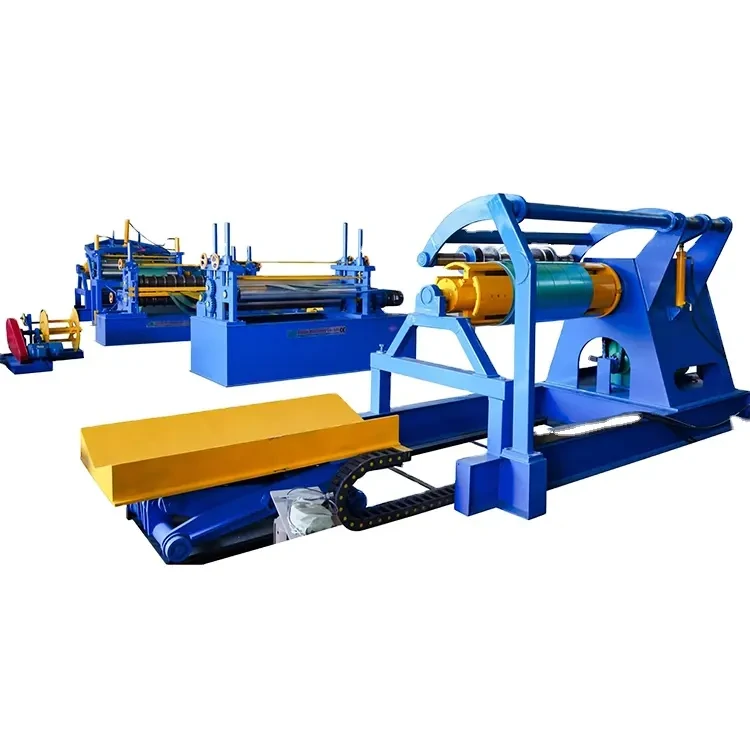
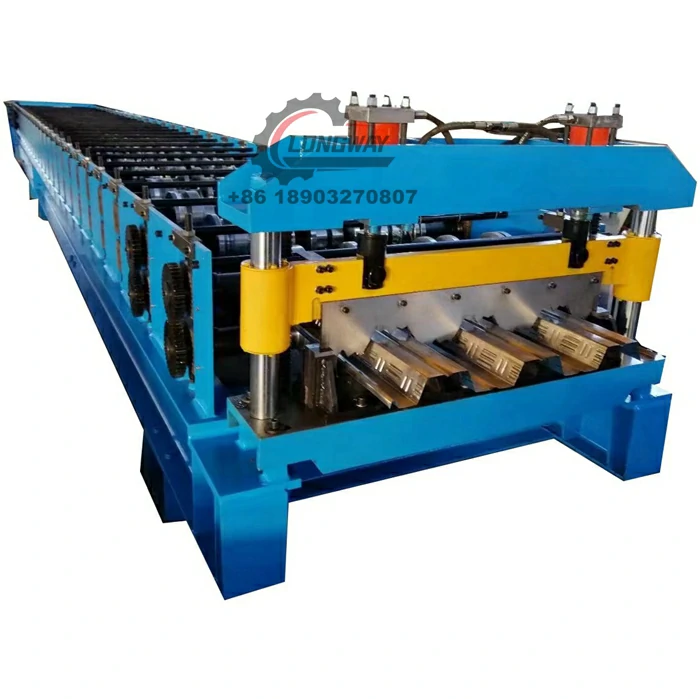
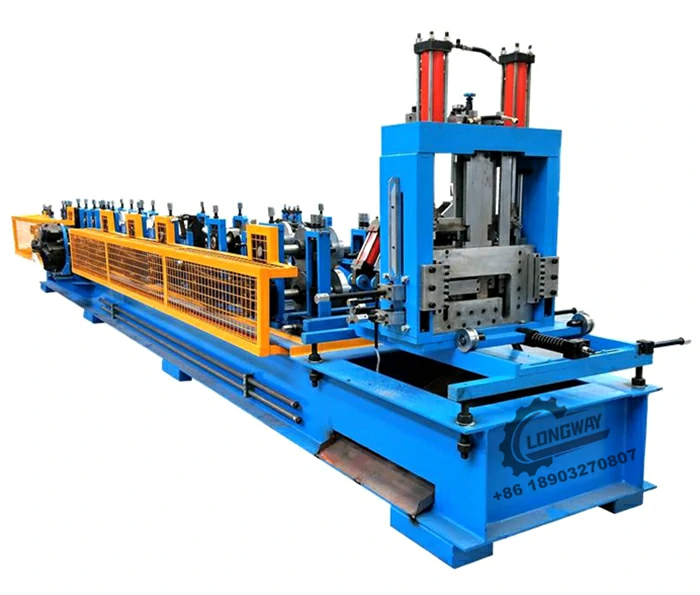
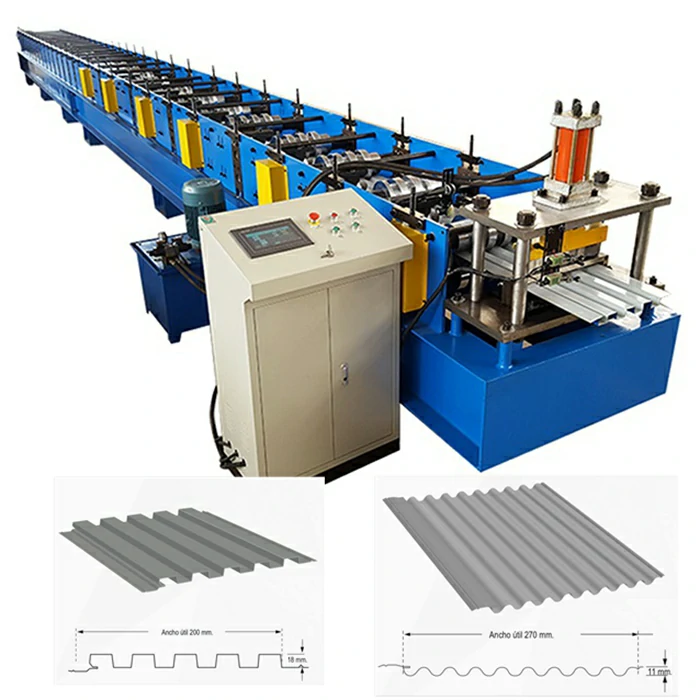
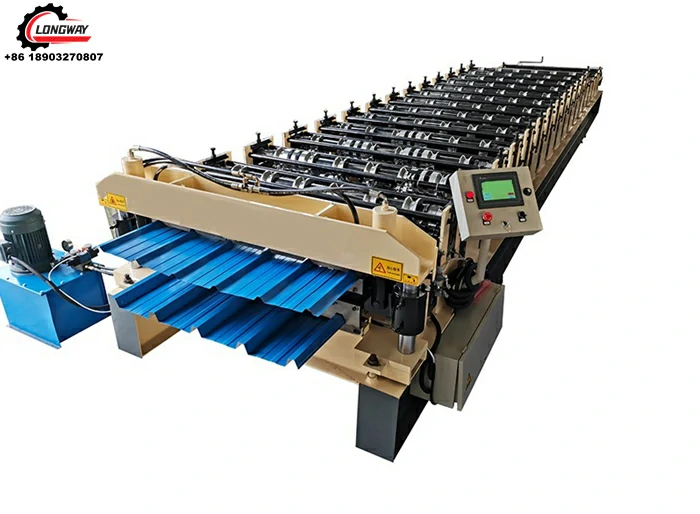
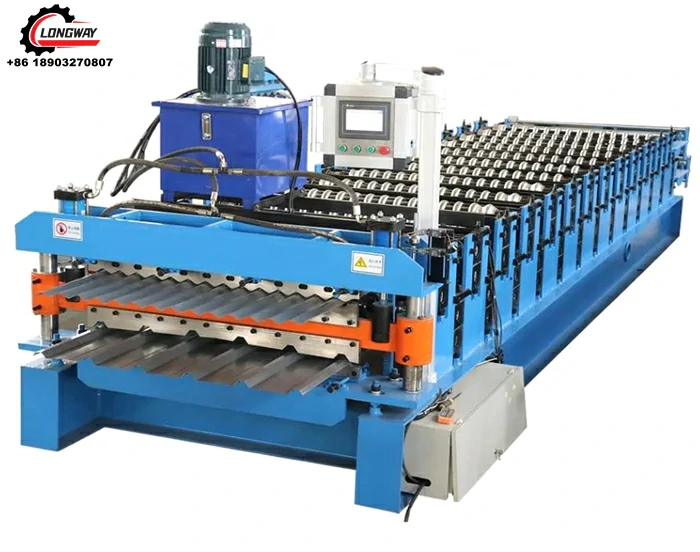
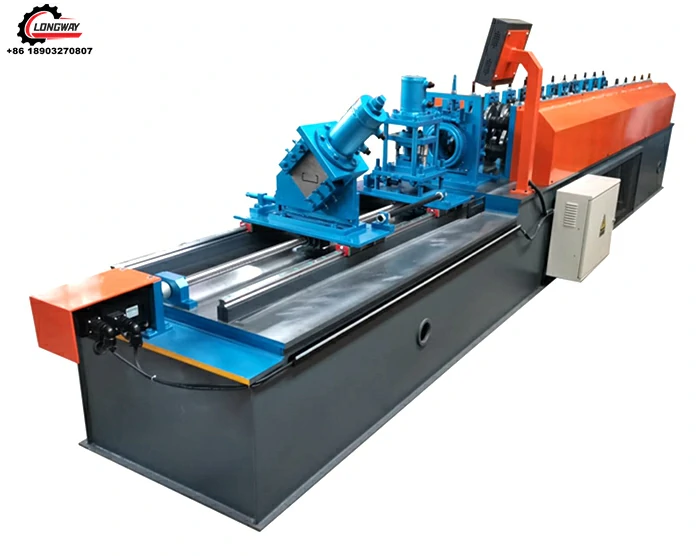
Galvanized Roof Sheet Roll Forming Machine High-Speed, Durable & Customizable
- Understanding the Role of Galvanized Roof Sheet Roll Forming Machines
- Technical Advantages Driving Modern Manufacturing Efficiency
- Comparative Analysis: Leading Manufacturers in the Industry
- Customized Solutions for Diverse Production Requirements
- Material Durability and Long-Term Performance Metrics
- Real-World Applications Across Construction Sectors
- Future Trends in Galvanized Roof Sheet Machinery Innovation
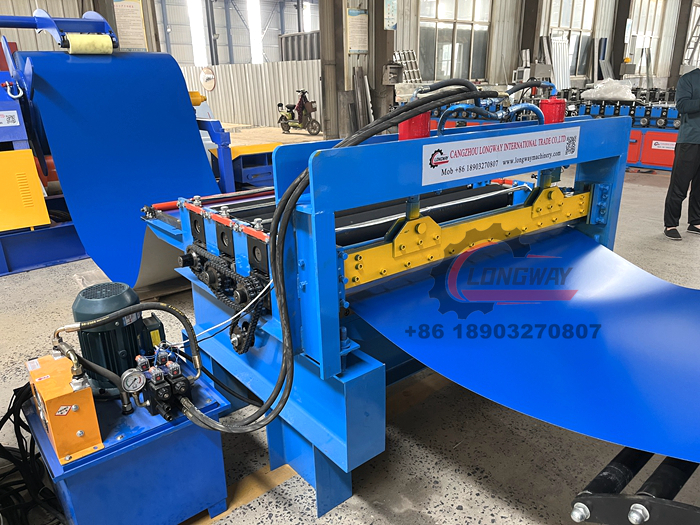

(galvanized roof sheet roll forming machine)
Why Galvanized Roof Sheet Roll Forming Machines Dominate Industrial Construction
Galvanized roof sheet roll forming machines have become indispensable for producing corrosion-resistant roofing materials. These systems process coated steel coils into precise profiles at speeds exceeding 40 meters per minute, with thickness handling capacities ranging from 0.2mm to 1.5mm. The zinc-aluminum coating adherence (120-275 g/m²) ensures 25+ years of weather resistance, directly impacting infrastructure longevity in coastal and high-humidity regions.
Technical Advantages Driving Modern Manufacturing Efficiency
Advanced PLC control systems enable ±0.1mm dimensional accuracy across 12-stage forming processes. Energy-efficient direct-drive motors reduce power consumption by 18-22% compared to traditional models, while automatic lubrication systems extend bearing life to 15,000 operational hours. Real-time thickness monitoring via laser sensors maintains material consistency, critical for achieving ASTM A653 and EN 10346 standards.
Comparative Analysis: Leading Manufacturers in the Industry
| Brand | Production Speed (m/min) | Material Thickness Range | Automation Level | Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FormTech Pro | 45 | 0.3-1.2mm | Full CNC | 22% Savings |
| RollMaster X7 | 38 | 0.25-1.5mm | Semi-Auto | 18% Savings |
| SteelCraft Ultra | 52 | 0.2-1.0mm | Hybrid Control | 25% Savings |
Customized Solutions for Diverse Production Requirements
Modular designs allow configuration of 6-24 forming stations to accommodate specific profile geometries. Power options range from 18.5kW to 55kW motors, supporting both single-phase and three-phase electrical systems. Quick-change tooling adapters enable profile switching within 45 minutes, while optional features like hydraulic punching or embossing units expand application possibilities.
Material Durability and Long-Term Performance Metrics
Galvanized coatings demonstrate 85% better corrosion resistance than untreated steel in salt spray tests (3000+ hours vs. 500 hours). Thermal expansion coefficients of 11.5 µm/m·°C ensure dimensional stability across -40°C to 120°C operating ranges. Impact resistance testing shows 8-12J energy absorption capacity, meeting IEC 61215 standards for severe weather conditions.
Real-World Applications Across Construction Sectors
Recent installations in Southeast Asian industrial parks have demonstrated 30% faster installation times compared to conventional roofing methods. A 2023 project in Florida utilized these machines to produce 85,000m² of hurricane-resistant roofing with 90° wind uplift resistance. Mining operations in Chile reported 40% maintenance reduction using machine-produced galvanized shelters in high-salinity environments.
Innovation Pathways for Galvanized Roof Sheet Machinery Development
Emerging technologies integrate AI-powered predictive maintenance algorithms that reduce downtime by 35%. Next-generation models feature 450MPa high-strength steel compatibility and 0.15mm ultrathin material processing capabilities. Industry 4.0 integration enables remote production monitoring with <2ms latency, while new eco-friendly zinc coatings achieve 99.8% recyclability rates.

(galvanized roof sheet roll forming machine)
FAQS on galvanized roof sheet roll forming machine
Q: What is a galvanized roof sheet roll forming machine used for?
A: A galvanized roof sheet roll forming machine manufactures corrugated or trapezoidal galvanized steel sheets for roofing. It shapes metal coils into precise profiles through a series of rollers. These sheets are durable, weather-resistant, and ideal for construction projects.
Q: How does a galvanized roofing sheet roll forming machine work?
A: The machine feeds galvanized steel coils through rollers that progressively bend the metal into the desired shape. The process is automated, ensuring consistent thickness and profile accuracy. Finished sheets are then cut to specific lengths.
Q: What are the advantages of using a galvanized sheet roll forming machine?
A: It offers high production efficiency, minimal material waste, and precise customization of sheet dimensions. The galvanized coating enhances corrosion resistance, making the sheets suitable for harsh environments. Automated controls reduce labor costs and errors.
Q: Can a galvanized roof sheet roll forming machine handle different materials?
A: While designed for galvanized steel, some machines can process pre-painted or coated metal coils. Material thickness and hardness must align with the machine’s specifications. Consult the manufacturer for compatibility details.
Q: How to maintain a galvanized roofing sheet roll forming machine?
A: Regularly clean rollers and lubricate moving parts to prevent wear. Inspect electrical components and alignment for optimal performance. Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule to ensure longevity and productivity.
-
Top Metal Roofing Machine ManufacturersNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Production Line with a Gutter Forming Machine for SaleNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Production Capacity with a Purlin Machine for SaleNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Exploring Roofing Sheets Manufacturing Machine PriceNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Drywall Roll Forming Machine for SaleNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Best Roof Panel Machine for SaleNewsAug.04, 2025
-
Roof Panel Machines: Buying Guide, Types, and PricingNewsJul.04, 2025