machinery and processes. Among these advancements, sheet metal roll forming machines have played a pivotal role, particularly for manufacturers aiming to produce high-quality metal components in a cost-effective manner. These machines are essential for a variety of industries, including automotive, construction, and appliance manufacturing.
Understanding Roll Forming
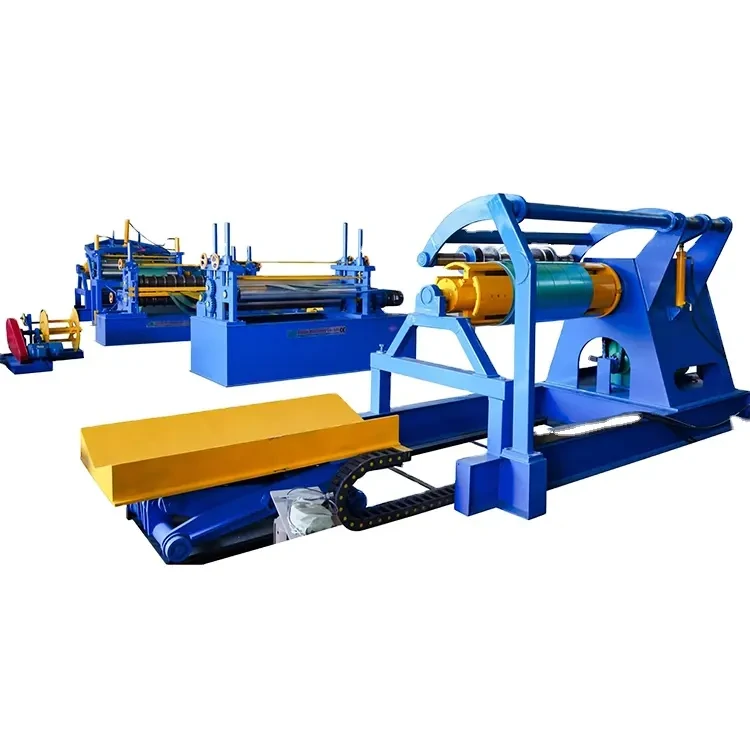
Roll forming is a continuous bending operation in which a long strip of sheet metal is gradually shaped into desired profiles. This process involves passing the metal through a series of rollers, each designed to progressively shape the metal into a specific cross-section. The result is a product that is not only structurally sound but also uniform in thickness and finish.
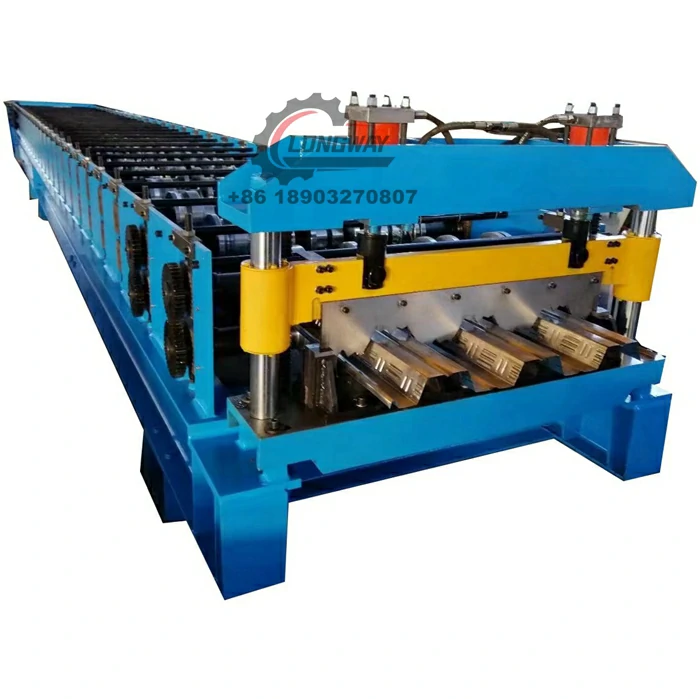
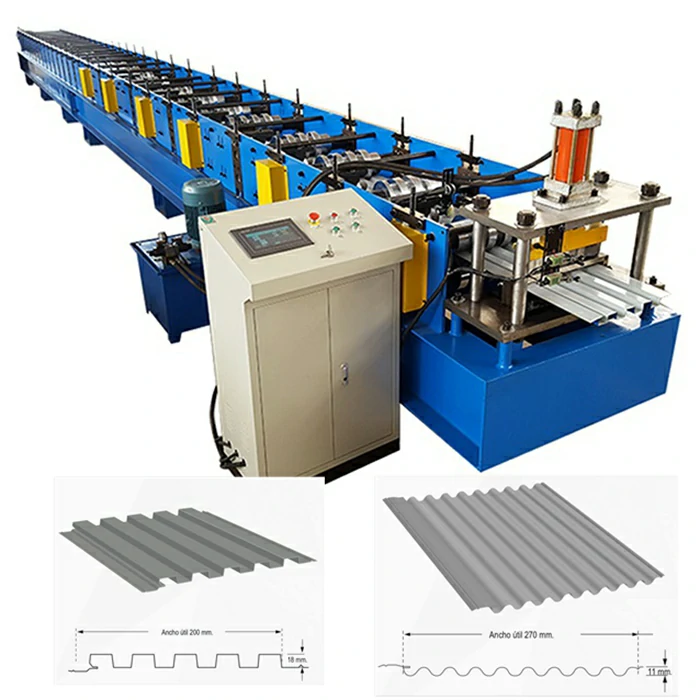
Sheet metal roll forming machines are highly versatile and can be customized to create an array of products, from simple angles and channels to complex shapes for roofing, siding, and other architectural components. The process is known for its efficiency, as it allows for high production rates with minimal waste, making it an ideal choice for large-scale manufacturing.
Key Features of Roll Forming Machines
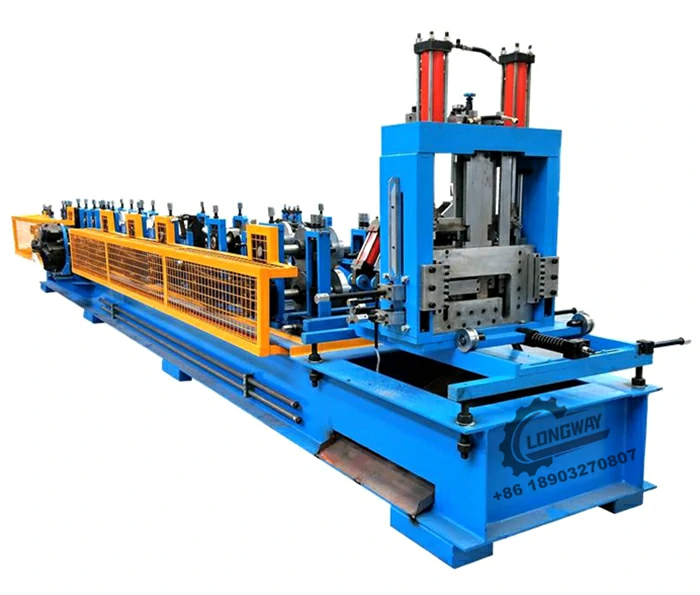
Modern sheet metal roll forming machines come equipped with a variety of features that enhance their functionality and utility. Among the most important are
1. Adjustable Roll Configurations Manufacturers can customize the roll tooling to create specific shapes and profiles according to their needs. This adaptability makes roll forming suitable for producing both standard and bespoke components.
2. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) CNC technology has revolutionized roll forming by allowing for precision control over the shaping process. This results in consistent output quality, reducing the likelihood of defects and minimizing material waste.
sheet metal roll forming machine manufacturer
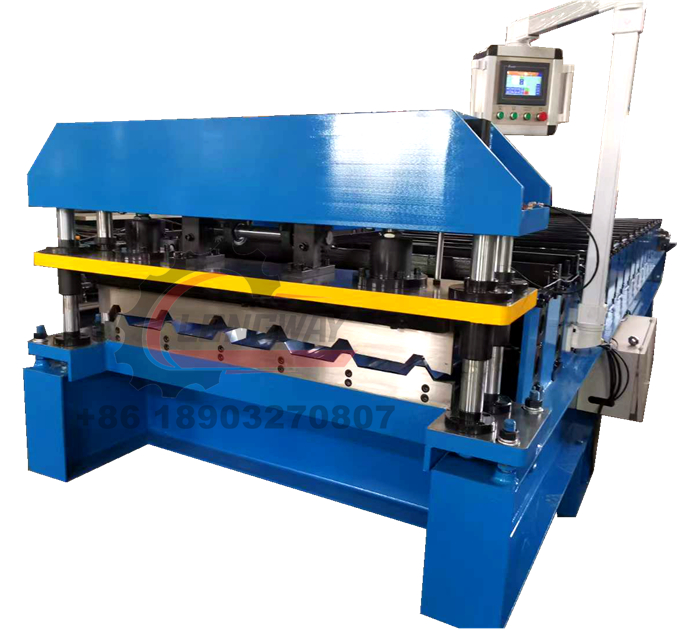

3. High-speed Production Advanced roll forming machines can operate at high speeds, often achieving production rates that rival or exceed those of traditional methods. This efficiency is crucial for meeting the demands of industries that require large volumes of product in short turnaround times.
4. Integration with Other Processes Many manufacturers are now integrating roll forming with other processes, such as welding, punching, and machining. This integration streamlines production workflows, further enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
The Advantages of Sheet Metal Roll Forming
The benefits of using sheet metal roll forming machines are numerous. One of the most significant advantages is the cost-effectiveness of the process. Because roll forming can produce long lengths of material with minimal waste and a high degree of automation, manufacturers can achieve significant savings in both material and labor costs.
Moreover, the durability and strength of the products produced through roll forming are unparalleled. The process works cold, preserving the integrity of the metal while enhancing its structural qualities. Additionally, the capacity for continuous operation allows manufacturers to maintain an unbroken workflow, reducing downtime and improving overall productivity.
Conclusion
As the manufacturing sector continues to evolve, the importance of efficient and precise machinery cannot be overstated. Sheet metal roll forming machines have become indispensable tools for manufacturers seeking to produce high-quality, cost-effective components. With their versatility and advanced technological features, these machines not only meet the demands of today’s industries but also pave the way for future innovations in manufacturing processes.
In a world where efficiency and precision are paramount, investing in high-quality sheet metal roll forming machines is essential for manufacturers looking to maintain a competitive edge. Whether for automotive parts, building materials, or customized solutions, these machines are the backbone of successful sheet metal production, embodying the future of advanced manufacturing.
-
Key Features to Look for in a Roof and Wall Panel MachineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Key Features of a Roller Shutter Door Forming MachineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Key Features of a Purlin Roll Forming MachineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Key Features of a Cut to Length & Slitting LineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Benefits of Using a Downspout Gutter Forming MachineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Advantages of Using a Steel Deck Floor Roll Forming MachineNewsMay.23, 2025
-
Revolutionize Your Gutter Production with a Gutter MachineNewsMay.23, 2025